Abstract
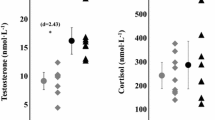
Lifestyles associated with different types and intensities of exercise result in improved health including positive changes in chronic low-grade inflammatory biomarkers. Alternatively, some forms of exercise adversely affect reproductive health of men, including changes in circulating reproductive hormones. To explore the associations between exercise intensity and circulating levels of reproductive hormones, and inflammatory analytes in serious leisure athletes (triathletes and cyclists) and recreational athletes. Male athletes 18–60 years old, 16 triathletes, 46 cyclists and 45 recreational athletes, were recruited to provide plasma for the measurement of total testosterone, estradiol, follicular stimulating hormone, luteinizing hormone (LH), sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG), cortisol, interleukin-6 (IL-6), and interleukin-1β (IL-1β) levels, and calculation of free androgen index (FAI) and the estradiol:SHBG ratio (ESR). Plasma estradiol concentrations were more than two times higher in cyclists than in triathletes and recreational athletes (p < 0.01). Testosterone levels were also higher in cyclists than recreational athletes (p < 0.01), but not significantly different from triathletes. SHBG levels were higher in triathletes and cyclists than in recreational athletes (p < 0.01). LH levels were lower in cyclists than in recreational athletes (p < 0.05). IL-6 and IL-1β levels were each two times lower in triathletes than in cyclists (p < 0.05) and IL-6 levels were lower in cyclists than in recreational athletes (p < 0.01). IL-1β levels were two times lower in triathletes than in cyclists (p < 0.05). Circulating estradiol and testosterone levels were elevated in serious leisure male cyclists. This effect is discussed in light in the absence of a substantial concomitant change in gonadotropin levels and other variables.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson JL, Vaccarino V (2002) Relationship between physical activity and inflammation among apparently healthy middle-aged and older US adults. Arch Intern Med 162(11):1286–1292
Ballard SL, Wellborn-Lim JJ, Clauson K (2010) Effects of commercial energy drink consumption on athletic performance and body composition. Phys Sportsmed 38(1):107–117
Bjerner J, Biernat D, Fosså SD, Bjøro T (2009) Reference intervals for serum testosterone, SHBG, LH and FSH in males from the NORIP project. Scand J Clin Lab Investig 69(8):873–879
Brown GA, Vukovich MD, Reifenrath TA, Uhl NL, Parsons KA, Sharp RL, King DS (2000) Effects of anabolic precursors on serum testosterone concentrations and adaptations to resistance training in young men. Int J Sport Nutr Exerc Metab 10(3):340–359
Buhr ED, Yoo SH, Takahashi JS (2010) Temperature as a universal resetting cue for mammalian circadian oscillators. Science 330(6002):379–385
Calippe B, Douin-Echinard V, Laffargue M, Laurell H, Rana-Poussine V, Pipy B, Guery JC, Bayard F, Arnal JF, Gourdy P (2008) Chronic estradiol administration in vivo promotes the proinflammatory response of macrophages to TLR4 activation: involvement of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Immunol 180(12):7980–7988
Celec P, Behuliak M (2010) Behavioural and endocrine effects of chronic cola intake. J Psychopharmacol 24(10):1569–1572
Chen SH, Chang FM, Niu KC, Lin MY, Lin MT (2006) Resuscitation from experimental heatstroke by estrogen therapy. Crit Care Med 34(4):1113–1118
Cheung SS, McLellan TM, Tenaglia S (2000) The thermophysiology of uncompensable heat stress: physiological manipulations and individual characteristics. Sports Med 29(5):329–359
Chrousos GP (2010) Stress and sex versus immunity and inflammation. Sci Signal 3(143):e36
Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjöström M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, Pratt M, Ekelund U, Yngve A, Sallis JF, Oja P (2003) International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Med Sci Sports Exerc 35(8):1381–1395
Darbre PD, Aljarrah A, Miller WR, Coldham NG, Sauer MJ, Pope GS (2004) Concentrations of parabens in human breast tumours. J Appl Toxicol 24(1):5–13
Di Carlo C, Tommaselli GA, Sammartino A, Bifulco G, Nasti A, Nappi C (2004) Serum leptin levels and body composition in postmenopausal women: effects of hormone therapy. Menopause 11:466–473
Dolomie-Fagour L, Gatta B, Nguyen TDT, Corcuff JBt (2008) Bioavailable estradiol in man: relationship with age and testosterone. Clin Chim Acta 398(1–2):145–147
Dressendorfer RH, Petersen SR, Moss Lovshin SE, Hannon JL, Lee SF, Bell GJ (2002) Performance enhancement with maintenance of resting immune status after intensified cycle training. Clin J Sport Med 12(5):301–307
Edwards KM, Burns VE, Ring C, Carroll D (2006) Individual differences in the interleukin-6 response to maximal and submaximal exercise tasks. J Sports Sci 24(8):855–862
Enns DL, Tiidus PM (2010) The influence of estrogen on skeletal muscle: sex matters. Sports Med 40(1):41–58
FitzGerald L, Carpenter C (2007) Bone mineral density results influencing health-related behaviors in male athletes at risk for osteoporosis. J Clin Densitometry 13(3):256–262
Fragala MS, Kraemer WJ, Denegar CR, Maresh CM, Mastro AM, Volek JS (2011) Neuroendocrine–immune interactions and responses to exercise. Sports Med 41(8):621–639
Frederiksen H, Jorgensen N, Andersson AM (2011) Parabens in urine, serum and seminal plasma from healthy Danish men determined by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 21(3):262–271
Ghisletti S, Meda C, Maggi A, Vegeto E (2005) 17+-Estradiol inhibits inflammatory gene expression by controlling NFκB intracellular localization. Mol Cell Biol 25(8):2957–2968
Hackney AC (2008) The effects of endurance exercise on the reproductive system of men: the “exercise-hypogonadal” male condition. J Endocrinol Invest 31:932–938
Hackney AC, Moore AW, Brownlee KK (2005) Testosterone and endurance exercise: development of the exercise-hypogonadal male condition. Acta Physiol Hung 92(2):121–137
Heckman MA, Weil J, Gonzalez De Mejia E (2011) Caffeine (1, 3, 7-trimethylxanthine) in foods: a comprehensive review on consumption, functionality, safety, and regulatory matters. J Food Sci 75(3):R77–R89
Hernandez-Avila M, Colditz GA, Stampfer MJ, Rosner B, Speizer FE, Willett WC (1991) Caffeine, moderate alcohol intake, and risk of fractures of the hip and forearm in middle-aged women. Am J Clin Nutr 54:157–163
Hiruntrakul A, Nanagara R, Emasithi A, Borer KT (2010) Effect of endurance exercise on resting testosterone levels in sedentary subjects. Cent Eur J Public Health 18(3):169–172
Izquierdo M, Ibáñez J, Häkkinen K, Kraemer WJ, Ruesta M, Gorostiaga EM (2004) Maximal strength and power, muscle mass, endurance and serum hormones in weightlifters and road cyclists. J Sports Sci 22(5):465–478
Jankord R, Jemiolo B (2004) Influence of physical activity on serum IL-6 and IL-10 levels in healthy older men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 36(6):960–964
Khosla S, Melton LJ, Riggs BL (2002) Estrogen and the male skeleton. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87(4):1443–1450
Knochenhauer ES, Boots LR, Potter HD, Azziz R (1998) Differential binding of estradiol and testosterone to SHBG. Relation to circulating estradiol levels. J Reprod Med 43(8):665–670
Kraemer WJ, Marchitelli L, Gordon SE, Harman E, Dziados JE, Mello R, Frykman P, McCurry D, Fleck SJ (1990) Hormonal and growth factor responses to heavy resistance exercise protocols. J Appl Physiol 69(4):1442–1450
Kraemer R, Hollander D, Reeves G, Francois M, Ramadan Z, Meeker B, Tryniecki J, Hebert E, Castracane V (2006) Similar hormonal responses to concentric and eccentric muscle actions using relative loading. Eur J Appl Physiol 96(5):551–557
Li Q, Verma IM (2002) NF-[kappa]B regulation in the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 2(10):725–734
Libby P (2002) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Nature 420(6917):868–874
Lin CY, Lin MT, Cheng RT, Chen SH (2010) Testosterone depletion by castration may protect mice from heat-induced multiple organ damage and lethality. J Biomed Biotechnol 2010:485306
Lira F, Rosa J, Pimentel G, Souza H, Caperuto E, Carnevali L, Seelaender M, Damaso A, Oyama L, de Mello M, Santos R (2010) Endotoxin levels correlate positively with a sedentary lifestyle and negatively with highly trained subjects. Lipids Health Dis 9(1):82
Maimoun L, Lumbroso S, Manetta J, Paris F, Leroux JL, Sultan C (2003) Testosterone is significantly reduced in endurance athletes without impact on bone mineral density. Horm Res Paediatr 59(6):285–292
Mastorakos G, Pavlatou M (2005) Exercise as a stress model and the interplay between the hypothalamus–pituitary–adrenal and the hypothalamus–pituitary–thyroid axes. Horm Metab Res 37(09):577–584
Mastorakos G, Pavlatou M, Diamanti-Kandarakis E, Chrousos GP (2005) Exercise and the stress system. Hormones 4(2):73–89
McLellan TM (2001) The importance of aerobic fitness in determining tolerance to uncompensable heat stress. Comparative biochemistry and physiology—part A: molecular & integrative physiology 128(4):691–700
Park J, Rho HK, Kim KH, Choe SS, Lee YS, Kim JB (2005) Overexpression of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase is associated with lipid dysregulation and insulin resistance in obesity. Mol Cell Biol 25(12):5146–5157
Pedersen BK, Febbraio M (2005) Muscle-derived interleukin-6—a possible link between skeletal muscle, adipose tissue, liver, and brain. Brain Behav Immun 19(5):371–376
Pedersen BK, Hoffman-Goetz L (2000) Exercise and the immune system: regulation, integration, and adaptation. Physiol Rev 80(3):1055–1081
Pickering TG, Hall JE, Appel LJ, Falkner BE, Graves J, Hill MN, Jones DW, Kurtz T, Sheps SG, Roccella EJ (2005) Recommendations for blood pressure measurement in humans and experimental animals: part 1: blood pressure measurement in humans: a statement for professionals from the subcommittee of professional and public education of the American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research. Hypertension 45(1):142–161
Rohrmann S, Nelson WG, Rifai N, Brown TR, Dobs A, Kanarek N, Yager JD, Platz EA (2007) Serum estrogen, but not testosterone, levels differ between black and white men in a nationally representative sample of Americans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(7):2519–2525
Sacheck JM, Cannon JG, Hamada K, Vannier E, Blumberg JB, Roubenoff R (2006) Age-related loss of associations between acute exercise-induced IL-6 and oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291(2):E340–E349
Shen KH, Lin CH, Chang HK, Chen WC, Chen SH (2008) Premarin can act via estrogen receptors to rescue mice from heatstroke-induced lethality. Shock 30(6):668–674
Soucy G, Boivin G, Labrie F, Rivest S (2005) Estradiol is required for a proper immune response to bacterial and viral pathogens in the female brain. J Immunol 174(10):6391–6398
Sousa e Silva T, Longui CA, Rocha MN, Faria CDC, Melo MR, Faria TG, de Souza JA, Rizzo LV (2010) Prolonged physical training decreases mRNA levels of glucocorticoid receptor and inflammatory genes. Horm Res Paediatr 74(1):6–14
Stephen J, Brufsky A, Weissfeld J, Trump DL, Dyky MA, Hadeed V (2001) Testosterone, sex hormone-binding globulin, and body composition in young adult African American and Caucasian men. Metabolism 50(10):1242–1247
Timmons BW, Tarnopolsky MA, Snider DP, Bar-OR O (2006a) Immunological changes in response to exercise: influence of age, puberty, and gender. Medicine Sci Sports Exerc 38(2):293–304
Timmons BW, Hamadeh MJ, Tarnopolsky MA (2006b) No effect of short-term 17beta-estradiol supplementation in healthy men on systemic inflammatory responses to exercise. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 291(2):R285–R290
Uchida Y, Kano M, Yasuhara S, Kobayashi A, Tokizawa K, Nagashima K (2010) Estrogen modulates central and peripheral responses to cold in female rats. J Physiol Sci 60(2):151–160
Vanderschueren D, Vandenput L, Boonen S, Lindberg MK, Bouillon R, Ohlsson C (2004) Androgens and bone. Endocr Rev 25(3):389–425
Vankrieken L (2000) Immulite® reproductive hormone assays, 4th edn. DPC Technical Report. Ref Type: Report
Varga-Pinter B, Horvath P, Kneffel Z, Major Z, Osvath P, Pavlik G (2011) Resting Blood Pressure Values of Adult Athletes. Kidney and blood pressure research 34(6):387–395
Vermeulen A, Verdonck L, Kaufman JM (1999) A critical evaluation of simple methods for the estimation of free testosterone in serum. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 84(10):3666–3672
Ware JE, Kosinski MK, Keller SD (1996) A 12-item short-form health survey: construction of scales and preliminary tests of reliability and validity. Med Care 34(3):220–233
Wittert GA, Livesey JH, Espiner EA, Donald RA (2012) Adaptation of the hypothalamopituitary adrenal axis to chronic exercise stress in humans. Med Sci Sports Exerc 28(8):1015–1019
Wright H, Selkirk G, McLellan T (2010) HPA and SAS responses to increasing core temperature during uncompensable exertional heat stress in trained and untrained males. Eur J Appl Physiol 108(5):987–997
Zanovec M, Johnson LG, Marx BD, Keenan MJ, Tuuri G (2009) Self-reported physical activity improves prediction of body fatness in young adults. Med Sci Sports Exerc 41(2):328–335
Acknowledgments
We would like to acknowledge the research participants, the General Clinical Research Center (GCRC) nursing staff at UCLA for their support and Mauricio Pena for his support in preparing the data for this manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors are not aware of any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by William J. Kraemer.
The findings and conclusions in this report are those of the authors and do not necessarily represent the views of the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
FitzGerald, L.Z., Robbins, W.A., Kesner, J.S. et al. Reproductive hormones and interleukin-6 in serious leisure male athletes. Eur J Appl Physiol 112, 3765–3773 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2356-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-012-2356-2