Abstract
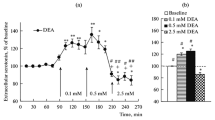
The nitric oxide (NO)-active drugs influence on the bioelectric activity of neurons of the pars reticulata of the substantia nigra was studied in urethane-anesthetized rats. A first group of animals was treated with 7-nitro-indazole (7-NI), a preferential inhibitor of neuronal NO synthase. In a second group of rats, electrophysiological recordings were coupled with microiontophoretic administration of Nω-nitro-l-arginine methyl ester (l-NAME, a NO synthase inhibitor), 3-morpholino-sydnonimin-hydrocloride (SIN-1, a NO donor) and 8-Br-cGMP (a cell-permeable analogue of cGMP, the main second-messenger of NO neurotransmission). 7-NI and l-NAME caused a statistically significant decrease in the firing rate of most of the responsive cells, while application of SIN-1 and 8-Br-CGMP induced statistically significant excitatory effects. The results suggest a NO mediated excitatory modulation of the SNr neurons activity with a possible involvement of the cGMP pathway.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahern GP, Klyachko VA, Jackson MB (2002) cGMP and S-nitrosylation: two routes for modulation of neuronal excitability by NO. Trends Neurosci 25:510–517
Atherton JF, Bevan MD (2005) Ionic mechanisms underlying autonomous action potential generation in the somata and dendrites of GABAergic substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons in vitro. J Neurosci 26:8272–8281
Bush MA, Pollack GM (2001) Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of 7-nitroindazole, a selective nitric oxide synthase inhibitor, in the rat hippocampus. Pharm Res 18:1607–1612
Calabresi P, Gubellini P, Centonze D, Sancesario G, Morello M, Giorgi M, Pisani A, Bernardi G (1999) A critical role of the nitric oxide/cGMP pathway in corticostriatal long-term depression. J Neurosci 19:2489–2499
Cox BA, Johnson SW (1998) Nitric oxide facilitates N-methyl-d-aspartate-induced burst firing in dopamine neurons from rat midbrain slices. Neurosci Lett 255:131–134
Cudeiro J, Rivadulla C, Rodríguez R, Grieve KL, Martínez-Conde S, Acuña C (1997) Actions of compounds manipulating the nitric oxide system in the cat primary visual cortex. J Physiol 504:467–478
De Vente J, Hopkins DA, Markerink-Van Ittersum M, Emson PC, Schmidt HH, Steinbusch HW (1998) Distribution of nitric oxide synthase and nitric oxide-receptive, cyclic GMP-producing structures in the rat brain. Neuroscience 87:207–241
Deniau JM, Mailly P, Maurice N, Charpier S (2007) The pars reticulata of the substantia nigra: a window to basal ganglia output. Prog Brain Res 160:151–172
Feil R, Kleppisch T (2008) NO/cGMP-dependent modulation of synaptic transmission. Handb Exp Pharmacol 184:529–560
Ferraro G, Montalbano ME, La Grutta V (1999) Nitric oxide and glutamate interaction in the control of cortical and hippocampal excitability. Epilepsia 40:830–836
Gonzalez-Forero D, Portillo F, Gomez L, Montero F, Kasparov S, Moreno-Lopez B (2007) Inhibition of resting potassium conductances by long-term activation of the NO/cGMP/protein kinase G pathway: a new mechanism regulating neuronal excitability. J Neurosci 27:6302–6312
González-Hernández T, Rodríguez M (2000) Compartmental organization and chemical profile of dopaminergic and GABAergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the rat. J Comp Neurol 421:107–135
Iwase K, Iyama K, Akagi K, Yano S, Fukunaga K, Miyamoto E, Mori M, Takiguchi M (1998) Precise distribution of neuronal nitric oxide synthase mRNA in the rat brain revealed by non-radioisotopic in situ hybridization. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 53:1–12
Kalisch BE, Connop BP, Jhamandas K, Beninger RJ, Boegman RJ (1996) Differential action of 7-nitro indazole on rat brain nitric oxide synthase. Neurosci Lett 219:75–78
Kara P, Friedlander MJ (1999) Arginine analogs modify signal detection by neurons in the visual cortex. J Neurosci 19:5528–5548
Kleppisch T, Feil R (2009) cGMP signalling in the mammalian brain: role in synaptic plasticity and behaviour. Handb Exp Pharmacol 191:549–579
Kolomiets BP, Deniau JM, Glowinski J, Thierry AM (2003) Basal ganglia and processing of cortical information: functional interactions between trans-striatal and trans-subthalamic circuits in the substantia nigra pars reticulata. Neuroscience 117:931–938
Korotkova TM, Eriksson KS, Haas HL, Brown RE (2002) Selective excitation of GABAergic neurons in the substantia nigra of the rat by orexin/hypocretin in vitro. Regul Pept 104:83–89
Kwan HY, Huang Y, Yao X (2004) Regulation of canonical transient receptor potential isoform 3 (TRPC3) channel by protein kinase G. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:2625–2630
Ledo A, Frade J, Barbosa RM, Laranjinha J (2004) Nitric oxide in brain: diffusion, targets and concentration dynamics in hippocampal subregions. Mol Aspects Med 25:75–89
Lovick TA, Key BJ (1996) Inhibitory effect of nitric oxide on neuronal activity in the periaqueductal grey matter of the rat. Exp Brain Res 108:382–388
Murer MG, Riquelme LA, Tseng KY, Pazo JH (1997) Substantia nigra pars reticulata single unit activity in normal and 60HDA-lesioned rats: effects of intrastriatal apomorphine and subthalamic lesions. Synapse 27:278–293
Ohkuma S, Katsura M (2001) Nitric oxide and peroxynitrite as factors to stimulate neurotransmitter release in the CNS. Prog Neurobiol 64:97–108
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in steretaxic co-ordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Percheron G, François C, Yelnik J, Fenelon G, Talbi B (1994) The basal ganglia related systems of primates: definition, description and informational analysis. In: Percheron G, McKenzie GM, Feger J (eds) The Basal Ganglia IV. Plenum Press, New York, pp 3–20
Prast H, Philippu A (2001) Nitric oxide as modulator of neuronal function. Prog Neurobiol 64:51–68
Sardo P, Ferraro G, Di Giovanni G, Galati S, La Grutta V (2002a) Inhibition of nitric oxide synthase influences the activity of striatal neurons in the rat. Neurosci Lett 325:179–182
Sardo P, Ferraro G, Di Giovanni G, Galati S, La Grutta V (2002b) Influence of nitric oxide on the spontaneous activity of globus pallidus neurones in the rat. J Neural Transm 109:1373–1389
Sardo P, Ferraro G, Di Giovanni G, La Grutta V (2003) Nitric oxide-induced inhibition on striatal cells and excitation on globus pallidus neurons: a microiontophoretic study in the rat. Neurosci Lett 343:101–104
Sardo P, Ferraro G, Carletti F, D’Agostino S, La Grutta V (2006a) The discharge of subthalamic neurons is modulated by inhibiting the nitric oxide synthase in the rat. Neurosci Lett 396:252–256
Sardo P, Carletti F, D’Agostino S, Rizzo V, Ferraro G (2006b) Effects of nitric oxide-active drugs on the discharge of subthalamic neurons: microiontophoretic evidence in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 24:1995–2002
Shaw PJ, Salt TE (1997) Modulation of sensory and excitatory amino acid responses by nitric oxide donors and glutathione in the ventrobasal thalamus of the rat. Eur J Neurosci 9:1507–1513
Threlfell S, Cragg SJ, Kallo I, Turi GF, Coen CW, Greenfield SA (2004) Histamine H3 receptors inhibit serotonin release in substantia nigra pars reticulata. J Neurosci 24:8704–8710
Trabace L, Kendrick KM (2000) Nitric oxide can differentially modulate striatal neurotransmitter concentrations via soluble guanylate cyclase and peroxynitrite formation. J Neurochem 75:1664–1674
Vincent SR, Kimura H (1992) Histochemical mapping of nitric oxide synthase in the rat brain. Neuroscience 46:755–784
Wallmichrath I, Szabo B (2002) Cannabinoids inhibit striatonigral GABAergic neurotransmission in the mouse. Neuroscience 113:671–682
Yao X (2007) TRPC, cGMP-dependent protein kinases and cytosolic Ca2+. Handb Exp Pharmacol 179:527–540
Yoshida T, Inoue R, Morii T, Takahashi N, Yamamoto S, Hara Y, Tominaga M, Shimizu S, Sato Y, Mori Y (2006) Nitric oxide activates TRP channels by cysteine S-nitrosylation. Nat Chem Biol 2:596–607
Yung WH, Häusser MA, Jack JJ (1991) Electrophysiology of dopaminergic and non-dopaminergic neurones of the guinea-pig substantia nigra pars compacta in vitro. J Physiol 436:643–667
Zamir N, Skofitsch G, Eskay RL, Jacobowitz DM (1986) Distribution of immunoreactive atrial natriuretic peptides in the central nervous system of the rat. Brain Res 365:105–111
Zhang J, Freeman AS (1994) Electrophysiological effects of cholecystokinin on neurons in rat substantia nigra pars reticulata. Brain Res 652:154–156
Zhou FW, Matta SG, Zhou FM (2008) Constitutively active TRPC3 channels regulate basal ganglia output neurons. J Neurosci 28:473–482
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carletti, F., Ferraro, G., Rizzo, V. et al. Nitric oxide- and cGMP-active compounds affect the discharge of substantia nigra pars reticulata neurons: in vivo evidences in the rat. J Neural Transm 116, 539–549 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0216-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0216-y