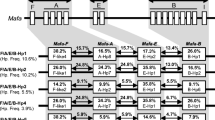
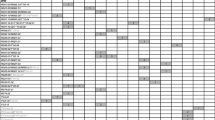
Abstract
The rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta) is an excellent model for human disease and vaccine research. Two populations exhibiting distinctive morphological and physiological characteristics, Indian- and Chinese-origin rhesus macaques, are commonly used in research. Genetic analysis has focused on the Indian macaque population, but the accessibility of these animals for research is limited. Due to their greater availability, Chinese rhesus macaques are now being used more frequently, particularly in vaccine and biodefense studies, although relatively little is known about their immunogenetics. In this study, we discovered major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I cDNAs in 12 Chinese rhesus macaques and detected 41 distinct Mamu-A and Mamu-B sequences. Twenty-seven of these class I cDNAs were novel, while six and eight of these sequences were previously reported in Chinese and Indian rhesus macaques, respectively. We then performed microsatellite analysis on DNA from these 12 animals, as well as an additional 18 animals, and developed sequence specific primer PCR (PCR-SSP) assays for eight cDNAs found in multiple animals. We also examined our cohort for potential admixture of Chinese and Indian origin animals using a recently developed panel of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). The discovery of 27 novel MHC class I sequences in this analysis underscores the genetic diversity of Chinese rhesus macaques and contributes reagents that will be valuable for studying cellular immunology in this population.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen TM, Mothé BR, Sidney J, Jing P, Dzuris JL, Liebl ME, Vogel TU, O’Connor DH, Wang X, Wussow MC, Thomson JA, Altman JD, Watkins DI, Sette A (2001) CD8+ Lymphocytes from Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Macaques Recognize 14 Different Epitopes Bound by the Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Molecule Mamu-A*01: Implications for Vaccine Design and Testing. J Virol 75:738–749
Boyson JE, Shufflebotham C, Cadavid LF, Urvater JA, Knapp LA, Hughes AL, Watkins DI (1996) The MHC Class I Genes of the Rhesus Monkey: Different Evolutionary Histories of MHC Class I and II Genes in Primates. J Immunol 156:4656–4665
Champoux M, Higley JD, Suomi SJ (1997) Behavioral and Physiological Characteristics of Indian and Chinese-Indian Hybrid Rhesus Macaque Infants. Dev Psychobiol 31:49–63
Clarke MR, O’Neil JAS (1999) Morphometric Comparison of Chinese-Origin and Indian-Derived Rhesus Monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Am J Primatol 47:335–346
Daza-Vamenta R, Glusman G, Rowen L, Guthrie B, Geraghty DE (2004) Genetic Divergence of the Rhesus Macaque Major Histocompatibility Complex. Genome Res 14:1501–1515
Doxiadis GGM, Otting N, de Groot NG, de Groot N, Rouweler AJM, Noort R, Verschoor EJ, Bontjer I, Bontrop RE (2003) Evolutionary stability of MHC class II haplotypes in diverse rhesus macaque populations. Immunogenetics 55:540–551
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence Limits on Phylogenies: An Approach Using the Bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Ferguson B, Street SL, Wright H, Pearson C, Jia Y, Thompson SL, Allibone P, Dubay CJ, Spindel E, Norgren Jr RB (2007) Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) distinguish Indian-origin and Chinese-origin rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). BMC Genomics 8:43
Joag SV, Stephens EB, Adams RJ, Foresman L, Narayan O (1994) Pathogenesis of SIVmac Infection in Chinese and Indian Rhesus Macaques: Effects of Splenectomy on Virus Burden. Virology 200:436–446
Kaizu M, Borchardt GJ, Glidden CE, Fisk DL, Loffredo JT, Watkins DI, Rehrauer WM (2007) Molecular typing of major histocompatibility complex class I alleles in the Indian rhesus macaque which restrict SIV CD8+ T cell epitopes. Immunogenetics 59:693–703
Knapp LA, Lehmann E, Piekarczyk MS, Urvater JA, Watkins DI (1997) A high frequency of Mamu-A*01 in the rhesus macaque detected by polymerase chain reaction with sequence-specific primers and direct sequencing. Tissue Antigens 50:657–661
Ling B, Veazey RS, Luckay A, Penedo C, Xu K, Lifson JD, Marx PA (2002) SIVmac pathogenesis in rhesus macaques of Chinese and Indian origin compared with primary HIV infections in humans. AIDS 16:1489–1496
Marcondes MCG, Penedo MCT, Lanigan C, Hall D, Watry DD, Zandonatti M, Fox HS (2006) Simian Immunodeficiency Virus-Induced CD4+ T Cell Deficits in Cytokine Secretion Profile Are Dependent on Monkey Origin. Viral Immunol 19:679–689
Marthas ML, Lu D, Penedo MCT, Hendrickx AG, Miller CJ (2001) Titration of an SIVmac251 Stock by Vaginal Inoculation of Indian and Chinese Origin Rhesus Macaques: Transmission Efficiency, Viral Loads, and Antibody Responses. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 17:1455–1466
Mothé BR, Sidney J, Dzuris JL, Liebl ME, Fuenger S, Watkins DI, Sette A (2002) Characterization of the Peptide-Binding Specificity of Mamu-B*17 and Identification of Mamu-B*17-Restricted Epitopes Derived from Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Proteins. J Immunol 168:210–219
Otting N, Heijmans CMC, Noort RC, de Groot NG, Doxiadis GGM, van Rood JJ, Watkins DI, Bontrop RE (2005) Unparalleled complexity of the MHC class I region in rhesus macaques. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:1626–1631
Otting N, de Vos-Rouweler AJM, Heijmans CMC, de Groot NG, Doxiadis GGM, Bontrop RE (2007) MHC class I A region diversity and polymorphism in macaque species. Immunogenetics 59:367–375
Penedo MCT, Bontrop RE, Heijmans CMC, Otting N, Noort R, Rouweler AJM, de Groot N, de Groot NG, Ward T, Doxiadis GGM (2005) Microsatellite typing of the rhesus macaque MHC region. Immunogenetics 57:198–209
Reimann KA, Parker RA, Seaman MS, Beaudry K, Beddall M, Peterson L, Williams KC, Veazey RS, Montefiori DC, Mascola JR, Nable GJ, Letvin NL (2005) Pathogenicity of Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus SHIV-89.6P and SIVmac Is Attenuated in Cynomolgus Macaques and Associated with Early T-Lymphocyte Responses. J Virol 79:8878–8885
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (2000) Primer3 on the WWW for general users and for biologist programmers. In: Krawetz S, Misener S (eds) Bioinformatics Methods and Protocols: Methods in Molecular Biology. Humana Press, Totowa NJ, pp 365–386
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Shimizu Y, DeMars R (1989) Production of human cells expressing individual transferred HLA-A,-B,-C genes using an HLA-A,-B,-C null human cell line. J Immunol 142:3320–3328
Takahata N, Nei M (1990) Allelic Genealogy Under Overdominant and Frequency-Dependent Selection and Polymorphism of Major Histocompatibility Complex Loci. Genetics 124:967–978
Tamura K (1992) The rate and pattern of nucleotide substitution in Drosophila mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol 9:814–825
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The CLUSTAL X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 25:4876–4882
Trichel AM, Rajakumar PA, Murphy-Corb M (2002) Species-specific variation in SIV disease progression between Chinese and Indian subspecies of rhesus macaque. J Med Primatol 31:171–178
Urvater JA, Otting N, Loehrke JH, Rudersdorf R, Slukvin II, Piekarczyk MS, Golos TG, Hughes AL, Bontrop RE, Watkins DI (2000a) Mamu-I: A Novel Primate MHC Class I B-Related Locus with Unusually Low Variability. J Immunol 164:1386–1398
Urvater JA, McAdam SN, Loehrke JH, Allen TM, Moran JL, Rowell TJ, Rojo S, López de Castro JA, Taurog JD, Watkins DI (2000b) A high incidence of Shigella-induced arthritis in a primate species: major histocompatibility complex class I molecules associated with resistance and susceptibility, and their relationship to HLA-B27. Immunogenetics 51:314–325
Viray J, Rolfs B, Smith DG (2001) Comparison of the Frequencies of Major Histocompatibility (MHC) Class-II DQA1 and DQB1 Alleles in Indian and Chinese Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta). Comparative Med 51:555–561
Vogel T, Norley S, Beer B, Kurth R (1995) Rapid screening for Mamu-A1-positive rhesus macaques using a SIVmac Gag peptide-specific cytotoxic T-lymphocyte assay. Immunology 84:482–487
Voss G, Letvin NL (1996) Definition of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 gp120 and gp41 Cytotoxic T-Lymphocyte Epitopes and Their Restricting Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Alleles in Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus-Infected Rhesus Monkeys. J Virol 70:7335–7340
Wiseman RW, Wojcechowskyj JA, Greene JM, Blasky AJ, Gopon T, Soma T, Friedrich TC, O’Connor SL, O’Connor DH (2007) Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIVmac239 Infection of Major Histocompatibility Complex-Identical Cynomolgus Macaques from Mauritius. J Virol 81:349–361
Yant LJ, Friedrich TC, Johnson RC, May GE, Maness NJ, Enz AM, Lifson JD, O’Connor DH, Carrington M, Watkins DI (2006) The High-Frequency Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Allele Mamu-B*17 Is Associated with Control of Simian Immunodeficiency Virus SIVmac239 Replication. J Virol 80:5074–5077
Yasutomi Y, McAdam SN, Boyson JE, Piekarczyk MS, Watkins DI, Letvin NL (1995) A MHC Class I B Locus Allele-Restricted Simian Immunodeficiency Virus Envelope CTL Epitope in Rhesus Monkeys. J Immunol 154:2516–2522
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Natasja de Groot, Nel Otting, and IMGT Non-human Primate Nomenclature Committee for naming the Mamu-A and Mamu-B sequences. We thank Jason Wojcechowskyj for microsatellite primer design, Chad Pendley and Ericka Becker for assistance with cloning and sequencing, and members of the O’Connor group for helpful discussions. This work was supported by subcontract from the Battelle Biomedical Research Center under NIAID contract N01-A1-30061. This publication was made possible in part by Grant Number P51 RR000167 from the National Center for Research Resources (NCRR), a component of the National Institutes of Health (NIH), to the Wisconsin National Primate Research Center, University of Wisconsin-Madison. This research was conducted in part at a facility constructed with support from Research Facilities Improvement Program grant numbers RR15459-01 and RR020141-01. This publication’s contents are solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of NCRR, NIAID, or NIH.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karl, J.A., Wiseman, R.W., Campbell, K.J. et al. Identification of MHC class I sequences in Chinese-origin rhesus macaques. Immunogenetics 60, 37–46 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-007-0267-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00251-007-0267-x