Abstract
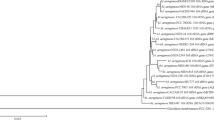
Pseudomonas alkylphenolia is known to form different types of multicellular structures depending on the environmental stimuli. Aerial structures formed during vapor p-cresol utilization are unique. Transposon mutants that showed a smooth colony phenotype failed to form a differentiated biofilm, including aerial structures and pellicles, and showed deficient surface spreading motility. The transposon insertion sites were located to a gene cluster designated epm (extracellular polymer matrix), which comprises 11 ORFs in the same transcriptional orientation. The putative proteins encoded by the genes in the epm cluster showed amino acid sequence homology to those found in the alginate biosynthesis gene clusters, e.g., in Pseudomonas aeruginosa at similarity levels of 32.3–86.4 %. This overall resemblance indicated that the epm gene cluster encodes proteins that mediate the synthesis of an exopolysaccharide composed of uronic acid(s) similar to alginate. Our preliminary results suggested that the epm-derived polymer is a substituted polymannuronic acid. Gene clusters homologous to the epm gene cluster are found in the genomes of a few species of the genera Pseudomonas, Alcanivorax, and Marinobacter. A mutational analysis showed that the epmJ and epmG genes encoding putative exopolysaccharide-modifying enzymes are required to form multicellular structures. An analysis of the activity of the promoter P epmD using a transcriptional fusion to the green fluorescence protein gene showed that the epm genes are strongly expressed at the tips of the specialized aerial structures. Our results suggested that the epm gene cluster is involved in the formation of a scaffold polysaccharide that is required to form multicellular structures in P. alkylphenolia.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Branda SS, Vik S, Friedman L, Kolter R (2005) Biofilms: the matrix revisited. Trends Microbiol 13:20–26
Chang WS, van de Mortel M, Nielsen L, Nino de Guzman G, Li X, Halverson LJ (2007) Alginate production by Pseudomonas putida creates a hydrated microenvironment and contributes to biofilm architecture and stress tolerance under water-limiting conditions. J Bacteriol 189:8290–8209
Cho JH, Jung DK, Lee K, Rhee S (2009) Crystal structure and functional analysis of the extradiol dioxygenase LapB from a long-chain alkylphenol degradation pathway in Pseudomonas. J Biol Chem 284:34321–34330
Choi KS, Veeranagouda Y, Cho KM, Lee SO, Jo GR, Cho K, Lee K (2007) Effect of gacS and gacA mutations on colony architecture, surface motility, biofilm formation and chemical toxicity in Pseudomonas sp. KL28. J Microbiol 45:492–498
Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Greenberg EP (1999) Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science 284:1318–1322
Davey ME, O’Toole GA (2000) Microbial biofilms: from ecology to molecular genetics. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 64:847–867
de Lorenzo V (2000) Pseudomonas entering the post-genomic era. Environ Microbiol 2:349–354
Dhungana S, Anthony CR 3rd, Hersman LE (2007) Effect of exogenous reductant on growth and iron mobilization from ferrihydrite by the Pseudomonas mendocina ymp strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:3428–3430
Doco T, O’Neill MA, Pellerin P (2001) Determination of the neutral and acidic glcosyl-residue compositions of plant polysaccharides by GC-EI-MS analysis of the trimethylsilyl methyl glycoside derivatives. Carbohydr Polym 46:249–259
Franklin MJ, Ohman DE (2002) Mutant analysis and cellular localization of the AlgI, AlgJ, and AlgF proteins required for O acetylation of alginate in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol 184:3000–3007
Franklin MJ, Nivens DE, Weadge JT, Howell PL (2011) Biosynthesis of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa extracellular polysaccharides, alginate, Pel, and Psl. Front Microbiol 2:167
Friedman L, Kolter R (2004) Genes involved in matrix formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa PA14 biofilms. Mol Microbiol 51:675–690
Fux CA, Costerton JW, Stewart PS, Stoodley P (2005) Survival strategies of infectious biofilms. Trends Microbiol 13:34–40
Ghafoor A, Hay ID, Rehm BH (2011) Role of exopolysaccharides in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation and architecture. Appl Environ Microbiol 77:5238–5246
Gibson DT, Parales RE (2000) Aromatic hydrocarbon dioxygenases in environmental biotechnology. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:236–243
Green DH, Bowman JP, Smith EA, Gutierrez T, Bolch CJ (2006) Marinobacter algicola sp. nov., isolated from laboratory cultures of paralytic shellfish toxin-producing dinoflagellates. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 56:523–527
Hay ID, Gatland K, Campisano A, Jordens JZ, Rehm BH (2009) Impact of alginate overproduction on attachment and biofilm architecture of a supermucoid Pseudomonas aeruginosa strain. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:6022–6025
Hay ID, Rehman ZU, Ghafoor A, Rehm BHA (2010) Bacterial biosynthesis of alginates. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 85:752–759
Hay ID, Schmidt O, Filitcheva J, Rehm BH (2012) Identification of a periplasmic AlgK-AlgX-MucD multiprotein complex in Pseudomonas aeruginosa involved in biosynthesis and regulation of alginate. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93:215–227
Hay ID, Rehman ZU, Moradali MF, Wang Y, Rehm BH (2013) Microbial alginate production, modification and its applications. Microb Biotechnol 6:doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12076
Hentzer M, Teitzel GM, Balzer GJ, Heydorn A, Molin S, Givskov M, Parsek MR (2001) Alginate overproduction affects Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm structure and function. J Bacteriol 183:5395–5401
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77:51–59
Jain S, Franklin MJ, Ertesvag H, Valla S, Ohman DE (2003) The dual roles of AlgG in C-5-epimerization and secretion of alginate polymers in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Mol Microbiol 47:1123–1133
Jeong JJ, Kim JH, Kim CK, Hwang I, Lee K (2003) 3- and 4-alkylphenol degradation pathway in Pseudomonas sp. strain KL28: genetic organization of the lap gene cluster and substrate specificities of phenol hydroxylase and catechol 2,3-dioxygenase. Microbiology 149:3265–3277
Keiski CL, Harwich M, Jain S, Neculai AM, Yip P, Robinson H, Whitney JC, Riley L, Burrows LL, Ohman DE, Howell PL (2010) AlgK is a TPR-containing protein and the periplasmic component of a novel exopolysaccharide secretin. Structure 18:265–273
Kovach ME, Elzer PH, Hill DS, Robertson GT, Farris MA, Roop RM 2nd, Peterson KM (1995) Four new derivatives of the broad-host-range cloning vector pBBR1MCS, carrying different antibiotic-resistance cassettes. Gene 166:175–176
Larsen RA, Wilson MM, Guss AM, Metcalf WW (2002) Genetic analysis of pigment biosynthesis in Xanthobacter autotrophicus Py2 using a new, highly efficient transposon mutagenesis system that is functional in a wide variety of bacteria. Arch Microbiol 178:193–201
Lee K, Veeranagouda Y (2009) Ultramicrocells form by reductive division in macroscopic Pseudomonas aerial structures. Environ Microbiol 11:1117–1125
Lloret L, Barreto R, Leon R, Moreno S, Martinez-Salazar J, Espin G, Soberon-Chavez G (1996) Genetic analysis of the transcriptional arrangement of Azotobacter vinelandii alginate biosynthetic genes: identification of two independent promoters. Mol Microbiol 21:449–457
Manilla-Perez E, Reers C, Baumgart M, Hetzler S, Reichelt R, Malkus U, Kalscheuer R, Waltermann M, Steinbuchel A (2010) Analysis of lipid export in hydrocarbonoclastic bacteria of the genus Alcanivorax: identification of lipid export-negative mutants of Alcanivorax borkumensis SK2 and Alcanivorax jadensis T9. J Bacteriol 192:643–656
Mann EE, Wozniak DJ (2012) Pseudomonas biofilm matrix composition and niche biology. FEMS Microbiol Rev 36:893–916
Miller WG, Leveau JH, Lindow SE (2000) Improved gfp and inaZ broad-host-range promoter-probe vectors. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 13:1243–1250
Molin S, Tolker-Nielsen T (2003) Gene transfer occurs with enhanced efficiency in biofilms and induces enhanced stabilisation of the biofilm structure. Curr Opin Biotechnol 14:255–261
Nadell CD, Xavier JB, Foster KR (2009) The sociobiology of biofilms. FEMS Microbiol Rev 33:206–224
Nielsen L, Li X, Halverson LJ (2011) Cell–cell and cell–surface interactions mediated by cellulose and a novel exopolysaccharide contribute to Pseudomonas putida biofilm formation and fitness under water-limiting conditions. Environ Microbiol 13:1342–1356
Nilsson M, Chiang WC, Fazli M, Gjermansen M, Givskov M, Tolker-Nielsen T (2011) Influence of putative exopolysaccharide genes on Pseudomonas putida KT2440 biofilm stability. Environ Microbiol 13:1357–1369
O’Toole G, Kaplan HB, Kolter R (2000) Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu Rev Microbiol 54:49–79
Paletta JL, Ohman DE (2012) Evidence for two promoters internal to the alginate biosynthesis operon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Curr Microbiol 65:770–775
Rehm BH (1996) The Azotobacter vinelandii gene algJ encodes an outer-membrane protein presumably involved in export of alginate. Microbiology 142:873–880
Rehm B (2010a) Bacterial polymers: biosynthesis, modifications and applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:578–592
Rehm BHA (2010b) Pseudomonas applications. Encycl Ind Biotechnol 6:4185–4197
Rehman ZU, Rehm BH (2013) Dual roles of Pseudomonas aeruginosa AlgE in secretion of the virulence factor alginate and formation of the secretion complex. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:2002–2011
Rehman ZU, Wang Y, Moradali MF, Hay ID, Rehm BH (2013) Insights into the assembly of the alginate biosynthesis machinery in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 79:3264–3272
Remminghorst U, Rehm BH (2006a) Bacterial alginates: from biosynthesis to applications. Biotechnol Lett 28:1701–1712
Remminghorst U, Rehm BH (2006b) In vitro alginate polymerization and the functional role of Alg8 in alginate production by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Appl Environ Microbiol 72:298–305
Remminghorst U, Hay ID, Rehm BH (2009) Molecular characterization of Alg8, a putative glycosyltransferase, involved in alginate polymerisation. J Biotechnol 140:176–183
Sabirova JS, Becker A, Lunsdorf H, Nicaud JM, Timmis KN, Golyshin PN (2011) Transcriptional profiling of the marine oil-degrading bacterium Alcanivorax borkumensis during growth on n-alkanes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 319:160–168
Schafer A, Tauch A, Jager W, Kalinowski J, Thierbach G, Puhler A (1994) Small mobilizable multi-purpose cloning vectors derived from the Escherichia coli plasmids pK18 and pK19: selection of defined deletions in the chromosome of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Gene 145:69–73
Schultz J, Milpetz F, Bork P, Ponting CP (1998) SMART, a simple modular architecture research tool: identification of signaling domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:5857–5864
Shapiro JA (1998) Thinking about bacterial populations as multicellular organisms. Annu Rev Microbiol 52:81–104
Skjak-Braek G, Grasdalen H, Larsen B (1986) Monomer sequence and acetylation pattern in some bacterial alginates. Carbohydr Res 154:239–250
Spiers AJ, Kahn SG, Bohannon J, Travisano M, Rainey PB (2002) Adaptive divergence in experimental populations of Pseudomonas fluorescens. I. Genetic and phenotypic bases of wrinkly spreader fitness. Genetics 161:33–46
Stanier RY, Palleroni NJ, Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxomonic study. J Gen Microbiol 43:159–271
Stoodley P, Sauer K, Davies DG, Costerton JW (2002) Biofilms as complex differentiated communities. Annu Rev Microbiol 56:187–209
Sutherland IW (2001) The biofilm matrix—an immobilized but dynamic microbial environment. Trends Microbiol 9:222–227
Timmis KN (2002) Pseudomonas putida: a cosmopolitan opportunist par excellence. Environ Microbiol 4:779–781
Uchino M, Shida O, Uchimura T, Komagata K (2001) Recharacterization of Pseudomonas fulva Iizuka and Komagata 1963, and proposals of Pseudomonas parafulva sp. nov. and Pseudomonas cremoricolorata sp. nov. J Gen Appl Microbiol 47:247–261
Vargas-Garcia MC, Lopez MJ, Elorrieta MA, Suarez F, Moreno J (2003) Properties of polysaccharide produced by Azotobacter vinelandii cultured on 4-hydroxybenzoic acid. J Appl Microbiol 94:388–395
Veeranagouda Y, Lim EJ, Kim DW, Kim JK, Cho K, Heipieper HJ, Lee K (2009) Formation of specialized aerial architectures by Rhodococcus during utilization of vaporized p-cresol. Microbiology 155:3788–3796
Veeranagouda Y, Basavaraja C, Bae H-S, Liu K-H, Lee K (2011a) Augmented production of poly-β-d-mannuronate and its acetylated forms by Pseudomonas. Process Biochem 46:328–334
Veeranagouda Y, Lee K, Cho AR, Cho K, Anderson EM, Lam JS (2011b) Ssg, a putative glycosyltransferase, functions in lipo- and exopolysaccharide biosynthesis and cell surface-related properties in Pseudomonas alkylphenolia. FEMS Microbiol Lett 315:38–45
Vodovar N, Vallenet D, Cruveiller S, Rouy Z, Barbe V, Acosta C, Cattolico L, Jubin C, Lajus A, Segurens B, Vacherie B, Wincker P, Weissenbach J, Lemaitre B, Medigue C, Boccard F (2006) Complete genome sequence of the entomopathogenic and metabolically versatile soil bacterium Pseudomonas entomophila. Nat Biotechnol 24:673–679
Wang S, Parsek MR, Wozniak DJ, Ma LZ (2013) A spider web strategy of type IV pili-mediated migration to build a fibre-like Psl polysaccharide matrix in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Environ Microbiol 15:2238–2253
Webb JS, Givskov M, Kjelleberg S (2003) Bacterial biofilms: prokaryotic adventures in multicellularity. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:578–585
Yakimov MM, Golyshin PN, Lang S, Moore ER, Abraham WR, Lunsdorf H, Timmis KN (1998) Alcanivorax borkumensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new, hydrocarbon-degrading and surfactant-producing marine bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 48:339–348
Yun JI, Cho KM, Kim JK, Lee SO, Cho K, Lee K (2007) Mutation of rpoS enhances Pseudomonas sp. KL28 growth at higher concentrations of m-cresol and changes its surface-related phenotypes. FEMS Microbiol Lett 269:97–103
Zhao K, Tseng BS, Beckerman B, Jin F, Gibiansky ML, Harrison JJ, Luijten E, Parsek MR, Wong GC (2013) Psl trails guide exploration and microcolony formation in Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Nature 497:388–391
Zogaj X, Nimtz M, Rohde M, Bokranz W, Romling U (2001) The multicellular morphotypes of Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli produce cellulose as the second component of the extracellular matrix. Mol Microbiol 39:1452–1463
Acknowledgement
This research was financially supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology (no. 2009–0073913 and 2011–0022133) and by the framework of international cooperation program managed by National Research Foundation of Korea (no. 2013K2A1B8053138).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 463 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, K., Lim, E.J., Kim, K.S. et al. An alginate-like exopolysaccharide biosynthesis gene cluster involved in biofilm aerial structure formation by Pseudomonas alkylphenolia . Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 98, 4137–4148 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5529-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-014-5529-6