Abstract
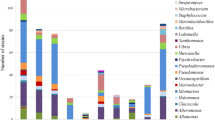
The diversity of culturable bacteria associated with sea ice from four permanently cold fjords of Spitzbergen, Arctic Ocean, was investigated. A total of 116 psychrophilic and psychrotolerant strains were isolated under aerobic conditions at 4°C. The isolates were grouped using amplified rDNA restriction analysis fingerprinting and identified by partial sequencing of 16S rRNA gene. The bacterial isolates fell in five phylogenetic groups: subclasses α and γ of Proteobacteria, the Bacillus–Clostridium group, the order Actinomycetales, and the Cytophaga–Flexibacter–Bacteroides (CFB) phylum. Over 70% of the isolates were affiliated with the Proteobacteria γ subclass. Based on phylogenetic analysis (<98% sequence similarity), over 40% of Arctic isolates represent potentially novel species or genera. Most of the isolates were psychrotolerant and grew optimally between 20 and 25°C. Only a few strains were psychrophilic, with an optimal growth at 10–15°C. The majority of the bacterial strains were able to secrete a broad range of cold-active hydrolytic enzymes into the medium at a cultivation temperature of 4°C. The isolates that are able to degrade proteins (skim milk, casein), lipids (olive oil), and polysaccharides (starch, pectin) account for, respectively, 56, 31, and 21% of sea-ice and seawater strains. The temperature dependences for enzyme production during growth and enzymatic activity were determined for two selected enzymes, α-amylase and β-galactosidase. Interestingly, high levels of enzyme productions were measured at growth temperatures between 4 and 10°C, and almost no production was detected at higher temperatures (20–30°C). Catalytic activity was detected even below the freezing point of water (at −5°C), demonstrating the unique properties of these enzymes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abyzov SS, Mitskevich IN, Poglasova MN (1998) Microflora of the deep glacier horisonts of central Africa. Microbiology 67:451–458
Amann RI, Ludwig W, Schleifer KH (1995) Phylogenetic identification and in situ detection of individual microbial cell without cultivation. Microbiol Rev 59:143–169
Bano N, Hollibaugh JT (2002) Phylogenetic composition of bacterioplankton assemblages from the Arctic Ocean. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:505–518
Barbaro SE, Trevors JT, Inniss WE (2001) Effects of low temperature, cold shock, and various carbon sources on esterase and lipase activities and exopolysaccharide production by a psychrotrophic Acinetobacter sp. Can J Microbiol 47:194–205
Bernfeld P (1955) Amylases α and β. Methods Enzymol 1:149–155
Bianchi A, Giuliano L (1996) Enumeration of viable bacteria in marine pelagic environment. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:174–177
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Brown JL, Nichols PD, McMeekin TA (1997a) Psychroserpens burtonensis gen. nov., sp. nov., and Gelidibacter algens gen. nov., sp. nov., psychrophilic bacteria isolated from Antarctic lacustrine and sea ice habitats. Int J Syst Bacteriol 47:670–677
Bowman JP, McCammon SA, Brown MV, Nichols DS, McMeekin TA (1997b) Diversity and association of psychrophilic bacteria in Antarctic sea ice. Appl Environ Microbiol 63:3068–3078
Bowman JP, Rea SM, McCammon SA, McMeekin TA (2000) Diversity and community structure within anoxic sediment from marine salinity meromictic lakes and a coastal meromictic marine basin, Vestfold Hilds, Eastern Antarctica. Environ Microbiol 2:227–237
Brambilla E, Hippe H, Hagelstein A, Tindall BJ, Stackebrandt E (2001) 16S rDNA diversity of cultured and uncultured prokaryotes of a mat sample from Lake Fryxell, McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica. Extremophiles 5:23–33
Brown MV, Bowman JP (2001) A molecular phylogenetic survey of sea-ice microbial communities (SIMCO). FEMS Microbiol Ecol 35:267–275
Buchholz-Cleven BEE, Rattunde B, Straub KL (1997) Screening for genetic diversity of isolates of anaerobic Fe(II)-oxidizing bacteria using DGGE and whole-cell hybridization. Syst Appl Microbiol 20:301–309
Buchon L, Laurent P, Gounot AM, Guespin-Michel JF (2000) Temperature dependence of extracellular enzymes production by psychrotrophic and psychrophilic bacteria. Biotech Lett 22:1577–1581
Chrost RJ (1991) Environmental control of the synthesis and activity of aquatic microbial ectoenzymes, In: Chrost RJ (ed) Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 60–83
Cleveland TE, Cotty PJ (1991) Invasiveness of Aspergillus flavus isolates in wounded cotton bolls is associated with production of a specific fungal polygalacturonase. Phytopathology 81:155–158
DeLong EF, Wu KY, Prezelin BB, Jovine RV (1994) High abundance of Archaea in Antarctic marine picoplankton. Nature 371:695–697
Eilers H, Pernthaler J, Amann R (2000) Succession of pelagic marine bacteria during enrichment: a close look at cultivation-induced shifts. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:4634–4640
Feller G, Gerday C (1997) Psychrophilic enzymes: molecular basis of cold adaptation. Cell Mol Life Sci 53:830–841
Feller G, Lonhienne T, Deroanne C, Libioulle C, Van Beeumen J, Gerday C (1992) Purification, characterization, and nucleotide sequence of the thermolabile alpha-amylase from the Antarctic psychrotroph Alteromonas haloplanctis A23. J Biol Chem 267:5217–5221
Felsenstein J (1993) PHYLIP (PHYlogenetic Inference Package) version 3.57c. Department of Genetics, University of Washington, Seattle
Fridmann EI (1980) Endolithic microbial life in hot and cold deserts. Orig Life 10:223–235
Gerday C, Aittaleb M, Bentahir M, Chessa JP, Claverie P, Collins T, D’Amico S, Dumont J, Garsoux G, Georlette D, Hoyoux A, Lonhienne T, Meuwis MA, Feller G (2000) Cold-adapted enzymes: from fundamentals to biotechnology. Trends Biotechnol 18:103–107
Giuliano L, De Domenico M, De Domenico E, Hofle MG, Yakimov MM (1999) Identification of culturable oligotrophic bacteria within naturally occurring bacterioplankton communities of the Ligurian sea by 16S rRNA sequencing and probing. Microb Ecol 37:77–85
Gugi B, Orange N, Hellio F, Burini JF, Guillou C, Leriche F, Guespin-Michel JF (1991) Effect of growth temperature on several exported enzyme activities in the psychrotrophic bacterium Pseudomonas fluorescens. J Bacteriol 173:3814–3820
Helmke E, Weyland H (1995) Bacteria in sea ice and underlying water of the eastern Weddell Sea in midwinter. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 117:269–288
Hiraishi A, Ueda Y (1994) Intragenetic structure of the genus Rhodobacter: transfer of Rhodobacter sulfidophilus and related marine species to the genus Rhodovulum gen. nov. Int J Syst Bacteriol 44:15–23
Hoppe HG (1991) Microbial extracellular enzyme activity: a new key parameter in aquatic ecology. In: Chrost RJ (ed) Microbial enzymes in aquatic environments. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 60–83
Huston AL, Krieger-Brockett BB, Deming JW (2000) Remarkably low temperature optima for extracellular enzyme activity from Arctic bacteria and sea ice. Environ Microbiol 2:383–388
Jorgensen S, Vorgias CE, Antranikian G (1997) Cloning, sequencing, characterization, and expression of an extracellular alpha-amylase from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus in Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem 272:16335–16342
Junge K, Imhoff F, Staley T, Deming JW (2002) Phylogenetic diversity of numerically important Arctic sea-ice bacteria cultured at subzero temperature. Microb Ecol 43:315–328
Knoblauch C, Jorgensen BB (1999) Effect of temperature on sulphate reduction, growth rate and growth yield in five psychrophilic sulphate-reducing bacteria from Arctic sediments. Environ Microbiol 1:457–467
Knoblauch C, Jorgensen BB, Harder J (1999) Community size and metabolic rates of psychrophilic sulfate-reducing bacteria in Arctic marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:4230–4233
Kottmeier ST, Sullivan CW (1990) Bacterial biomass and production in pack ice of Antarctic marginal ice age zones. Deep-Sea Res 37:1311–1330
Kouker G, Jaeger KE (1987) Specific and sensitive plate assay for bacterial lipases. Appl Environ Microbiol 53:211–213
Massana RT, Murray AE, Wu KY, Jeffrey WH, DeLong E (1998) Vertical distribution and temporal variation of marine planktonic archaea in the Gerlache Strain, Antarctica, during early spring. Limnol Oceanogr 43:607–617
Morita RY (1975) Psychrophilic bacteria. Bacteriol Rev 39:144–167
Mountfort DO, Rainey FA, Burghardt J, Kaspar HF, Stackebrandt E (1998) Psychromonas antarcticus gen. nov., sp. nov., A new aerotolerant anaerobic, halophilic psychrophile isolated from pond sediment of the McMurdo Ice Shelf, Antarctica. Arch Microbiol 169:231–238
Palmisano AC, Garrison DL (1993) Microorganisms in Antarctic sea ice. In: Friedmann EI (ed) Antarctic microbiology. Wiley, New York, pp 167–219
Petri R, Imhoff JF (2001) Genetic analysis of sea ice bacterial communities of western Baltic Sea using an improved double gradient method. Polar Biol 24:252–257
Priscu JC, Fritsen CH, Adams EE, Giovannoni SJ, Paerl HW, McKay CP, Doran PT, Gordon DA, Lanoil BD, Pinckney JL (1998) Perennial Antarctic lake ice: an oasis for life in a polar desert. Science 280:2095–2098
Ravenschlag K, Sahm K, Pernthaler J, Amann R (1999) High bacterial diversity in permanently cold marine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3982–3989
Reichardt W (1988) Impact of the Antarctic Benthic fauna on the enrichment of biopolymer degrading psychrophilic bacteria. Microb Ecol 15:311–321
Riemann L, Steward GF, Azam F (2000) Dynamics of bacterial community composition and activity during a mesocosm diatom bloom. Appl Environ Microbiol 66:578–587
Rivkin RB, Putt M, Alexander SP, Meritt D, Gaudet L (1989) Biomass and production in polar planktonic and sea ice microbial communities: a comparative study. Mar Biol 101:273–283
Russell NJ (2000) Toward a molecular understanding of cold activity of enzymes from psychrophiles. Extremophiles 4:83–90
Sahm K, Knoblauch C, Amann R (1999) Phylogenetic affiliation and quantification of psychrophilic sulfate-reducing isolates in marine Arctic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3976–3981
Schafer H, Servais P, Muyzer G (2000) Successional changes in the genetic diversity of a marine bacterial assemblage during confinement. Arch Microbiol 173:138–145
Schinner F, Margesin R, Pümpel T (1992) Extracellular protease-producing psychrotrophic bacteria from high Alpine habitats. Arctic Alpine Res 24:88–92
Smilbert RM (1994) Phenotypic characterization. In: Gerhardt P, Murray REG, Wood WA, Krieg NR (eds) Methods for general and molecular microbiology. American Society for Microbiology, Washington, pp 611–654
Smith MC, Bowman JP, Scott FJ, Line MA (2000) Sublithic bacteria associated with Antarctic quartz stones. Antarctic Sci 12:177–184
Staley JT, Gosink JJ (1999) Poles apart: biodiversity and biogeography of sea ice bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol 53:189–215
Yumoto I, Kawasaki K, Iwata H, Matsuyama H, Okuyama H (1998) Assignment of Vibrio sp. strain ABE-1 to Colwellia maris sp. nov., a new psychrophilic bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:1357–1362
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the Deutsche Bundesstiftung Umwelt and “Fonds der Chemischen Industrie” for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by K. Horikoshi
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Groudieva, T., Kambourova, M., Yusef, H. et al. Diversity and cold-active hydrolytic enzymes of culturable bacteria associated with Arctic sea ice, Spitzbergen. Extremophiles 8, 475–488 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0409-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-004-0409-0