Abstract
Background
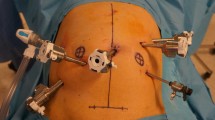
The use of the da Vinci robotic platform for total colectomy has been limited by the need to reposition the patient-side surgical cart from one side of the patient to the other, which increases operative time. In this study, we examined the feasibility of robotic total colectomy using the da Vinci Xi model, which offers a rotating boom-mounted system and laser-targeted trocar positioning.
Methods
The study cohort consisted of 23 patients who underwent minimally invasive total colectomy for cancer or polyposis syndromes at a comprehensive cancer center between 2015 and 2017. Of the 23 colectomies, 15 were robotic and eight were laparoscopic. For the robotic colectomies, trocars were placed in the supraumbilical region and all four quadrants. The da Vinci Xi robot was placed between the patient’s legs, and the boom was rotated from left to right and then to the middle in order to work sequentially on the right colon, the left colon, and the pelvis. Operating time and short-term outcomes were compared between the patients who underwent robotic surgery and the patients who underwent laparoscopic surgery.
Results
The two groups of patients were comparable in age, gender, BMI, physical status, and disease types. In the robotic group, median length of stay (4 vs. 6 days, p = 0.047) was significantly shorter and median operative time (243 vs. 263 min, p = 0.97) and median estimated blood loss (50 vs. 100 ml; p = 0.08) were similar between the groups.
Conclusions
With the da Vinci Xi boom-mounted system, total abdominal colectomy can be performed without the need to move the patient-side surgical cart and is associated with shorter length of stay and similar operative time compared to the laparoscopic approach.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
D’Annibale A, Morpurgo E, Fiscon V, Trevisan P, Sovernigo G, Orsini C, Guidolin D (2004) Robotic and laparoscopic surgery for treatment of colorectal diseases. Dis Colon Rectum 47:2162–2168
Hellan M, Anderson C, Ellenhorn JD, Paz B, Pigazzi A (2007) Short-term outcomes after robotic-assisted total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer. Ann Surg Oncol 14:3168–3173
Zhang X, Wei Z, Bie M, Peng X, Chen C (2016) Robot-assisted versus laparoscopic-assisted surgery for colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. Surg Endosc 30:5601–5614
Moghadamyeghaneh Z, Hanna MH, Carmichael JC, Pigazzi A, Stamos MJ, Mills S (2016) Comparison of open, laparoscopic, and robotic approaches for total abdominal colectomy. Surg Endosc 30:2792–2798
Hanai T, Maeda K, Masumori K, Katsuno H, Matsuoka H (2015) Technique of robotic-assisted total proctocolectomy with lymphadenectomy and ileal pouch-anal anastomosis for transverse colitic cancer of ulcerative colitis, using the single cart position. Surg Technol Int 27:86–92
Baik SH, Kwon HY, Kim JS, Hur H, Sohn SK, Cho CH, Kim H (2009) Robotic versus laparoscopic low anterior resection of rectal cancer: short-term outcome of a prospective comparative study. Ann Surg Oncol 16:1480–1487
Heemskerk J, de Hoog DE, van Gemert WG, Baeten CG, Greve JW, Bouvy ND (2007) Robot-assisted vs. conventional laparoscopic rectopexy for rectal prolapse: a comparative study on costs and time. Dis Colon Rectum 50:1825–1830
Prete FP, Pezzolla A, Prete F, Testini M, Marzaioli R, Patriti A, Jimenez-Rodriguez RM, Gurrado A, Strippoli GFM (2017) Robotic versus laparoscopic minimally invasive surgery for rectal cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Ann Surg 267:1034–1046
Protyniak B, Jorden J, Farmer R (2017) Multiquadrant robotic colorectal surgery: the da Vinci Xi vs Si comparison. J Robot Surg 12:67–74
Morelli L, Di Franco G, Guadagni S, Palmeri M, Gianardi D, Bianchini M, Moglia A, Ferrari V, Caprili G, D’Isidoro C, Melfi F, Di Candio G, Mosca F (2017) Full robotic colorectal resections for cancer combined with other major surgical procedures: early experience with the da Vinci Xi. Surg Innov 24:321–327
Morelli L, Di Franco G, Guadagni S, Rossi L, Palmeri M, Furbetta N, Gianardi D, Bianchini M, Caprili G, D’Isidoro C, Mosca F, Moglia A, Cuschieri A (2017) Robot-assisted total mesorectal excision for rectal cancer: case-matched comparison of short-term surgical and functional outcomes between the da Vinci Xi and Si. Surg Endosc 32:589–600
Funding
NCI Grant P30 CA008748.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Garrett Nash: Conference expenses paid by NOVADAQ (2015), J J Smith has received travel support for fellow education from Intuitive Surgical Inc. and is an advisor for Endogenesis Inc. E Pappou has received support for a robotic training course by Intuitive (2015), J Garcia-Aguilar has received support from Medtronic, Johnson and Johnson and Intuitive Inc. R Jimenez-Rodriguez, F Quezada, M Tchack, I Wei, J Guillem, P Paty and M Weiser have no conflicts of interest or financial ties to disclose.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary material 1 (MP4 202397 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jimenez-Rodriguez, R.M., Quezada-Diaz, F., Tchack, M. et al. Use of the Xi robotic platform for total abdominal colectomy: a step forward in minimally invasive colorectal surgery. Surg Endosc 33, 966–971 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6529-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-018-6529-x