Abstract
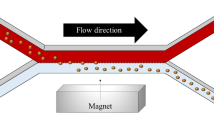
A bubble cell capillary classically used to extend the optical path length for UV–vis detection is employed here to trap magnetic beads. With this system, a large amount of beads can be captured without inducing a strong pressure drop, as it is the case with magnetic beads trapped in a standard capillary, thereby having less effect on the experimental conditions. Using numerical simulations and microscopic visualizations, the capture of beads inside a bubble cell was investigated with two magnet configurations. Pressure-driven and electro-osmotic flow velocities were measured for different amounts of protein-A-coated beads or C18-functionalized beads (RPC-18). Solid-phase extraction of a model antibody on protein-A beads and preconcentration of fluorescein on RPC-18 beads were performed as proof of concept experiments.

Isovalues of the magnetic induction produced by two permanent magnets in attraction configuration with a capillary placed between them.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Breadmore MC, Dawod M, Quirino JP (2011) Recent advances in enhancing the sensitivity of electrophoresis and electrochromatography in capillaries and microchips (2008–2010). Electrophoresis 32(1):127–148
Hempel G (2000) Strategies to improve the sensitivity in capillary electrophoresis for the analysis of drugs in biological fluids. Electrophoresis 21(4):691–698
Tempels FWA, Underberg WJM, Somsen GW, de Jong GJ (2008) Design and applications of coupled SPE-CE. Electrophoresis 29(1):108–128
Saavedra L, Barbas C (2007) Chromatography-based on- and in-line pre-concentration methods in capillary electrophoresis. J Biochem Bioph Meth 70(2):289–297
Puig P, Borrull F, Calull M, Aguilar C (2007) Recent advances in coupling solid-phase extraction and capillary electrophoresis (SPE-CE). Trac-Trend Anal Chem 26(7):664–678
Ramautar R, Somsen GW, de Jong GJ (2010) Recent developments in coupled SPE-CE. Electrophoresis 31(1):44–54
Guzman NA, Blanc T, Phillips TM (2008) Immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis as a powerful strategy for the quantification of low-abundance biomarkers, drugs, and metabolites in biological matrices. Electrophoresis 29(16):3259–3278
Augustin V, Proczek G, Dugay J, Descroix S, Hennion MC (2007) Online preconcentration using monoliths in electrochromatography capillary format and microchips. J Sep Sci 30(17):2858–2865
Puig P, Borrull F, Calull M, Aguilar C (2008) Sorbent preconcentration procedures coupled to capillary electrophoresis for environmental and biological applications. Analytica Chimica Acta 616(1):1–18
Peterson DS (2005) Solid supports for micro analytical systems. Lab Chip 5(2):132–139
Pamme N (2006) Magnetism and microfluidics. Lab Chip 6(1):24–38
Gijs MA, Lacharme F, Lehmann U (2010) Microfluidic applications of magnetic particles for biological analysis and catalysis. Chem Rev 110(3):1518–1563
Doyle PS, Bibette J, Bancaud A, Viovy JL (2002) Self-assembled magnetic matrices for DNA separation chips. Science 295(5563):2237
Kaneta T, Inoue J, Koizumi M, Imasaka T (2006) On-column capture of a specific protein in capillary electrophoresis using magnetic beads. Electrophoresis 27(16):3218–3223
Jankovicova B, Rosnerova S, Slovakova M, Zverinova Z, Hubalek M, Hernychova L, Rehulka P, Viovy JL, Bilkova Z (2008) Epitope mapping of allergen ovalbumin using biofunctionalized magnetic beads packed in microfluidic channels. The first step towards epitope-based vaccines. J Chromatogr A 1206(1):64–71
Okamoto Y, Kitagawa F, Otsuka K (2007) Online concentration and affinity separation of biomolecules using multifunctional particles in capillary electrophoresis under magnetic field. Anal Chem 79(8):3041–3047
Tennico YH, Remcho VT (2010) In-line extraction employing functionalized magnetic particles for capillary and microchip electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 31(15):2548–2557
Slovakova M, Minc N, Bilkova Z, Smadja C, Faigle W, Futterer C, Taverna M, Viovy JL (2005) Use of self assembled magnetic beads for on-chip protein digestion. Lab Chip 5(9):935–942
Le Nel A, Minc N, Smadja C, Slovakova M, Bilkova Z, Peyrin JM, Viovy JL, Taverna M (2008) Controlled proteolysis of normal and pathological prion protein in a microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 8(2):294–301
Rashkovetsky LG, Lyubarskaya YV, Foret F, Hughes DE, Karger BL (1997) Automated microanalysis using magnetic beads with commercial capillary electrophoretic instrumentation. J Chromatogr A 781(1–2):197–204
Hayes MA, Polson NA, Phayre AN, Garcia AA (2001) Flow-based microimmunoassay. Anal Chem 73:5896–5902
Chen HX, Busnel JM, Gassner AL, Peltre G, Zhang XX, Girault HH (2008) Capillary electrophoresis immunoassay using magnetic beads. Electrophoresis 29(16):3414–3421
Chen HX, Busnel JM, Peltre G, Zhang XX, Girault HH (2008) Magnetic beads based immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis of total serum IgE with laser-induced fluorescence detection. Anal Chem 80(24):9583–9588
Lacharme F, Vandevyver C, Gijs MA (2008) Full on-chip nanoliter immunoassay by geometrical magnetic trapping of nanoparticle chains. Anal Chem 80(8):2905–2910
Hahn YK, Jin Z, Kang JH, Oh E, Han MK, Kim HS, Jang JT, Lee JH, Cheon J, Kim SH, Park HS, Park JK (2007) Magnetophoretic immunoassay of allergen-specific IgE in an enhanced magnetic field gradient. Anal Chem 79(6):2214–2220
Do J, Ahn CH (2008) A polymer lab-on-a-chip for magnetic immunoassay with on-chip sampling and detection capabilities. Lab on a Chip 8(4):542–549
Gassner AL, Abonnenc M, Chen HX, Morandini J, Josserand J, Rossier JS, Busnel JM, Girault HH (2009) Magnetic forces produced by rectangular permanent magnets in static microsystems. Lab Chip 9(16):2356–2363
Oleschuk RD, Shultz-Lockyear LL, Ning YB, Harrison DJ (2000) Trapping of bead-based reagents within microfluidic systems: on-chip solid-phase extraction and electrochromatography. Anal Chem 72(3):585–590
Strausbauch MA, Landers JP, Wettstein PJ (1996) Mechanism of peptide separations by solid phase extraction capillary electrophoresis at low pH. Anal Chem 68(2):306–314
Lara FJ, Lynen F, Sandra P, Garcia-Campana AM, Ales-Barrero F (2008) Evaluation of a molecularly imprinted polymer as in-line concentrator in capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 29(18):3834–3841
Gassner AL, Morandini J, Josserand J, Girault HH (2011) Ring magnets for magnetic beads trapping in a capillary. Analytical Methods 3(3):614–621
Hayes MA, Polson NA, Garcia AA (2001) Active control of dynamic supraparticle structures in microchannels. Langmuir 17(9):2866–2871
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank the Swiss National Science Foundation for financial support, grant entitled “Supramolecular phases for protein adsorption” (grant no. 404740-117321). The authors also thank the “Agilent Technologies Foundation” for a research award and Dr. Stéphanie Descroix for helpful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Anne-Laure Gassner and Gaëlle Proczek have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 221 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gassner, AL., Proczek, G. & Girault, H.H. Bubble cell for magnetic bead trapping in capillary electrophoresis. Anal Bioanal Chem 401, 3239–3248 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5417-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-011-5417-1