Summary.
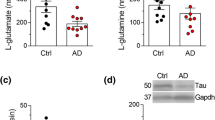
We measured the CSF levels of 21 and the plasma levels of 24 amino acids in 37 patients with Alzheimer's disease (AD) and in 32 matched controls. We used an ion-exchange chromatography method. When compared with controls, AD patients had lower CSF levels of phosphoserine, citrulline, alfa-aminobutyric acid, methionine, and ethanolamine; and higher CSF levels of threonine, serine, lysine, histidine and arginine. However, when expressed relative to CSF protein, CSF levels of serine, lysine, histidine, and arginine, were normal. AD patients had higher plasma levels of phosphoserine, threonine, citrulline, hydroxyproline, and proline; and lower plasma levels of alfa-aminobutyric acid, methionine, leucine and ethanolamine. The CSF/plasma ratios of phosphoserine, serine, citrulline, alfa-aminobutyric acid and arginine were significantly lower in AD patients than those of controls. CSF amino acid levels were not related with the duration and severity of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Accepted December 2, 1997; received August 30, 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Molina, J., Jiménez-Jiménez, F., Vargas, C. et al. Cerebrospinal fluid levels of non-neurotransmitter amino acids in patients with Alzheimer's disease. J Neural Transm 105, 279–286 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050057
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s007020050057