Abstract
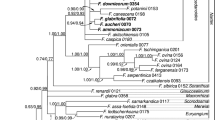
This paper presents phylogenies of the small but ecologically and horticulturally important Australian genus Correa (Rutaceae). Consensus phylogenies generated using parsimony were congruent with their counterparts generated by Bayesian analysis, although usually less well resolved. The phylogeny generated from the second internal transcribed spacer region of the nuclear ribosomal DNA supported the monophyly of Correa and identified two well supported clades (one comprising C. lawrenceana and C. baeuerlenii and the other containing all other species of the genus). Phylogenetic reconstructions based on the combined trnL-trnF spacer and the trnK intron (including the matK gene) regions of chloroplast DNA also supported the monophyly of Correa and of the C. lawrenceana/C. baeuerlenii clade, but the topology among the other species differed markedly from that in the ITS-based phylogeny. The major clades identified in the chloroplast phylogenies seemed to follow geographic patterns rather than species boundaries, with different samples of C. glabra bearing chloroplast genotypes from different clades. These patterns are likely to be because of independent evolution of the chloroplast and nuclear genomes, and are typical of cases of introgressive hybridisation among species or incomplete lineage sorting of chloroplast genomes leading to incongruence between chloroplast and nuclear phylogenies. Thus, the phylogenies based on nuclear DNA should reflect species relations better than the chloroplast phylogeny in Correa, and we propose a new subgeneric classification of the genus on the basis of the ITS-based phylogeny and morphology. Correa subgenus Persistens Othman, Duretto and G.J. Jord., containing C. lawrenceana and C. baeuerlenii, is formally described.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abkenar AA, Isshiki S, Tashiro Y (2004) Maternal inheritance of chloroplast DNA in intergeneric sexual hybrids of “true citrus fruit trees” revealed by PCR-RFLP analysis. J Hort Sci Biotech 79:360–363
Alvarez I, Wendel JF (2003) Ribosomal ITS sequences and plant phylogenetic inference. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29:417–434
Anderson R (1983) Variation and evolution in Correa (Rutaceae). Dissertation. La Trobe University
Australia’s Virtual Herbarium, available via Centre for Plant Biodiversity Research, Council of Heads of Australian Herbaria, http://www.cpbr.gov.au/cgi-bin/avh.cgi. Accessed September 2009
Avise JC (1989) Gene trees and organismal histories: a phylogenetic approach to population biology. Evolution 43:1192–1208
Baldwin BG, Sanderson MS, Porter JM, Wojciechowski MF, Campbell CS, Donoghue MJ (1995) The ITS region of nuclear ribosomal DNA: a valuable source of evidence on angiosperm phylogeny. Ann Mo Bot Gard 82:247–277
Chase MW, Morton CM, Kallunki JA (1999) Phylogenetic relationships of the Rutaceae: a cladistic analysis of the subfamilies using evidence from rbcL and atpB sequence variation. Amer J Bot 86:1191–1199
Chase MW, Fay MF, Savolainen V (2000) Higher-level classification in the angiosperms: new insights from the perspective of DNA sequence data. Taxon 49:685–704
Clegg MT, Durbin ML (1990) Molecular approaches to the study of plant biosystematics. Aust Syst Bot 3:1–8
Comes HP, Abbott RJ (2001) Molecular phylogeography, reticulation, and lineage sorting in Mediterranean Senecio sect. Senecio (Asteraceae). Evolution 55:1943–1962
de Candolle AP (1824) Prodromus 1:719
Engler A (1896) Rutaceae. In: Naturlichen Pflanzenfamilien, teil III abt. 4, W. Engelman, Leipzig, pp 95–201
Engler A (1931) Rutaceae. In: Engler A, Harms H (eds) Die Naturlichen Pflanzenfamilien, 2nd edn. W. Engelman, Leipzig, 19:187–358
Farris JS, Källersjö M, Kluge AG, Bult C (1995) Constructing a significance test for incongruence. Syst Biol 44:570–572
Gielly L, Taberlet P (1994) Chloroplast DNA polymorphism at the intrageneric level and plant phylogenies. C R Acad Sci 317:685–692
Grivet D, Petit RJ (2002) Phylogeography of the common ivy (Hedera sp.) in Europe: genetic differentiation through space and time. Mol Ecol 11:1351–1362
Groppo M, Pirani JR, Salatino MLF, Blanco SR, Kallunki JA (2008) Phylogeny of Rutaceae based on two non-coding regions from cpDNA. Am J Bot 8:985–1005
Heckman KL, Mariani CL, Rasoloarison R, Yoder AD (2007) Multiple nuclear loci reveal patterns of incomplete lineage sorting and complex species history within western mouse lemurs (Microcebus). Mol Phylogenet Evol 43:353–367
Hsiao C, Chatterton NJ, Asay KH, Jensen KB (1995) Molecular phylogeny of the Pooideae (Poaceae) based on nuclear rDNA (ITS) sequences. Theor Appl Genet 90:389–398
Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F (2001) MRBAYES: Bayesian inference of phylogeny. Bioinformatics 17:754–755
Johnson LA, Soltis DE (1994) matK DNA sequence and phylogenetic reconstruction in Saxifragaceae s. str. Syst Bot 19:143–156
Johnson LA, Soltis DE (1995) Phylogenetic inference in Saxifragaceae sensu stricto and Gilia (Polemoniaceae) using matK sequences. Ann Mo Bot Gard 82:149–175
Kita Y, Ueda K, Kadota Y (1995) Molecular phylogeny and evolution of the Asian Aconitum subgenus Aconitum (Ranunculaceae). J Plant Res 108:429–442
McKinnon GE, Jordan GJ, Vaillancourt RE, Steane DA, Potts BM (2004) Glacial refugia and reticulate evolution: the case of the Tasmanian eucalypts. Phil Trans R Soc Lond B 359:275–284
Nixon KC, Carpenter JM (1996) On simultaneous analysis. Cladistics 12:221–241
Ochieng JW, Henry RJ, Baverstock PR, Steane DA, Shepherd M (2007) Mol Phylogenet Evol 44:752–764
Othman RNA (2009). Systematic relationships within Correa. Dissertation. University of Tasmania
Posada D, Crandall KA (1998) Modeltest: testing the model of DNA substitution. Bioinformatics 14:817–818
Rieseberg LH, Wendel JF (1993) ‘Introgression and its consequences in plants’. In: Harrison RG (ed) Hybrid zones and the evolutionary process. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 70–109
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Simmons MP, Ochoterena H (2000) Gaps as characters in sequence-based phylogenetic analyses. Syst Biol 49:369–381
Soltis DE, Kuzoff RK (1995) Discordance between molecular and chloroplast phylogenies in the Heuchera group (Saxifragaceae). Syst Bot 49:727–742
Soltis DE, Soltis PS, Collier TG, Edgerton ML (1991) Chloroplast DNA variation within and among genera of the Heuchera group (Saxifragaceae): evidence for chloroplast capture and paraphyly. Am J Bot 78:1091–1112
Soltis DE, Johnson LA, Looney C (1996) Discordance between ITS and chloroplast topologies in the Boykinia group (Saxifragaceae). Syst Bot 21:169–176
Steane DA, Byrne M, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM (1998a) Chloroplast DNA polymorphism signals complex interspecific interactions in Eucalyptus (Myrtaceae). Aust Syst Bot 11:25–40
Steane DA, Byrne M, Vaillancourt RE, Potts BM (1998b) Complex interspecific interactions in Eucalyptus: evidence from the chloroplast. Aust Biol 11:39–46
Swofford DL (1998) PAUP*. Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony (*and other methods) (version4). Sinauer Associates, Sunderland
Taberlet P, Gielly L, Pautou G, Bouvet J (1991) Universal primers for amplification of three non-coding regions of chloroplast DNA. Plant Mol Biol 17:1105–1109
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Wilson PG (1961) A taxonomic revision of the genus Correa (Rutaceae). Trans Roy Soc S Aust 85:21–53
Wilson PG (1998) Notes on the genus Correa (Rutaceae). Nuytsia 12:89–105
Wilson PG (submitted) Correa (Rutaceae). Flora Aust
Wolfe KH, Li WH, Sharp PM (1987) Rates of nucleotide substitution vary greatly among plant mitochondrial, chloroplast and nuclear DNAs. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 84:9054–9058
Xiang QY, Crawford DJ, Wolfe AD, Tang YC, Depamphilis CW (1998) Origin and biogeography of Aesculus L. (Hippocastanaceae): a molecular phylogenetic perspective. Evolution 52:988–997
Yuan YM, Kupfer P, Doyle JJ (1996) Infrageneric phylogeny of the genus Gentiana (Gentianaceae) inferred from nucleotide sequences of the internal transcribed spacers (ITS) of nuclear ribosomal DNA. Am J Bot 83:641–652
Zander RH (2004) Minimal values for reliability of bootstrap and jackknife proportions, decay index, and bayesian posterior probability. Phyloinformatics 2:1–13
Zurawski G, Clegg MT (1987) Evolution of higher-plant DNA-encoded genes: implications for structure, function and phylogenetic studies. Ann Rev Plant Phys 38:391–418
Acknowledgments
We thank staff of the Australian National Botanic Garden and the Botanic Gardens of Adelaide (including Wittunga Botanic Gardens) for supplying plant material for this study. We also thank René Vaillancourt and Adam Smolenski for advice on suitable molecular methods.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Appendix 1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Othman, R.N.A., Jordan, G.J., Worth, J.R.P. et al. Phylogeny and infrageneric classification of Correa Andrews (Rutaceae) on the basis of nuclear and chloroplast DNA. Plant Syst Evol 288, 127–138 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-010-0315-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-010-0315-0