Abstract.
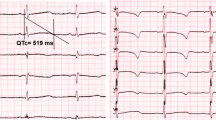
Mutation analysis of the TAZ (G4.5) gene was performed on a patient with Barth syndrome. The reverse transcription/polymerase chain reaction procedure showed aberrant splicing and elongation of exon 3 because of the insertion of 106 bases (IVS3+1 to +106) between exons 3 and 4. The genomic DNA revealed an intronic mutation four bases downstream from the new cleavage site (IVS3+110G→A). The IVS3+110G→A mutation created a novel 5' splice site that showed GC but not GT, and the additional splice site was used preferentially over the upstream authentic slice site. This is a new type of splicing mutation responsible for a human genetic disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakamoto, O., Ohura, T., Katsushima, Y. et al. A novel intronic mutation of the TAZ (G4.5) gene in a patient with Barth syndrome: creation of a 5' splice donor site with variant GC consensus and elongation of the upstream exon. Hum Genet 109, 559–563 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-001-0612-3
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-001-0612-3