Abstract
Introduction
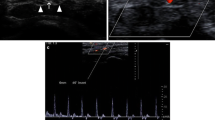
Compression of the median nerve at the wrist by a persistent median artery is one of the uncommon reasons for carpal tunnel syndrome. Most of the studies in the literature deal with thrombosed persistent median artery.
Materials and method
In this study, we present surgical treatment of four carpal tunnel syndromes, which had persistent median arteries. The mean age of the patients was 51 years. All four median arteries were patent and only transverse carpal ligament releases were performed using a standard anterior open approach for decompression of the carpal tunnel. Neither ligation nor transposition of the arteries was done.
Results
All patients became symptom free after a few weeks. Only one patient had a slight recurrence 13 months postoperatively. Splint use and modification of her activities reduced her disturbance, and no further treatment was applied.
Conclusion
If the patient has no additional anomaly, our clinical experiences lead us not to advise resection or transposition because simple release of the transverse carpal ligament can relieve symptoms.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balakrishnan C, Smith MF, Puri P (1999) Acute carpal tunnel syndrome from thrombosed persistent median artery. J Emerg Med 17:437–439
Barfred T, Hojlund AP, Bertheussen K (1985) Median artery in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg [Am] 10:864–867
Jones NF, Ming NL (1988) Persistent median artery as a cause of pronator syndrome. J Hand Surg [Am] 13:728–732
Kato T, Kuroshima N, Okutsu I, Ninomiya S (1994) Effects of endoscopic release of the transverse carpal ligament on carpal canal volume. J Hand Surg [Am] 19:416–419
Khashaba A (2002) Carpal tunnel syndrome from thrombosed persistent median artery. J Emerg Med 22:55–57
Olave E, Prates JC, Gabrielli C, Pardi P (1997) Median artery and superficial palmar branch of the radial artery in the carpal tunnel. Scand J Plast Reconstr Surg Hand Surg 31:13–16
Rose RE (1995) Acute carpal tunnel syndrome secondary to thrombosis of a persistent median artery. West Indian Med J 44:32–33
Zeiss J, Guilliam Haidet L (1993) MR demonstration of a persistent median artery in carpal tunnel syndrome. J Comput Assist Tomogr 17:482–484
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bilgin, S.S., Olcay, S.E., Derincek, A. et al. Can simple release relieve symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome caused by a persistent median artery?. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124, 154–156 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-004-0637-x
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-004-0637-x