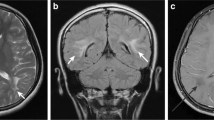
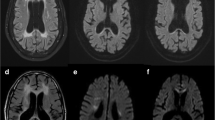
Abstract
Pediatric neurodegenerative white matter processes are complex, numerous and result from a vast array of causes ranging from white matter injury or inflammation to congenital metabolic disorders. When faced with a neurodegenerative white matter process on neuroimaging, the first step for the radiologist is to determine whether the findings represent a congenital metabolic leukodystrophy or one of various other white matter processes. In this review we first describe a general approach to neurodegenerative white matter disorders. We will briefly describe a few white matter diseases that mimic metabolic leukodystrophies. In the second half of the review we discuss an approach to distinguishing and classifying white matter leukodystrophies.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kristjansdottir R, Uvebrant P, Hagberg B et al (1996) Disorders of the cerebral white matter in children. The spectrum of lesions. Neuropediatrics 27:295–298
van der Knaap MS, Breiter SN, Naidu S et al (1999) Defining and categorizing leukoencephalopathies of unknown origin: MR imaging approach. Radiology 213:121–133
Barkovich AJ (2005) Pediatric neuroimaging. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 76–187
Van der Knaap MS, Valk J (2005) Magnetic resonance of myelination and myelin disorders. Springer-Verlag, Heidelberg
Haynes RL, Baud O, Li J et al (2005) Oxidative and nitrative injury in periventricular leukomalacia: a review. Brain Pathol 15:225–233
Idrissova Zh R, Boldyreva MN, Dekonenko EP et al (2003) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis in children: clinical features and HLA-DR linkage. Eur J Neurol 10:537–546
Menge T, Kieseier BC, Nessler S et al (2007) Acute disseminated encephalomyelitis: an acute hit against the brain. Curr Opin Neurol 20:247–254
Baum PA, Barkovich AJ, Koch TK et al (1994) Deep gray matter involvement in children with acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. AJNR 15:1275–1283
Honkaniemi J, Dastidar P, Kahara V et al (2001) Delayed MR imaging changes in acute disseminated encephalomyelitis. AJNR 22:1117–1124
American Academy of Pediatrics Committee on Infectious Diseases (2000) Prevention of Lyme disease. Pediatrics 105:142–147
Hoppa E, Bachur R (2007) Lyme disease update. Curr Opin Pediatr 19:275–280
Pachner AR, Steiner I (2007) Lyme neuroborreliosis: infection, immunity, and inflammation. Lancet Neurol 6:544–552
Cheon JE, Kim IO, Hwang YS et al (2002) Leukodystrophy in children: a pictorial review of MR imaging features. Radiographics 22:461–476
Brenner M, Johnson AB, Boespflug-Tanguy O et al (2001) Mutations in GFAP, encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein associated with Alexander disease. Nat Genet 27:117–120
Sener RN (2001) Demonstration of glycine peaks at 3.50 ppm in a patient with van der Knaap syndrome. AJNR 22:1587–1589
Matalon R, Michals K, Sebesta D et al (1988) Aspartoacylase deficiency and N-acetylaspartic aciduria in patients with Canavan disease. Am J Med Genet 29:463–471
Brismar J, Brismar G, Gascon G et al (1990) Canavan disease: CT and MR imaging of the brain. AJNR 11:805–810
Grodd W, Krageloh-Mann I, Petersen D et al (1990) In vivo assessment of N-acetylaspartate in brain in spongy degeneration (Canavan’s disease) by proton spectroscopy. Lancet 336:437–438
Topcu M, Gartioux C, Ribierre F et al (2000) Vacuoliting megalencephalic leukoencephalopathy with subcortical cysts, mapped to chromosome 22qtel. Am J Hum Genet 66:733–739
van der Knaap MS, Barth PG, Vrensen GF et al (1996) Histopathology of an infantile-onset spongiform leukoencephalopathy with a discrepantly mild clinical course. Acta Neuropathol 92:206–212
Gelal F, Calli C, Apaydin M et al (2002) van der Knaap’s leukoencephalopathy: report of five new cases with emphasis on diffusion-weighted MRI findings. Neuroradiology 44:625–630
van der Knaap MS, Kamphorst W, Barth PG et al (1998) Phenotypic variation in leukoencephalopathy with vanishing white matter. Neurology 51:540–547
van der Voorn JP, van Kollenburg B, Bertrand G et al (2005) The unfolded protein response in vanishing white matter disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 64:770–775
Donnell GN, Collado M, Koch R (1961) Growth and development of children with galactosemia. J Pediatr 58:836–844
Nelson MD Jr, Wolff JA, Cross CA et al (1992) Galactosemia: evaluation with MR imaging. Radiology 184:255–261
Otaduy MC, Leite CC, Lacerda MT et al (2006) Proton MR spectroscopy and imaging of a galactosemic patient before and after dietary treatment. AJNR 27:204–207
Munoz A, Mateos F, Simon R et al (1999) Mitochondrial diseases in children: neuroradiological and clinical features in 17 patients. Neuroradiology 41:920–928
Chu BC, Terae S, Takahashi C et al (1999) MRI of the brain in the Kearns-Sayre syndrome: report of four cases and a review. Neuroradiology 41:759–764
Seigel RS, Seeger JF, Gabrielsen TO et al (1979) Computed tomography in oculocraniosomatic disease (Kearns-Sayre syndrome). Radiology 130:159–164
Dinopoulos A, Cecil KM, Schapiro MB et al (2005) Brain MRI and proton MRS findings in infants and children with respiratory chain defects. Neuropediatrics 36:290–301
Barkovich AJ, Good WV, Koch TK et al (1993) Mitochondrial disorders: analysis of their clinical and imaging characteristics. AJNR 14:1119–1137
Itoh K, Kase R, Shimmoto M et al (1995) Protective protein as an endogenous endothelin degradation enzyme in human tissues. J Biol Chem 270:515–518
Chen CY, Zimmerman RA, Lee CC et al (1998) Neuroimaging findings in late infantile GM1 gangliosidosis. AJNR 19:1628–1630
Pavlu J, Jackson M, Panoskaltsis N (2006) GM1-gangliosidosis type I. Br J Haematol 135:422
Patay Z (2005) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging in leukodystrophies. Eur Radiol 15:2284–2303
Koelfen W, Freund M, Jaschke W et al (1994) GM-2 gangliosidosis (Sandhoff’s disease): two-year follow-up by MRI. Neuroradiology 36:152–154
Marsden DL, Nyhan WL (1992) Neurological diseases in disorders of organic acids. Curr Opin Neurol Neurosurg 5:349–354
Kaur M, Verma IC (1995) Enzyme studies in GM2 gangliosidosis, and their application in prenatal diagnosis. Ind J Pediatr 62:485–489
Mugikura S, Takahashi S, Higano S et al (1996) MR findings in Tay-Sachs disease. J Comput Assist Tomogr 20:551–555
Inglese M, Nusbaum AO, Pastores GM et al (2005) MR imaging and proton spectroscopy of neuronal injury in late-onset GM2 gangliosidosis. AJNR 26:2037–2042
Loes DJ, Peters C, Krivit W (1999) Globoid cell leukodystrophy: distinguishing early-onset from late-onset disease using a brain MR imaging scoring method. AJNR 20:316–323
Choi S, Enzmann DR (1993) Infantile Krabbe disease: complementary CT and MR findings. AJNR 14:1164–1166
Brockmann K, Dechent P, Wilken B et al (2003) Proton MRS profile of cerebral metabolic abnormalities in Krabbe disease. Neurology 60:819–825
Moser HW, Loes DJ, Melhem ER (2000) X-Linked adrenoleukodystrophy: overview and prognosis as a function of age and brain magnetic resonance imaging abnormality. A study involving 372 patients. Neuropediatrics 31:227–239
van Geel BM, Bezman L, Loes DJ et al (2001) Evolution of phenotypes in adult male patients with X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. Ann Neurol 49:186–194
Stephenson DJ, Bezman L, Raymond GV (2000) Acute presentation of childhood adrenoleukodystrophy. Neuropediatrics 31:293–297
Moser HW (1997) Adrenoleukodystrophy: phenotype, genetics, pathogenesis and therapy. Brain 120(8):1485–1508
Moser HW, Moser AB (1996) Peroxisomal disorders: overview. Ann N Y Acad Sci 804:427–441
Melhem ER, Loes DJ, Georgiades CS et al (2000) X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: the role of contrast-enhanced MR imaging in predicting disease progression. AJNR 21:839–844
Barkovich AJ, Ferriero DM, Bass N et al (1997) Involvement of the pontomedullary corticospinal tracts: a useful finding in the diagnosis of X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy. AJNR 18:95–100
Eichler FS, Itoh R, Barker PB et al (2002) Proton MR spectroscopic and diffusion tensor brain MR imaging in X-linked adrenoleukodystrophy: initial experience. Radiology 225:245–252
Brismar J, Aqeel A, Brismar G et al (1990) Maple syrup urine disease: findings on CT and MR scans of the brain in 10 infants. AJNR 11:1219–1228
Fariello G, Dionisi-Vici C, Orazi C et al (1996) Cranial ultrasonography in maple syrup urine disease. AJNR 17:311–315
Cavalleri F, Berardi A, Burlina AB et al (2002) Diffusion-weighted MRI of maple syrup urine disease encephalopathy. Neuroradiology 44:499–502
Heindel W, Kugel H, Wendel U et al (1995) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy reflects metabolic decompensation in maple syrup urine disease. Pediatr Radiol 25:296–299
Kingsley PB, Shah TC, Woldenberg R (2006) Identification of diffuse and focal brain lesions by clinical magnetic resonance spectroscopy. NMR Biomed 19:435–462
Kim TS, Kim IO, Kim WS et al (1997) MR of childhood metachromatic leukodystrophy. AJNR 18:733–738
Sener RN (2003) Metachromatic leukodystrophy. Diffusion MR imaging and proton MR spectroscopy. Acta Radiol 44:440–443
Watts RW, Spellacy E, Kendall BE et al (1981) Computed tomography studies on patients with mucopolysaccharidoses. Neuroradiology 21:9–23
Tzika AA, Ball WS Jr, Vigneron DB et al (1993) Clinical proton MR spectroscopy of neurodegenerative disease in childhood. AJNR 14:1267–1281; discussion 1282–1284
Suchy SF, Olivos-Glander IM, Nussabaum RL (1995) Lowe syndrome, a deficiency of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate 5-phosphatase in the Golgi apparatus. Hum Mol Genet 4:2245–2250
Lowe CU, Terrey M, MacLachlan EA (1952) Organic-aciduria, decreased renal ammonia production, hydrophthalmos, and mental retardation: a clinical entity. AMA Am J Dis Child 83:164–184
Carroll WJ, Woodruff WW, Cadman TE (1993) MR findings in oculocerebrorenal syndrome. AJNR 14:449–451
Schneider JF, Boltshauser E, Neuhaus TJ et al (2001) MRI and proton spectroscopy in Lowe syndrome. Neuropediatrics 32:45–48
Kim DS, Hayashi YK, Matsumoto H et al (2004) POMT1 mutation results in defective glycosylation and loss of laminin-binding activity in alpha-DG. Neurology 62:1009–1011
Kanoff RJ, Curless RG, Petito C et al (1998) Walker-Warburg syndrome: neurologic features and muscle membrane structure. Pediatr Neurol 18:76–80
Muntoni F, Brockington M, Torelli S et al (2004) Defective glycosylation in congenital muscular dystrophies. Curr Opin Neurol 17:205–209
Martin-Rendon E, Blake DJ (2003) Protein glycosylation in disease: new insights into the congenital muscular dystrophies. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:178–183
Dobyns WB, Pagon RA, Armstrong D et al (1989) Diagnostic criteria for Walker-Warburg syndrome. Am J Med Genet 32:195–210
Fukuyama Y, Osawa M, Suzuki H (1981) Congenital progressive muscular dystrophy of the Fukuyama type – clinical, genetic and pathological considerations. Brain Dev 3:1–29
Kondo-Iida E, Kobayashi K, Watanabe M et al (1999) Novel mutations and genotype-phenotype relationships in 107 families with Fukuyama-type congenital muscular dystrophy (FCMD). Hum Mol Genet 8:2303–2309
Aida N (1998) Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy: a neuroradiologic review. J Magn Reson Imaging 8:317–326
Aida N, Tamagawa K, Takada K et al (1996) Brain MR in Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy. AJNR 17:605–613
Aida N, Yagishita A, Takada K et al (1994) Cerebellar MR in Fukuyama congenital muscular dystrophy: polymicrogyria with cystic lesions. AJNR 15:1755–1759
Santavuori P, Somer H, Sainio K et al (1989) Muscle-eye-brain disease (MEB). Brain Dev 11:147–153
Santavuori P, Valanne L, Autti T et al (1998) Muscle-eye-brain disease: clinical features, visual evoked potentials and brain imaging in 20 patients. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 2:41–47
Valanne L, Pihko H, Katevuo K et al (1994) MRI of the brain in muscle-eye-brain (MEB) disease. Neuroradiology 36:473–476
Faerber EN, Poussaint TY (2002) Magnetic resonance of metabolic and degenerative diseases in children. Top Magn Reson Imaging 13:3–21
Barkovich AJ, Peck WW (1997) MR of Zellweger syndrome. AJNR 18:1163–1170
Powers JM (1995) The pathology of peroxisomal disorders with pathogenetic considerations. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 54:710–719
Poggi-Travert F, Fournier B, Poll-The BT et al (1995) Clinical approach to inherited peroxisomal disorders. J Inherit Metab Dis 18 [Suppl 1]:1–18
Paprocka J, Jamroz E, Adamek D et al (2007) Clinical and neuropathological picture of familial encephalopathy with bifunctional protein deficiency. Folia Neuropathol 45:213–219
Jose da Rocha A, Tulio Braga F, Carlos Martins Maia A Jr et al (2008) Lactate detection by MRS in mitochondrial encephalopathy: optimization of technical parameters. J Neuroimaging 18:1–8
Majoie CB, Akkerman EM, Blank C et al (2002) Mitochondrial encephalomyopathy: comparison of conventional MR imaging with diffusion-weighted and diffusion tensor imaging: case report. AJNR 23:813–816
Ohama E, Ohara S, Ikuta F et al (1987) Mitochondrial angiopathy in cerebral blood vessels of mitochondrial encephalomyopathy. Acta Neuropathol 74:226–233
Bianchi MC, Sgandurra G, Tosetti M et al (2007) Brain magnetic resonance in the diagnostic evaluation of mitochondrial encephalopathies. Biosci Rep 27:69–85
Pavlakis SG, Kingsley PB, Kaplan GP et al (1998) Magnetic resonance spectroscopy: use in monitoring MELAS treatment. Arch Neurol 55:849–852
Israels S, Haworth JC, Dunn HG et al (1976) Lactic acidosis in childhood. Adv Pediatr 22:267–303
DiMauro S, Andreu AL, De Vivo DC (2002) Mitochondrial disorders. J Child Neurol 17 [Suppl 3]:3S35–3S45; discussion 3S46–3S47
Sazgar M, Robinson JL, Chan AK et al (2003) Influenza B acute necrotizing encephalopathy: a case report and literature review. Pediatr Neurol 28:396–399
Arii J, Tanabe Y (2000) Leigh syndrome: serial MR imaging and clinical follow-up. AJNR 21:1502–1509
Crimi M, Papadimitriou A, Galbiati S et al (2004) A new mitochondrial DNA mutation in ND3 gene causing severe Leigh syndrome with early lethality. Pediatr Res 55:842–846
Savoiardo M, Ciceri E, D’Incerti L et al (1995) Symmetric lesions of the subthalamic nuclei in mitochondrial encephalopathies: an almost distinctive mark of Leigh disease with COX deficiency. AJNR 16:1746–1747
Detre JA, Wang ZY, Bogdan AR et al (1991) Regional variation in brain lactate in Leigh syndrome by localized 1H magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Ann Neurol 29:218–221
Grodd W, Krageloh-Mann I, Klose U et al (1991) Metabolic and destructive brain disorders in children: findings with localized proton MR spectroscopy. Radiology 181:173–181
Krageloh-Mann I, Grodd W, Schoning M et al (1993) Proton spectroscopy in five patients with Leigh’s disease and mitochondrial enzyme deficiency. Dev Med Child Neurol 35:769–776
Acknowledgement
This review is based on an electronic exhibit that won a Certificate of Merit at the Society for Pediatric Radiology meeting in Miami, FL, April 2007.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phelan, J.A., Lowe, L.H. & Glasier, C.M. Pediatric neurodegenerative white matter processes: leukodystrophies and beyond. Pediatr Radiol 38, 729–749 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-0817-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-008-0817-x