Abstract
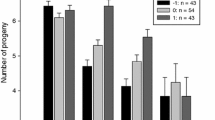
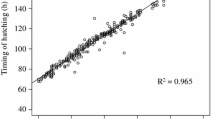
American white pelicans (Pelecanus erythrorhynchos) lay two eggs but typically rear only one young owing to siblicidal brood reduction affecting the later-hatched, or B-chick. When the A-offspring fails at an early age, the B-chick may survive as a replacement (insurance) offspring. Using a combination of nests with natural and artificially manipulated hatching asynchrony, I examined the hypothesis that hatching asynchrony in this species is adaptively tuned to permit B-chicks to survive during the time they are most likely to be needed as replacements, with brood reduction following when they become redundant. Hatching asynchrony over the natural range of 0–4 days significantly increased within-brood mass differentials and reduced B-chick lifespan. Full synchrony had a marginally negative effect on A-chick mass. Greater asynchrony did not significantly affect the number of days B-chicks survived after hatching of the A-chick, owing to a corresponding extension of time B-offspring were protected from harassment while still within the egg. This resulted in a high probability (> 0.8) of B-chicks surviving through the initial period (5–7 days) of maximum early A-chick loss. Redundant B-chicks were subject to heavy brood reduction, with both chicks likely to have survived at only one each of 94 natural and 84 manipulated (0, 2, and 4 days asynchrony) nests. Hatching asynchrony in American white pelicans, in combination with a rapid development of senior chick siblicidal competence, appears to result in a time course of brood reduction appropriate for an effective insurance reproductive strategy.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 February 1996 /Accepted after revision: 18 May 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Evans, R. Hatching asynchrony and survival of insurance offspring in an obligate brood reducing species, the American white pelican. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 39, 203–209 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650050282
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002650050282