Abstract
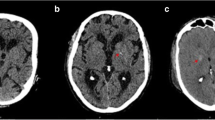
We evaluated the prevalence and the size of epithalamus calcifications (EC) and choroid plexus calcifications (CPC) on computed tomography (CT) scans in a group of 64 schizophrenic patients and in a group of 31 healthy controls. The associations between cerebral calcifications, demographic variables, and other brain morphological characteristics (particularly cerebral ventricular size and cortical atrophy) in both, patients and controls, were also considered. A significant increase in size of the epithalamic-region calcifications in schizophrenic patients was found, whereas there was no evidence of increase in both, dimension and prevalence, of choroid plexus calcification. Such dimensional increase was unrelated to the duration of illness and therefore did not seem to be iatrogenic or secondary to the disease. A correlation was found between epithalamus calcifications and cortical atrophy and third-ventricle enlargement, suggesting that calcifications of this cerebral region may be associated with lesions of third-periventricular areas and of circuitries hypothesized to be involved in the pathophysiology of schizophrenia.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 5 May 1997 / Accepted: 13 July 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caputo, A., Ghiringhelli, L., Dieci, M. et al. Epithalamus calcifications in schizophrenia. European Archives of Psychiatry and Clinical Neurosciences 248, 272–276 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004060050049
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004060050049