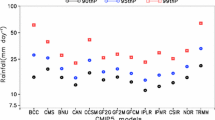
Abstract
This study investigates the projected changes in interannual variability of South Asian summer monsoon and changes of ENSO-monsoon relationships in the 21st century under the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) scenarios A1B and A2, respectively, by analyzing the simulated results of twelve Coupled Model Intercomparison Project Phase 3 (CMIP3) coupled models. The dynamical monsoon index (DMI) was adopted to describe the interannual variability of South Asian summer monsoon, and the standard deviation (SD) was used to illustrate the intensity of interannual variability. It was found that most models could project enhanced interannual variability of monsoon in the 21st century. The multi-model ensemble (MME) results showed increases in the interannual variability of DMI: 14.3% and 20.0% under scenarios A1B and A2, respectively. The MME result also showed increases in the rainfall variability are of about 10.2% and 22.0% under scenarios A1B and A2. The intensification of interannual variability tended to occur over the regions that have larger variability currently; that is, “the strong get stronger”. Another finding was that ENSO-monsoon relationships are likely to be enhanced in the 21st century. The dynamical component of the monsoon will be more closely correlated to ENSO in the future under global warming, although the ENSO-summer rainfall relationship cannot be reasonably projected by current models. This suggests that the South Asian summer monsoon is more predictable in the future, at least dynamically.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annamalai, H., K. Hamilton, and K. R. Sperber, 2007: The south Asian summer monsoon and its relationship with ENSO in the IPCC AR4 simulations. J. Climate, 20, 1071–1092, doi: 10.1175/JCLI4035.1.
Ashrit, R. G., H. Douville, and K. Rupa Kumar, 2003: Response of the Indian monsoon and ENSO-monsoon teleconnection to enhanced greenhouse effect in the CNRM coupled model. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 81, 779–803.
Ashrit, R. G., A. Kitoh, and S. Yukimoto, 2005: Transient response of ENSO-monsoon teleconnection in MRI-CGCM2.2 climate change simulations. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 83, 273–291.
Chen, H., and J. Sun, 2009: How the “best” models project the future precipitation change in China. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 26(4), 773–782, doi: 10.1007/s00376-009-8211-7.
Dairaku, K., S. Emori, and T. Nozawa, 2008: Impacts of global warming on hydrological cycles in the Asian monsoon region. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25(6), 960–973, doi: 10.1007/s00376-008-0960-1.
Hu, Z. Z., M. Latif, E. Roeckner, and L. Bengtsson, 2000: Intensified Asian summer monsoon and its variability in a coupled model forced by increasing greenhouse gas concentrations. Geophys. Res. Lett., 27, 2681–2684.
Kang, I. S., and Coauthors, 2002: Intercomparison of the climatological variations of Asian summer monsoon precipitation simulated by 10 GCMs. Climate Dyn., 19, 383–395.
Kitoh, A., S. Yukimoto, A. Noda, and T. Motoi, 1997: Simulated changes in the Asian summer monsoon at times of increased atmospheric CO2. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 75, 1019–1031.
Knopf, B., K. Zickfeld, M. Flechsig, and V. Petoukhov, 2008: Sensitivity of the Indian monsoon to human activities. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25(6), 932–945, doi: 10.1007/s00376-008-0932-5.
Kripalani, R. H., J. H. Oh, A. Kulkarni, S. S. Sabade, and H. S. Chaudhari, 2007: South Asian summer monsoon precipitation variability: Coupled climate model simulations and projections under IPCC AR4. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 90, 133–159, doi: 10.1007/s00704-006-0282-0.
Krishna Kumar, K., M. K. Soman, and K. Rupa Kumar, 1995: Seasonal forecasting of Indian summer monsoon rainfall: A Review. Weather, 50, 449–467.
Lu, R., W. Chen, and B. Dong, 2008: How does a weakened Atlantic thermohaline circulation lead to an intensification of the ENSO-south Asian summer monsoon interaction? Geophys. Res. Lett., 35, L08706, doi: 10.1029/2008GL033394.
Lu, R., and Y. Fu, 2010: Intensification of East Asian summer rainfall interannual variability in the twenty-first century simulated by 12 CMIP3 coupled models. J. Climate, doi: 10.1175/2009JCLI3130.1.
Turner, A. G., P. M. Inness, and J. M. Slingo, 2005: The role of the basic state in the ENSO-monsoon relationship and implications for predictability. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 131, 781–804.
Turner, A. G., P. M. Inness, and J. M. Slingo, 2007: The effect of doubled CO2 and model basic state biases on the monsoon-ENSO system. I: Mean response and interannual variability. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 133, 1143–1157.
Webster, P. J., and S. Yang, 1992: Monsoon and ENSO: Selectively interactive systems. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 118, 877–926.
Wei, M., 2005: A coupled model study on the intensification of the Asian summer monsoon in IPCC SRES scenarios. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 22, 798–806.
Zhu, C., C. K. Park, W. S. Lee, and W. T. Yun, 2008: Statistical downscaling for multi-model ensemble prediction of summer monsoon rainfall in the Asia-Pacific region using geopotential height field. Adv. Atmos. Sci., 25(5), 867–884, doi: 10.1007/s00376-008-0867-x.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, Y., Lu, R. Simulated change in the interannual variability of South Asian summer monsoon in the 21st century. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 27, 992–1002 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9124-1
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-009-9124-1