Abstract
Background
Mizoribine (MZR) has been developed as an immunosuppressive agent, but has a less potent immunosuppressive effect up to 3 mg/kg/day MZR. Therefore, we investigated whether high-dose MZR, at 6 mg/kg/day, would be effective and safe for kidney transplant patients in conjunction with cyclosporine (CsA), basiliximab, and corticosteroids.
Methods
A total of 40 living related patients were administered MZR (6 mg/kg/day), CsA (7 mg/kg/day), prednisolone (maintenance dose 10 mg/day), and basiliximab (20 mg/body). A control group (n = 38) treated with CsA, mycophenolate mofetil (MMF, 25 mg/kg/day), basiliximab, and corticosteroids was also employed in this study.
Results
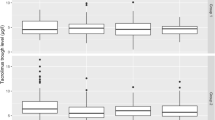
The 2-year graft survival rates for the MZR and MMF groups were 100 and 94.7 %, respectively. The rejection rate in the MZR group (25 %) was not significantly higher than that in the MMF group (16 %). Serum creatinine level was not significant between the two groups. The number of patients who developed cytomegalovirus (CMV) disease was 0 (0 %) in the MZR group and 7 (18.4 %) in the MMF group (P < 0.05). The number of patients treated with ganciclovir was 3 (7.5 %) and 11 (28.9 %) (P < 0.05), respectively.
Conclusions
The combination of high-dose MZR with CsA, basiliximab, and corticosteroids can establish not only satisfactory immunosuppression but also a low rate of CMV infection in vivo.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mizuno K, Tsujino M, Takada M, Hayashi M, Atsumi K, Asano K, et al. Studies on bredinin. I. Isolation, characterization and biological properties. J Antibiot. 1974;27:775–82.
Ishikawa H. Mizoribine and mycophenolate mofetil. Curr Med Chem. 1999;6:575–97.
Inou T. Immunosuppressive effects of bredinin on renal transplantation (in Japanese). Jpn J Transplant (Tokyo). 1982;17(suppl):547–61.
Inou T, Kusaba R, Takahashi I, Sugimoto H, Kuzuhara K, Yamada Y, et al. Clinical trial of bredinin in renal transplantation. Transpl Proc. 1981;13:315–8.
Amemiya H, Suzuki S, Niiya S, Watanabe H, Kotake T. Synergistic effect of cyclosporine and mizoribine on survival of dog renal allografts. Transplantation. 1988;46:768–71.
Hosokawa S, Ogino T, Ihara H, Shimada K, Arima M, Ikoma F, et al. Triple-drug therapy with mizoribine, cyclosporine and methylprednisolone (in Japanese). Jpn J Transplant. 1989;24:21–7.
Hosotsubo H, Takahara S, Taenaka N. Simplified high-performance liquid chromatographic method for determination of mizoribine in human serum. J Chromatogr. 1988;432:340–5.
Tanabe K, Tokumoto T, Ishikawa N, Kanematsu A, Oshima T, Harano M, et al. Long-term results in mizoribine-treated renal transplant recipients: a prospective, randomized trial of mizoribine and azathioprine under cyclosporine-based immunosuppressant. Transpl Proc. 1999;31:2877–9.
Sonda K, Takahashi K, Tanabe K, Fuchinoue S, Hayasaka Y, Kawaguchi H, et al. Clinical pharmacokinetic study of mizoribine in renal transplantation patients. Transpl Proc. 1996;28:3643–8.
Tanabe K. Re-evaluation of mizoribine for renal transplantation (Japanese). Ther Res. 2002;23:992–7.
Akiyama T, Okazaki H, Takahashi K, Hasegawa A, Tanabe K, Uchida K, et al. Mizoribine in combination therapy with tacrolimus for living donor renal transplantation. Transpl Proc. 2005;37:843–5.
Basic-Jukic N, Kes P, Bubic-Filipi LJ, Puretic Z, Brunetta B, Pasini J. Does mycophenolate mofetil increases the incidence of cytomegalovirus disease compared with azathioprine after cadaveric kidney transplantation. Transpl Proc. 2005;37:850–1.
Sarmiento JM, Dockrell DH, Schwab TR, Munn SR, Paya CV. Mycophenolate mofetil increases cytomegalovirus invasive organ disease in renal transplant patients. Clin Transpl. 2000;14:136–8.
Shiraki K, Ishibashi M, Okuno T, Kokado Y, Takahara S, Yamanishi K, et al. Effects of cyclosporine, azathioprine, mizoribine, and prednisolone on replication of human cytomegalovirus. Transpl Proc. 1990;22:1682–5.
Darji P, Vijayaraghavan R, Thiagarajan CM, Sharma RK, Subbarao B, Pishardy R, et al. Conversion from mycophenolate mofetil to enteric-coated mycophenolate sodium in renal transplant recipients with gastrointestinal tract disorders. Transpl Proc. 2008;40:2262–7.
Acknowledgments
Presentation of material in submitted manuscript: Presented in part at the World Transplant Congress, Boston, MA, July 22–27, 2006.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yoshimura, N., Ushigome, H., Akioka, K. et al. The beneficial effect of high-dose mizoribine combined with cyclosporine, basiliximab, and corticosteroids on CMV infection in renal transplant recipients. Clin Exp Nephrol 17, 127–133 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0669-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10157-012-0669-4