Abstract
Background
The efficacy and limitations of salvage gamma knife surgery (GKS) have not been thoroughly described. This study evaluated the efficacy of GKS for treating brain metastases associated with small-cell lung cancer (SCLC) after whole-brain radiotherapy (WBRT) as the first-line radiation therapy.
Methods
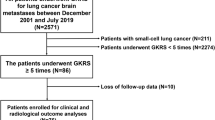
Forty-four patients with recurrent or new SCLC-associated brain metastases underwent GKS after receiving WBRT (median age, 62 years; median duration between WBRT and first GKS, 8.8 months). The median Karnofsky performance status (KPS) score was 100 (range, 40–100), and the median number of brain metastases at the first GKS was five. Ten patients who partially or completely responded to chemotherapy received prophylactic cranial irradiation (PCI) for limited disease.
Results
The median prescribed dose and number of lesions treated with the initial GKS were 20.0 Gy and 3.5, respectively, and the tumor control rate was 95.8 % (median follow-up period, 4.0 months). The 6-month new lesion-free survival, functional preservation rates, and overall survival were 50.0 %, 94.7 %, and 5.8 months, respectively. Neurological death occurred in 17.9 % of cases. The poor prognostic factors for new lesion-free survival time and functional preservation were >5 brain metastases and carcinomatous meningitis, respectively. Poor prognostic factors for survival time were KPS <70, >10 brain metastases, diameter of the largest tumor >20 mm, and carcinomatous meningitis. Median overall survival time from brain metastasis diagnosis was 16.9 months.
Conclusions
GKS may be an effective option for controlling SCLC-associated brain metastases after WBRT and for preventing neurological death in patients without carcinomatous meningitis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aupérin A, Arriagada R, Pignon JP, Le Péchoux C, Gregor A, Stephens RJ, Kristjansen PE, Johnson BE, Ueoka H, Wagner H, Aisner J (1999) Prophylactic cranial irradiation overview collaborative group. Prophylactic cranial irradiation for patients with small-cell lung cancer in complete remission. N Engl J Med 341:476–484
Castrucci WA, Knisely JPS (2008) An update on the treatment of CNS metastases in small cell lung cancer. Cancer J 14:138–146
Chen G, Huynh M, Chen A, Fehrenbacher L, Gandara D, Lau D (2008) Chemotherapy for brain metastases in small-cell lung cancer. Clin Lung Cancer 9:35–38
Cooper JS, Steinfeld AD, Lerch IA (1990) Cerebral metastases: value of reirradiation in selected patients. Radiology 174:883–885
Govindan R, Page N, Morgensztern D, Read W, Tierney R, Vlahiotis A, Spitznagel EL, Piccirillo J (2006) Changing epidemiology of small-cell lung cancer in the United States over the last 30 years: analysis of the surveillance, epidemiologic, and end results database. J Clin Oncol 24:4539–4544
Grandhi R, Kondziolka D, Panczykowski D, Monaco EA 3rd, Kano H, Niranjan A, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery using the Leksell Gamma Knife Perfexion unit in the management of patients with 10 or more brain metastases. J Neurosurg. doi:10.3171/2012.4.JNS11870
Grossi F, Scolaro T, Tixi L, Loprevite M, Ardizzoni A (2001) The role of systemic chemotherapy in the treatment of brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 37:61–67
Higuchi Y, Serizawa T, Nagano O, Matsuda S, Ono J, Sato M, Iwadate Y, Saeki N (2009) Three-staged stereotactic radiotherapy without whole brain irradiation for large metastatic brain tumors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 74:1543–1548
Hochstenbag MM, Twijnstra A, Wilmink JT, Wouters EF, ten Velde GP (2000) Asymptomatic brain metastases (BM) in small cell lung cancer (SCLC): MR-imaging is useful at initial diagnosis. J Neurooncol 48:243–248
Korfel A, Oehm C, von Pawel J, Keppler U, Deppermann M, Kaubitsch S, Thiel E (2002) Response to topotecan of symptomatic brain metastases of small-cell lung cancer also after whole-brain irradiation. A multicenter phase II study. Eur J Cancer 38:1724–1729
Maranzano E, Trippa F, Pacchiarini D, Chirico L, Basagni ML, Rossi R, Bellavita R, Schiavone C, Italiani M, Muti M (2005) Re-irradiation of brain metastases and metastatic spinal cord compression: clinical practice suggestions. Tumori 91:325–330
Postmus PE, Haaxma-Reiche H, Gregor A, Groen HJ, Lewinski T, Scolard T, Kirkpatrick A, Curran D, Sahmoud T, Giaccone G (1998) Brain-only metastases of small cell lung cancer; efficacy of whole brain radiotherapy. An EORTC phase II study. Radiother Oncol 46:29–32
Quan AL, Videtic GM, Suh JH (2004) Brain metastases in small cell lung cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 18:961–972, discussion 974, 979–87
Serizawa T, Higuchi Y, Ono J, Matsuda S, Nagano O, Iwadate Y, Saeki N (2006) Gamma knife surgery for metastatic brain tumors without prophylactic whole-brain radiotherapy: results in 1000 consecutive cases. J Neurosurg 105(Suppl):86–90
Serizawa T, Ono J, Iichi T, Matsuda S, Sato M, Odaki M, Hirai S, Osato K, Saeki N, Yamaura A (2002) Gamma knife radiosurgery for metastatic brain tumors from lung cancer: a comparison between small cell and non-small cell carcinoma. J Neurosurg 97(Suppl):484–488
Serizawa T, Saeki N, Higuchi Y, Ono J, Iuchi T, Nagano O, Yamaura A (2005) Gamma knife surgery for brain metastases: indications for and limitations of a local treatment protocol. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:721–726
Seute T, Leffers P, Wilmink JT, ten Velde GP, Twijnstra A (2006) Response of asymptomatic brain metastases from small-cell lung cancer to systemic first-line chemotherapy. J Clin Oncol 24:2079–2083
Sheehan J, Kondiolka D, Flickinger J, Lunsford LD (2005) Radiosurgery for patients with recurrent small cell lung carcinoma metastatic to the brain: outcomes and prognostic factors. J Neurosurg 102(Suppl):247–254
Soltman B, Faivre-Finn C, Kramer G, Rankin E, Snee M, Hatton M, Postmus P, Collette L, Musat E, Senan S, EORTC Radiation Oncology Group and Lung Cancer Group (2007) Prophylactic cranial irradiation in extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 357:664–672
von Pawel J (2003) The role of topotecan in treating small cell lung cancer: second-line treatment. Lung Cancer 41(Suppl 4):S3–S8
Wegener RE, Olson AC, Kondziolka D, Niranjan A, Lunsford D, Flickinger JC (2011) Streotactic radiosurgery for patients with brain metastases from small cell lung cancer. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 81:e21–e27
Wong WW, Schild SE, Sawyer TE, Shaw EG (1996) Analysis of outcome in patients reirradiated for brain metastases. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 34:585–590
Yamamoto M, Barfold BE, Urakawa Y (2009) Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for brain metastases of non-lung cancer origin: focusing on multiple brain lesions. In: Yamamoto M (ed) Japanese experience with Gamma Knife Radiosurgery. (Progress Neurological Surgery) Kargar, Basel, pp 154–169
Yamamoto M, Ide M, Nishio S, Urakawa Y (2002) Gamma Knife radiosurgery for numerous brain metastases: is this a safe treatment? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 53:1279–1283
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Comment
The authors present a series of 44 patients whose brain metastases were complicating small-cell lung cancer. This is a highly unusual series for several reasons. This pathology is usually considered to be unsuitable because of the disseminated nature of this particular cancer, and indeed 38 of their patients had uncontrolled systemic disease. Their patient selection allowed patients with simultaneously existing carcinomatous meningitis (5 cases) and up to 36 metastases in one treatment. With retreatment up to five times, they treated up to 69 tumors in one patient, and in some cases treated large tumors in three stages with the Gamma Knife. Despite this approach they found that radiosurgery was, in itself, safe. The systemic disease is of course beyond the reach of the Gamma Knife, but such an aggressive approach may be able to delay or even prevent neurological death.
Andras Kemeny
Sheffield, UK
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakazaki, K., Higuchi, Y., Nagano, O. et al. Efficacy and limitations of salvage gamma knife radiosurgery for brain metastases of small-cell lung cancer after whole-brain radiotherapy. Acta Neurochir 155, 107–114 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1520-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-012-1520-0