Abstract
Midgut remodeling is a complex physiological process in holometabolous insects. During midgut remodeling, the larval midgut is decomposed by apoptosis or autophagy during metamorphosis, and the degraded larval midgut is partially absorbed as nutrients by the imaginal midgut for its formation. The molecular mechanism involved in this process is not clear. Here, we found that a Rab protein, which we have named HaRab32, is related to the organogenesis of insect imaginal midgut. Results show that HaRab32 is up-regulated in epidermis and midgut during metamorphosis. Its expression could be up-regulated by 20E. Immunohistochemistry shows Rab32 is distributed in the epithelium of the imaginal midgut during metamorphosis. Knockdown of HaRab32 by RNA interference disturbs the formation of the imaginal midgut. These data imply HaRab32 plays important roles in midgut remodeling by participating in the imaginal midgut formation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alone DP, Tiwari AK, Mandal L, Li M, Mechler BM, Roy JK (2005) Rab11 is required during Drosophila eye development. Int J Dev Biol 49:873–879
Bhuin T, Roy JK (2009a) Rab11 is required for embryonic nervous system development in Drosophila. Cell Tissue Res 335:349–356
Bhuin T, Roy JK (2009b) Rab11 is required for myoblast fusion in Drosophila. Cell Tissue Res 336:489–499
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cakouros D, Daish TJ, Kumar S (2004) Ecdysone receptor directly binds the promoter of the Drosophila caspase dronc, regulating its expression in specific tissues. J Cell Biol 165:631–640
Casartelli M, Corti P, Giovanna Leonardi M, Fiandra L, Burlini N, Pennacchio F, Giordana B (2005) Absorption of albumin by the midgut of a lepidopteran larva. J Insect Physiol 51:933–940
Casartelli M, Corti P, Cermenati G, Grimaldi A, Fiandra L, Santo N, Pennacchio F, Giordana B (2007) Absorption of horseradish peroxidase in Bombyx mori larval midgut. J Insect Physiol 53:517–525
Hakim RS, Baldwin K, Smagghe G (2009) Regulation of midgut growth, development, and metamorphosis. Annu Rev Entomol 55:593–608
Harper MS, Hopkins TL (1997) Peritrophic membrane structure and secretion in European corn borer larvae (Ostrinia nubilalis). Tissue Cell 29:463–475
Hiragaki S, Uno T, Takeda M (2009) Putative regulatory mechanism of prothoracicotropic hormone (PTTH) secretion in the American cockroach, Periplaneta americana as inferred from co-localization of Rab8, PTTH, and protein kinase C in neurosecretory cells. Cell Tissue Res 335:607–615
Hirota Y, Tanaka Y (2009) A small GTPase, human Rab32, is required for the formation of autophagic vacuoles under basal conditions. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:2913–2932
Hiruma K, Riddiford LM (2001) Regulation of transcription factors MHR4 and betaFTZ-F1 by 20-hydroxyecdysone during a larval molt in the tobacco hornworm, Manduca sexta. Dev Biol 232:265–274
Jordens I, Marsman M, Kuijl C, Neefjes J (2005) Rab proteins, connecting transport and vesicle fusion. Traffic 6:1070–1077
Nishimura N, Sasaki T (2008) Regulation of epithelial cell adhesion and repulsion: role of endocytic recycling. J Med Invest 55:9–16
Nishimura N, Sasaki T (2009) Rab family small G proteins in regulation of epithelial apical junctions. Front Biosci 14:2115–2129
Nishiura JT, Ray K, Murray J (2005) Expression of nuclear receptor-transcription factor genes during Aedes aegypti midgut metamorphosis and the effect of methoprene on expression. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 35:561–573
Parthasarathy R, Palli SR (2007) Developmental and hormonal regulation of midgut remodeling in a lepidopteran insect, Heliothis virescens. Mech Dev 124:23–34
Parthasarathy R, Palli SR (2008) Proliferation and differentiation of intestinal stem cells during metamorphosis of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. Dev Dyn 237:893–908
Pereira-Leal JB, Seabra MC (2001) Evolution of the Rab family of small GTP-binding proteins. J Mol Biol 313:889–901
Rabossi A, Stoka V, Puizdar V, Turk V, Quesada-Allue LA (2004) Novel aspartyl proteinase associated to fat body histolysis during Ceratitis capitata early metamorphosis. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 57:51–67
Riddiford LM (1993) Hormone receptors and the regulation of insect metamorphosis. Receptor 3:203–209
Rodriguez-Fernandez IA, Dell’Angelica EC (2009) A data-mining approach to rank candidate protein-binding partners––the case of biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-1 (BLOC-1). J Inherit Metab Dis 32:190–203
Ryerse JS, Purcell JP, Sammons RD (1994) Structure and formation of the peritrophic membrane in the larva of the southern corn rootworm, Diabrotica undecimpunctata. Tissue Cell 26:431–437
Shao HL, Zheng WW, Liu PC, Wang Q, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2008) Establishment of a new cell line from lepidopteran epidermis and hormonal regulation on the genes. PLoS One 3:e3127
Sui YP, Liu XB, Chai LQ, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2009) Characterization and influences of classical insect hormones on the expression profiles of a molting carboxypeptidase A from the cotton bollworm (Helicoverpa armigera). Insect Mol Biol 18:353–363
Takai Y, Sasaki T, Matozaki T (2001) Small GTP-binding proteins. Physiol Rev 81:153–208
Tettamanti G, Grimaldi A, Casartelli M, Ambrosetti E, Ponti B, Congiu T, Ferrarese R, Rivas-Pena ML, Pennacchio F, Eguileor M (2007a) Programmed cell death and stem cell differentiation are responsible for midgut replacement in Heliothis virescens during prepupal instar. Cell Tissue Res 330:345–359
Tettamanti G, Grimaldi A, Pennacchio F, de Eguileor M (2007b) Lepidopteran larval midgut during prepupal instar: digestion or self-digestion? Autophagy 3:630–631
Tian H, Peng H, Yao Q, Chen H, Xie Q, Tang B, Zhang W (2009) Developmental control of a lepidopteran pest Spodoptera exigua by ingestion of bacteria expressing dsRNA of a non-midgut gene. PLoS One 4:e6225
Timmons L, Court DL, Fire A (2001) Ingestion of bacterially expressed dsRNAs can produce specific and potent genetic interference in Caenorhabditis elegans. Gene 263:103–112
Uno T, Nakao A, Katsurauma C (2004) Phosphorylation of Rab proteins from the brain of Bombyx mori. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 57:68–77
Uwo MF, Ui-Tei K, Park P, Takeda M (2002) Replacement of midgut epithelium in the greater wax moth, Galleria mellonela, during larval–pupal moult. Cell Tissue Res 308:319–331
Wang JL, Jiang XJ, Wang Q, Hou LJ, Xu DW, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2007) Identification and expression profile of a putative basement membrane protein gene in the midgut of Helicoverpa armigera. BMC Dev Biol 7:76
Wang JL, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2008) Molecular cloning and expression profiles of the acyl-CoA-binding protein gene from the cotton bollworm Helicoverpa armigera. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 68:79–88
Yang XM, Hou LJ, Wang JX, Zhao XF (2007) Expression and function of cathepsin B-like proteinase in larval hemocytes of Helicoverpa armigera during metamorphosis. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 64:164–174
Zhao XF, Wang JX, Wang YX (1998) Purification and characterization of a cysteine proteinase from eggs of the cotton boll worm, Helicoverpa armigera. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 28:259–264
Zhao XF, An XM, Wang JX, Dong DJ, Du XJ, Sueda S, Kondo H (2005) Expression of the Helicoverpa cathepsin B-like proteinase during embryonic development. Arch Insect Biochem Physiol 58:39–46
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the National Basic Research Program of China (2006CB102001) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30710103901). We thank Dr. Marek Jindra and Masako Asahina in Biology Center, Czech Academy of Sciences and Department of Molecular Biology, University of South Bohemia, Czech Republic, for providing the plasmid L4440 and the HT115(DE3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The nucleotide sequence reported in this paper has been submitted to GenBank with accession number: HM037181.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
726_2010_720_MOESM1_ESM.tif
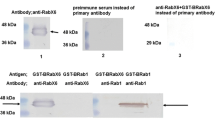
Analysis of the expressed and purified the recombinant HaRab32 protein. A. 12.5% SDS-PAGE, Lane 1; low-molecular-weight marker, Lane 2; protein extracts from E. coli before IPTG induction, Lane 3; extracts of E. coli after induced with IPTG for 3 h, Lane 4; purified HaRab32. B. Western blot, Lane 1, showing the specificity of the antiserum against HaRab32 from the midgut of the larvae at the metamorphic stage (100 µg midgut protein was used)
726_2010_720_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of HaRab32. The arrows indicate the forward and reverse primers for RT-PCR. The sequence in gray indicates the Rab subfamily domain. The panes show the PKC phosphorylation site. The stop codon is indicated by an asterisk
726_2010_720_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Phylogenetic analysis of Rab32. A. Alignment of Rab32 proteins from various species. B. Phylogenetic analysis of HaRab32 with orthologs known from other species: A. aegypti XP_001652315, B. mori NP_001040211, C. quinquefasciatus XP_001862890, D. melanogaster BAA88238, D. rerio AAH66502, H. sapiens NP_006825, Mus musculus AAH16409, Synthetic construct AAV38818, X. laevis NP_001090131, C. familiaris XP_850212, H. sapiens NP_071732, R. norvegicus NP_665717, Bos Taurus NP_001092564
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, L., Wang, JX. & Zhao, XF. Rab32 and the remodeling of the imaginal midgut in Helicoverpa armigera. Amino Acids 40, 953–961 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0720-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-010-0720-2