Abstract
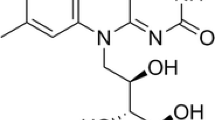
Improved strains for the production of riboflavin (vitamin B2) were constructed through metabolic engineering using recombinant DNA techniques in Corynebacterium ammoniagenes. A C. ammoniagenes strain harboring a plasmid containing its riboflavin biosynthetic genes accumulated 17-fold as much riboflavin as the host strain. In order to increase the expression of the biosynthetic genes, we isolated DNA fragments that had promoter activities in C. ammoniagenes. When the DNA fragment (P54-6) showing the strongest promoter activity in minimum medium was introduced into the upstream region of the riboflavin biosynthetic genes, the accumulation of riboflavin was 3-fold elevated. In that strain, the activity of guanosine 5′-triphosphate (GTP) cyclohydrolase II, the first enzyme in riboflavin biosynthesis, was 2.4-fold elevated whereas that of riboflavin synthase, the last enzyme in the biosynthesis, was 44.1-fold elevated. Changing the sequence containing the putative ribosome-binding sequence of 3,4-dihydroxy-2-butanone 4-phosphate synthase/GTP cyclohydrolase II gene led to higher GTP cyclohydrolase II activity and strong enhancement of riboflavin production. Throughout the strain improvement, the activity of GTP cyclohydrolase II correlated with the productivity of riboflavin. In the highest producer strain, riboflavin was produced at the level of 15.3 g l−1 for 72 h in a 5-l jar fermentor without any end product inhibition.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 23 August 1999 / Received revision: 13 October 1999 / Accepted: 5 November 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koizumi, S., Yonetani, Y., Maruyama, A. et al. Production of riboflavin by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium ammoniagenes . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 53, 674–679 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002539900295
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002539900295