Abstract
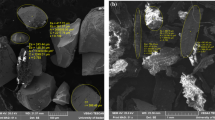
Magnetic solid-phase extraction is one of the most promising new extraction methods for liquid samples before ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) analysis. Several types of materials, including carbonaceous ones, have been prepared for this purpose. In this paper, for the first time, the preparation, characterization, and sorption capability of Fe3O4-graphitized carbon black (mGCB) composite toward some compounds of environmental interest were investigated. The synthesized mGCB consisted of micrometric GCB particles with 55 m2 g−1 surface area bearing some carbonyl and hydroxyl functionalities and the surface partially decorated by Fe3O4 microparticles. The prepared mGCB was firstly tested as an adsorbent for the extraction from surface water of 50 pollutants, including estrogens, perfluoroalkyl compounds, UV filters, and quinolones. The material showed good affinity to many of the tested compounds, except carboxylates and glucoronates; however, some compounds were difficult to desorb. Ten UV filters belonging to the chemical classes of benzophenones and p-aminobenzoates were selected, and parameters were optimized for the extraction of these compounds from surface water before UHPLC–MS/MS determination. Then, the method was validated in terms of linearity, trueness, intra-laboratory precision, and detection and quantification limits. In summary, the method performance (trueness, expressed as analytical recovery, 85–114%; RSD 5–15%) appears suitable for the determination of the selected compounds at the level of 10–100 ng L−1, with detection limits in the range of 1–5 ng L−1. Finally, the new method was compared with a published one, based on conventional solid-phase extraction with GCB, showing similar performance in real sample analysis.

Workflow of the analytical method based on magnetic solid-phase extraction followed by LC-MS/MS determination



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armenta S, Garrigues S, de la Guardia M. Green analytical chemistry. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2008;27:497–511.
Gałuszka A, Migaszewski Z, Namieśnik J. The 12 principles of green analytical chemistry and the significance mnemonic of green analytical practices. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2013;50:78–84.
Płotka-Wasylka J, Szczepańska N, de la Guardia M, Namieśnik J. Modern trends in solid phase extraction: new sorbent media. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2016;77:23–43.
Wen Y, Chen L, Li J, Liu D, Chen L. Recent advances in solid-phase sorbents for sample preparation prior to chromatographic analysis. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2014;59:26–41.
Li J, Wang Y-B, Li K-Y, Cao Y-Q, Wu S, Wu L. Advances in different configurations of solid-phase microextraction and their applications in food and environmental analysis. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2015;72:141–52.
Leong M-I, Fuh M-R, Huang S-D. Beyond dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1335:2–14.
Płotka-Wasylka J, Szczepańska N, de la Guardia M, Namieśnik J. Miniaturized solid-phase extraction techniques. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2015;73:19–38.
Ocaña-González JA, Fernández-Torres R, Bello-López MÁ, Ramos-Payán M. New developments in microextraction techniques in bioanalysis. A review. Anal Chim Acta. 2016;905:8–23.
Kokosa JM. Recent trends in using single-drop microextraction and related techniques in green analytical methods. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2015;71:194–204.
Wierucka M, Biziuk M. Application of magnetic nanoparticles for magnetic solid-phase extraction in preparing biological, environmental and food samples. TRAC-Trend Anal Chem. 2014;59:50–8.
Wang Q, Huang L, Yu P, Wang J, Shen S. Magnetic solid-phase extraction and determination of puerarin in rat plasma using C18-functionalized magnetic silica nanoparticles by high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr B. 2013;912:33–7.
Gao Q, Lin CY, Luo D, Suo LL, Chen JL, Feng YQ. Magnetic solid-phase extraction using magnetic hyper cross linked polymer for rapid determination of illegal drugs in urine. J Sep Sci. 2011;34:3083–91.
Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, La Barbera G, Piovesana S, Samperi R, Zenezini Chiozzi R, Laganà A. Polydopamine-coated magnetic nanoparticles for isolation and enrichment of estrogenic compounds from surface water samples followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry determination. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2016;408:4011–20.
Speltini A, Sturini M, Maraschi F, Profumo A. Recent trends in the application of the newest carbonaceous materials for magnetic solid-phase extraction of environmental pollutants. Trends Env Anal Chem. 2016;10:11–23.
Luo Y-B, Shi Z-G, Gao Q, Feng Y-Q. Magnetic retrieval of graphene: extraction of sulfonamide antibiotics from environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218:1353–8.
Heidari H, Razmi H. Multi-response optimization of magnetic solid phase extraction based on carbon coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles using desirability function approach for the determination of the organophosphorus pesticides in aquatic samples by HPLC–UV. Talanta. 2012;99:13–21.
Liu L, Hao Y, Ren Y, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z. Magnetic nanoporous carbon as an adsorbent for the extraction of phthalate esters in environmental water and aloe juice samples. J Sep Sci. 2015;38:1411–8.
Diao C, Yang X, Sun A, Liu R. A combined technique for the pretreatment of ultra trace bisphenol A in environmental water based on magnetic matrix solid phase extraction assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction. Anal Methods. 2015;7:10170–6.
Sarafraz-Yazdi A, Rokhian T, Amiri A, Ghaemi F. Carbon nanofibers decorated with magnetic nanoparticles as a new sorbent for the magnetic solid phase extraction of selected polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons from water samples. New J Chem. 2015;39:5621–7.
Amoli-Diva M, Pourghazi K, Hajjaran S. Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction using magnetic nanoparticle modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes coupled with surfactant-enhanced spectrofluorimetry for sensitive determination of lomefloxacin and ofloxacin from biological samples. Mater Sci Eng. 2016;60:30–6.
Campanella L, Di Corcia A, Samperi R, Gambacorta A. The nature of surface chemical heterogeneities of graphitized carbon black. Materials Chem. 1982;7:429–38.
Laganà A, Fago G, Marino A. Simultaneous determination of imidazolinone herbicides from soil and natural waters using soil column extraction and off-line solid-phase extraction followed by liquid chromatography with UV detection or liquid chromatography/electrospray mass spectroscopy. Anal Chem. 1998;70:121–30.
Zheng HB, Zhao Q, Mo JZ, Huang YQ, Luo YB, Yu QW, Feng YQ. Quick, easy, cheap, effective, rugged and safe method with magnetic graphitized carbon black and primary secondary amine as adsorbent and its application in pesticide residue analysis. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1300:127–33.
Ramos S, Homem V, Alves A, Santos L. Advances in analytical methods and occurrence of organic UV-filters in the environment—a review. Sci Total Environm. 2015;526:278–311.
Gago-Ferrero P, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D. Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry for the multi-residue analysis of organic UV filters and their transformation products in the aquatic environment. Anal Method. 2013;5:355–66.
Richardson SD, Ternes TA. Water analysis: emerging contaminants and current issues. Anal Chem. 2014;86:2813–48.
Gago-Ferrero P, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D. An overview of UV-absorbing compounds (organic UV filters) in aquatic biota. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2012;404:2597–610.
Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products. O J European Communities. 2009;OJ:L342/59.
Giokas DL, Salvador A, Chisvert A. UV filters: from sunscreens to human body and the environment. Trends Anal Chem. 2007;26:360–74.
Gago-Ferrero P, Mastroianni N, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D. Fully automated determination of nine ultraviolet filters and transformation products in natural waters and wastewaters by on-line solid phase extraction–liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1294:106–16.
Zhang H, Lee HK. Simultaneous determination of ultraviolet filters in aqueous samples by plunger-in-needle solid-phase microextraction with graphene-based sol–gel coating as sorbent coupled with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;742:67–73.
Li J, Ma L, Tang M, Xu L. C12-Ag wire as solid-phase microextraction fiber for determination of benzophenone ultraviolet filters in river water. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1298:1–8.
Wu J-W, Chen H-C, Ding W-H. Ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction plus simultaneous silylation for rapid determination of salicylate and benzophenone-type ultraviolet filters in aqueous samples. J Chromatogr A. 2013;1302:20–7.
Zhang P-P, Shi Z-G, Yu Q-W, Feng Y-Q. A new device for magnetic stirring-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of UV filters in environmental water samples. Talanta. 2011;83:1711–5.
Pedrouzo M, Borrull F, Marcé R, Pocurull E. Stir-bar-sorptive extraction and ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry for simultaneous analysis of UV filters and antimicrobial agents in water samples. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2010;397:2833–9.
Nguyen KTN, Scapolla C, Di Carro M, Magi E. Rapid and selective determination of UV filters in seawater by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry combined with stir bar sorptive extraction. Talanta. 2011;85:2375–84.
Ye L, Liu J, Yang X, Peng Y, Xu L. Orthogonal array design for the optimization of ionic liquid-based dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of benzophenone-type UV filters. J Sep Sci. 2011;34:700–6.
Zhang Y, Lee HK. Ionic liquid-based ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed high-performance liquid chromatography for the determination of ultraviolet filters in environmental water samples. Anal Chim Acta. 2012;750:120–6.
Ge D, Lee HK. A new 1-hexyl-3-methylimidazolium tris(pentafluoroethyl)trifluorophosphate ionic liquid based ultrasound-assisted emulsification microextraction for the determination of organic ultraviolet filters in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A. 2012;1251:27–32.
Vidal L, Chisvert A, Canals A, Salvador A. Ionic liquid-based single-drop microextraction followed by liquid chromatography–ultraviolet spectrophotometry detection to determine typical UV filters in surface water samples. Talanta. 2010;81:549–55.
Ge D, Lee HK. Ionic liquid based hollow fiber supported liquid phase microextraction of ultraviolet filters. J of Chromatogr A. 2012;1229:1–5.
Rodil M, Schrader S, Moeder M. Non-porous membrane-assisted liquid–liquid extraction of UV filter compounds from water samples. J Chromatogr A. 2009;1216:4887–94.
Román IP, Chisvert A, Canals A. Dispersive solid-phase extraction based on oleic acid-coated magnetic nanoparticles followed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for UV-filter determination in water samples. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218:2467–75.
Benedé JL, Chisvert A, Giokasb DL, Salvador A. Development of stir bar sorptive-dispersive microextraction mediatedby magnetic nanoparticles and its analytical application to thedetermination of hydrophobic organic compounds in aqueous media. J Chromatogr A. 2014;1362:25–33.
Yan Y, Zheng Z, Deng C, Zhang X, Yang P. Selective enrichment of phosphopeptides by titania nanoparticles coated magnetic carbon nanotubes. Talanta. 2014;118:14–20.
Cavaliere C, Capriotti AL, Ferraris F, Foglia P, Samperi R, Ventura S, Laganà A. Multiresidue analysis of endocrine-disrupting compounds and perfluorinated sulfates and carboxylic acids in sediments by ultra-high-performance liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2016;1438:133–42.
Nathanail V, Syvähuoko J, Malachová A, Jestoi M, Varga E, Michlmayr H, Adam G, Sieviläinen E, Berthiller F, Peltonen F. Simultaneous determination of major type A and B trichothecenes, zearalenone and certain modified metabolites in Finnish cereal grains with a novel liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometric method. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2015;407:4745–55.
Matuszewski BK, Constanzer ML, Chavez-Eng CM. Strategies for the assessment of matrix effect in quantitative bioanalytical methods based on HPLC−MS/MS. Anal Chem. 2003;75:3019–30.
Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, Piovesana S, Samperi R, Stampachiacchiere S, Ventura S, Laganà A. Multiresidue determination of UV filters in water samples by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with tandem mass spectrometry analysis. J Sep Sci. 2014;37:2882–91.
Kharissova OV, Rasika Dias HV, Kharisov BI. Magnetic adsorbents based on micro- and nanostructured materials. RSC Adv. 2015;5:6695–719.
Barcellos Hoff R, Rübensam G, Jank L, Barreto F, Ruaro Peralba MC, Pizzolato TM, Díaz-Cruz MS, Barceló D. Analytical quality assurance in veterinary drug residue analysis methods: matrix effects determination and monitoring for sulfonamides analysis. Talanta. 2015;132:443–50.
Serrano AB, Capriotti AL, Cavaliere C, Piovesana S, Samperi R, Ventura S, Laganà A. Development of a rapid LC-MS/MS method for the determination of emerging fusarium mycotoxins enniatins and beauvericin in human biological fluids. Toxins. 2015;7:3554–71.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Dr. Pettiti for the porosimetry measurements and Dr. Marchesan for all the other characterization analyses.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 0.99 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piovesana, S., Capriotti, A.L., Cavaliere, C. et al. A new carbon-based magnetic material for the dispersive solid-phase extraction of UV filters from water samples before liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry analysis. Anal Bioanal Chem 409, 4181–4194 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0368-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-017-0368-9