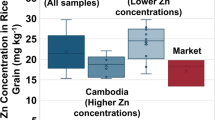
Abstract
Rice is a staple food yet is a significant dietary source of inorganic arsenic, a class 1, nonthreshold carcinogen. Establishing the location and speciation of arsenic within the edible rice grain is essential for understanding the risk and for developing effective strategies to reduce grain arsenic concentrations. Conversely, selenium is an essential micronutrient and up to 1 billion people worldwide are selenium-deficient. Several studies have suggested that selenium supplementation can reduce the risk of some cancers, generating substantial interest in biofortifying rice. Knowledge of selenium location and speciation is important, because the anti-cancer effects of selenium depend on its speciation. Germanic acid is an arsenite/silicic acid analogue, and location of germanium may help elucidate the mechanisms of arsenite transport into grain. This review summarises recent discoveries in the location and speciation of arsenic, germanium, and selenium in rice grain using state-of-the-art mass spectrometry and synchrotron techniques, and illustrates both the importance of high-sensitivity and high-resolution techniques and the advantages of combining techniques in an integrated quantitative and spatial approach.

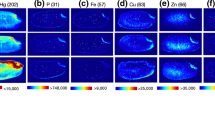
Synchrotron X-ray Fluorescence microtomography images for a virtual cross section of a husked immature rice grain pulsed with 133 μM germanic acid through the excised panicle stem



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fageria NK (2007) J Plant Nutr 30:843
Meharg AA, Williams PN, Adomako E, Lawgali YY, Deacon C, Villada A, Cambell RCJ, Sun G, Zhu YG, Feldmann J, Raab A, Zhao F, Islam R, Hossain S, Yanai J (2009) Environ Sci Technol 43:1612–1617
Meharg AA, Sun G, Williams PN, Adomako E, Deacon C, Zhu YG, Feldmann J, Raab A (2008) Environ Pollut 152:746–749
Combs GF Jr (2001) Br J Nutr 85:517
Clark LC, Combs GF Jr, Turnbull BW, Slate EH, Chalker DK, Chow J, Davis LS, Glover RA, Graham GF, Gross EG, Krongrad A, Lesher JL Jr, Park HK, Sanders BB Jr, Smith CL, Taylor JR (1996) J Am Med Assoc 276:1957–1963
Ellis DR, Salt DE (2003) Curr Opin Plant Biol 6:273–279
Whanger PD (2004) Br J Nutr 91:11
Rayman MP, Infante HG, Sargent M (2008) Br J Nutr 100:238
Tsubura A, Lai Y, Kuwata M, Uehara N, Yoshizawa K (2011) Anti-Cancer Agent ME 11:249–253
Dennert G, Zwahlen M, Brinkman M, Vinceti M, Zeegers MP A, Horneber M (2011) Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, Issue 5. Art. No.: CD005195. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005195.pub2
Zhu YG, Pilon-Smits EAH, Zhao FJ, Williams PN, Meharg AA (2009) Trends Plant Sci 14:436–442
Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2009) Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:373–380
Feldmann J, Salaün P, Lombi E (2009) Environ Chem 6:275–289
Husted S, Persson DP, Laursen KH, Hansen TH, Pedas P, Schiller M, Hegelund JN, Schjoerring JK (2011) J Anal At Spectrom 26:52–79
Schoof RA, Yost LJ, Eickhoff J, Crecelius EA, Cragin DW, Meacher DM, Menzel DB (1999) Food Chem Toxicol 37:839–846
Heitkemper DT, Vela NP, Stewart KR, Westphal CS (2001) J Anal At Spectrom 16:299–306
Williams PN, Price AH, Raab A, Hossain SA, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2005) Environ Sci Technol 39:5531–5540
Sun GX, Williams PN, Carey AM, Zhu YG, Deacon C, Raab A, Feldmann J, Islam RM, Meharg AA (2008) Environ Sci Technol 42:7542–7546
Norton GJ, Islam MR, Deacon CM, Zhao F, Stroud JL, Mcgrath SP, Islam S, Jahiruddin M, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2009) Environ Sci Technol 43:6070–6075
Norton GJ, Duan G, Dasgupta T, Islam MR, Lei M, Zhu Y, Deacon CM, Moran AC, Islam S, Zhao F, Stroud JL, Mcgrath SP, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2009) Environ Sci Technol 43:8381–8386
Williams PN, Islam MR, Adomako EE, Raab A, Hossain SA, Zhu YG, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2006) Environ Sci Technol 40:4903–4908
Zavala YJ, Gerads R, Gürleyük H, Duxbury JM (2008) Environ Sci Technol 42:3861–3866
Zhu YG, Sun GX, Lei M, Teng M, Liu YX, Chen NC, Wang LH, Carey AM, Deacon C, Raab A, Meharg AA, Williams PN (2008) Environ Sci Technol 42:5008–5013
Adomako EE, Solaiman ARM, Williams PN, Deacon C, Rahman GKMM, Meharg AA (2009) Environ Int 35:476–479
Kohlmeyer U, Jantzen E, Kuballa J, Jakubik S (2003) Anal Bioanal Chem 377:6–13
Hansen HR, Raab A, Price AH, Duan G, Zhu Y, Norton GJ, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2011) J Environ Monit 13:32–34
Beilstein MA, Whanger PD, Yang GQ (1991) Biomed Environ Sci 4:392–398
Williams PN, Lombi E, Sun GX, Scheckel K, Zhu YG, Feng X, Zhu J, Carey AM, Adomako E, Lawgali Y, Deacon C, Meharg AA (2009) Environ Sci Technol 43:6024–6030
Fang Y, Zhang Y, Catron B, Chan Q, Hu Q, Caruso JA (2009) J Anal At Spectrom 24:1657–1664
Sun GX, Liu X, Williams PN, Zhu YG (2010) Environ Sci Technol 44:6706–6711
Li HF, Lombi E, Stroud JL, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2010) J Agric Food Chem 58:11837–11843
Zhao Y, Zheng J, Yang M, Yang G, Wu Y, Fu F (2011) Talanta 84:983–988
Lombi E, Scheckel KG, Pallon J, Carey AM, Zhu YG, Meharg AA (2009) New Phytol 184:193–201
Carey A, Scheckel KG, Lombi E, Newville M, Choi Y, Norton GJ, Charnock JM, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2010) Plant Physiol 152:309–319
Lombi E, Susini J (2009) Plant Soil 320:1–35
Lombi E, Scheckel KG, Kempson IM (2011) Environ Exp Bot 72:3–17
Smith E, Kempson I, Juhasz AL, Weber J, Skinner WM, Gräfe M (2009) Chemosphere 76:529–535
Ren XL, Liu QL, Wu DX, Shu Q (2006) Rice Sci 13:170–178
Rahman MA, Hasegawa H, Rahman MM, Rahman MA, Miah MAM (2007) Chemosphere 69:942–948
Punshon T, Guerinot ML, Lanzirotti A (2009) Ann Bot- London 103:665–672
Krishnan S, Dayanandan P (2003) J Biosci 28:455–469
Seyfferth AL, Webb SM, Andrews JC, Fendorf S (2011) Geochim Cosmochim Acta 75:6655–6671
Zheng MZ, Cai C, Hu Y, Sun GX, Williams PN, Cui HJ, Li G, Zhao FJ, Zhu YG (2011) New Phytol 189:200–209
Carey A, Norton GJ, Deacon C, Scheckel KG, Lombi E, Punshon T, Guerinot ML, Lanzirotti A, Newville M, Choi Y, Price AH, Meharg AA (2011) New Phytol 192:87–98
Kim SA, Punshon T, Lanzirotti A, Li A, Alonso JM, Ecker JR, Kaplan J, Guerinot ML (2006) Science 314:1295–1298
Abedin MJ, Feldmann J, Meharg AA (2002) Plant Physiol 128:1120–1128
Zhao FJ, Stroud JL, Khan MA, McGrath SP (2011) Plant Soil In press doi: 10.1007/s11104-011-0926-4
Rivers M (2010) 4,000 Spectra or 4,000,000 ROIs per Second: EPICS Support for High-Speed Digital X-ray Spectroscopy with the XIA xMap", XRM 2010, 10th International Conference on X-ray Microscopy, 2010. See also http://cars9.uchicago.edu/software/epics/dxp.html for DXP 3.0 release (accessed 3-Dec-2010)
Ryan CG, Siddons DP, Moorhead G, Kirkham R, De Geronimo G, Etschmann B E, Dragone A, Dunn P A, Kuczewski A, Davey P, Jensen M, Ablett JM, Kuczewski J, Hough R, Paterson D (2009) J Physics: Conference Series 186: 012013
Ryan CG, Kirkham R, Hough RM, Moorhead G, Siddons DP, de Jonge MD, Paterson DJ, De Geronimo G, Howard DL, Cleverley JS (2010) Nucl Instr Meth A 619:37–43
Kirkham R, Dunn PA, Kucziewski A, Siddons DP, Dodanwela R, Moorhead G, Ryan CG, De Geronimo G, Beuttenmuller R, Pinelli D, Pfeffer M, Davey P, Jensen M, Paterson D, de Jonge MD, Kusel M, McKinlay J (2010) AIP Conf Ser 1234:240
Lombi E, de Jonge MD, Donner E, Kopittke PM, Howard DL, Kirkham R, Ryan CG, Paterson D (2011) PLoS One 6:e20626. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0020626
Paterson DJ, Boldeman JW, Cohen DD, Ryan CG (2007) AIP Conf Proc 879:864–867
de Jonge MD, Vogt S (2010) Curr Op Str Biol 20:606–614
Ma JF, Tamai K, Ichii M, Wu GF (2002) Plant Physiol 130:2111–2117
Nikolic M, Nikolic N, Liang Y, Kirkby EA, Romheld V (2007) Plant Physiol 143:495–503
Ma JF, Yamaji N (2008) Cell Mol Life Sci 65:3049–3057
Ma F, Yamaji N, Mitani N, Xu XY, Su YH, McGrath SP, Zhao FJ (2008) Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 105:9931–9935
Norton GJ, Dasgupta T, Islam MR, Islam S, Deacon CM, Zhao F, Stroud JL, McGrath SP, Feldmann J, Price AH, Meharg AA (2010) Environ Sci Technol 44:8284–8288
Punshon T, Jackson BP, Bertsch PM, Burger J (2004) J Environ Monitor 6:153–159
Jackson BP, Hopkins WA, Baionno J (2003) Environ Sci Technol 37:2511–2515
Moore KL, Schröder M, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP, Hawkesford MJ, Shewry PR, Grovenor CRM (2010) New Phytol 185:434–445
Lombi E, de Jonge MD, Donner E, Ryan CG, Paterson D (2011) Anal Bioanal Chem 400:1637–1644
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council Doctoral Training Grant. Part of this research was undertaken on the X-ray fluorescence microscopy beamline at the Australian synchrotron, Victoria, Australia. The authors thank Drs David Paterson and Daryl Howard for their help in collecting the germanium microtomography images.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Published in the special paper collection Elemental Imaging and Speciation in Plant Science with guest editors J. Feldmann and E. Krupp.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00216-012-5786-0.
Glossary of terms
- Aleurone
-
The aleurone cells house hormones and enzymes instrumental in the germination and development of the grain and are rich in phytic acid. Phytic acid, or phytate, a salt of phytic acid, is the main grain store of phosphorus and is known to chelate cations including those of many micronutrients, for example iron, zinc, and calcium. The aleurone is understood to specifically accumulate phytate and metals for germination and growth of the rice seed.
- Anthesis
-
Anthesis refers to the period of flowering. The point of anthesis is the point at which the anthers have emerged, demonstrating that the flower has reached the reproductive stage.
- Bran
-
The bran comprises the pericarp, testa, and aleurone cells and is rich in micro and macronutrients, B vitamins, protein, and fibre.
- Caryopsis
-
The caryopsis is the whole grain (not including the husk/hull).
- Embryo
-
The embryo, or germ, is the point at which the new plant develops and contains abundant proteins, lipids, and vitamins. In the processing of rice grain for consumption, the bran and embryo are removed together, leaving the sub-aleurone and endosperm to make up the polished (white) rice that is commonly consumed.
- Endosperm
-
The inner starchy part of a grain which serves as food reserves for the seed’s development. In contrast with the embryo and bran layer, the endosperm contains relatively less protein, lipids, and nutrients and is mainly composed of starch and non-starch polysaccharides.
- Husk
-
The husk, or hull, is the outermost layer of a rice grain, a silica-rich envelope that protects against predation and disease.
- Internode
-
The node is the section of stem between two nodes.
- Node
-
Nodes are joints along the plant stem at which leaves and buds develop. They are also the points at which vascular contents are transferred to leaf and/or panicle.
- Nucellar tissue
-
The nucellar tissue is the tissue that initially surrounds the embryo. As the starchy endosperm develops and expands, the nucellar tissue becomes stretched, and is eventually crushed in the mature grain.
- Panicle
-
The panicle is the flower head of the rice plant. Technically, a panicle is an inflorescence in which each flower is on its own stalk.
- Peduncle
-
The peduncle is the panicle stem, i.e. the stem supporting the inflorescence (group of flowers).
- Pericarp
-
Pericarp is the ripened ovary wall. In the rice grain this thin, fibrous layer offers protection against moulds and oxidation.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Carey, AM., Lombi, E., Donner, E. et al. A review of recent developments in the speciation and location of arsenic and selenium in rice grain. Anal Bioanal Chem 402, 3275–3286 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5579-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5579-x