Abstract
Rationale
Adolescent binge drinking is concerning, as important neurodevelopments occur during this stage. Previous research suggests that binge drinking may disrupt typical brain development, and females may be particularly vulnerable.
Objectives
We used magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to examine cortical thickness in adolescent females and males with and without histories of binge drinking.
Methods
Participants (N = 59) were 16–19-year-old adolescents recruited from local schools. Recent binge drinkers (n = 29, 48% female) were matched to non-drinkers (n = 30, 50% female) on age, gender, pubertal development, and familial alcoholism. Participants completed a neuropsychological battery and MRI session. Cortical surfaces were reconstructed with FreeSurfer.
Results
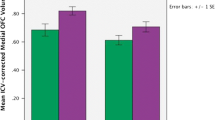
Binge × gender interactions (p < .05) were seen for cortical thickness in four left frontal regions: frontal pole, pars orbitalis, medial orbital frontal, and rostral anterior cingulate. For all interactions, female bingers had thicker cortices than female controls, while male bingers had thinner cortices than male controls. Thicker left frontal cortices corresponded with poorer visuospatial, inhibition, and attention performances for female bingers (r = −0.69 to 0.50, p < 0.05) and worse attention for male bingers (r = −0.69, p = 0.005).
Conclusions
Adolescent females with recent binge drinking showed ~8% thicker cortices in left frontal regions than demographically similar female non-drinkers, which was linked to worse visuospatial, inhibition, and attention performances. In contrast, adolescent binge-drinking males showed ~7% thinner cortices in these areas than non-drinking males. These cross-sectional data suggest either different gray matter risk factors for males as for females toward developing heavy drinking, or differential adverse sequelae.


Similar content being viewed by others

References
Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA (2001) Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms and Profiles. University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, and Families, Burlington
APA (1994) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, vol DSM-IV, 4th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington
Bava S, Frank LR, McQueeny T, Schweinsburg BC, Schweinsburg AD, Tapert SF (2009) Altered white matter microstructure in adolescent substance users. Psychiatry Res: Neuroimaging 173:228–237
Bava S, Thayer R, Jacobus J, Ward M, Jernigan TL, Tapert SF (2010) Longitudinal characterization of white matter maturation during adolescence. Brain Res 1327:38–46
Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK (1996) Manual for the Beck Depression Inventory-2. Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Brown SA, Myers MG, Lippke L, Tapert SF, Stewart DG, Vik PW (1998) Psychometric evaluation of the Customary Drinking and Drug Use Record (CDDR): a measure of adolescent alcohol and drug involvement. J Stud Alcohol 59:427–438
Brown SA, McGue M, Maggs J, Schulenberg J, Hingson R, Swartzwelder S, Martin C, Chung T, Tapert SF, Sher K, Winters KC, Lowman C, Murphy S (2008) A developmental perspective on alcohol and youths 16 to 20 years of age. Pediatrics 121(Supplement 4):S290–S310
Caldwell LC, Schweinsburg AD, Nagel BJ, Barlett VC, Brown SA, Tapert SF (2005) Gender and adolescent alcohol use disorders on BOLD (blood oxygen level dependent) response to spatial working memory. Alcohol Alcohol 40:194–200
Dale AM, Sereno MI (1993) Improved localization of cortical activity by combining EEG and MEG with MRI cortical surface reconstruction: a linear approach. J Cogn Neurosci 5:162–176
Dale AM, Fischl B, Sereno MI (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. I. Segmentation and surface reconstruction. NeuroImage 9:179–194
Delis DC, Kaplan E, Kramer JH (2001) The Delis-Kaplan executive function system: examiner’s manual. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Desikan RS, Segonne F, Fischl B, Quinn BT, Dickerson BC, Blacker D, Buckner RL, Dale AM, Maguire RP, Hyman BT, Albert MS, Killiany RJ (2006) An automated labeling system for subdividing the human cerebral cortex on MRI scans into gyral based regions of interest. NeuroImage 31:968–980
Emanuele NV, LaPaglia N, Steiner J, Kirsteins L, Emanuele MA (2001) Effect of chronic ethanol exposure on female rat reproductive cyclicity and hormone secretion. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1025–1029
Fischl B, Dale AM (2000) Measuring the thickness of the human cerebral cortex from magnetic resonance images. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:11050–11055
Fischl B, Sereno MI, Dale AM (1999) Cortical surface-based analysis. II: inflation, flattening, and a surface-based coordinate system. NeuroImage 9:195–207
Fischl B, van der Kouwe A, Destrieux C, Halgren E, Segonne F, Salat DH, Busa E, Seidman LJ, Goldstein J, Kennedy D, Caviness V, Makris N, Rosen B, Dale AM (2004) Automatically parcellating the human cerebral cortex. Cereb Cortex 14:11–22
Fitzgerald EF (1995) Intoxication test evidence, 2nd edn. Clark Boardman Callaghan, Deerfield
Frezza M, di Padova C, Pozzato G, Terpin M, Baraona E, Lieber CS (1990) High blood alcohol levels in women. The role of decreased gastric alcohol dehydrogenase activity and first-pass metabolism. N Engl J Med 322:95–99
Giedd JN (2004) Structural magnetic resonance imaging of the adolescent brain. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1021
Gogtay N, Giedd JN, Lusk L, Hayashi KM, Greenstein D, Vaituzis AC, Nugent TFr, Herman DH, Clasen LS, Toga AW, Rapoport JL, Thompson PM (2004) Dynamic mapping of human cortical development during childhood through early adulthood. Proc Natl Acad Sci 101:8174–8179
Hollingshead AB (1965) Two-factor index of social position. Yale University, New Haven
Hommer DW, Momenan R, Rawlings R, Ragan P, Williams W, Rio D, Eckardt M (1996) Decreased corpus callosum size among alcoholic women. Arch Neurol 53:359–363
Hommer DW, Momenan R, Kaiser E, Rawlings RR (2001) Evidence for a gender-related effect of alcoholism on brain volumes. Am J Psychiatry 158:198–204
Jacobson R (1986) The contributions of sex and drinking history to the CT brain scan changes in alcoholics. Psychol Med 16:547–549
Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2009) Monitoring the Future national results on adolescent drug use: overview of key findings, 2008 (NIH Publication No. 09–7401). National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda
Johnston LD, O’Malley PM, Bachman JG, Schulenberg JE (2011) Monitoring the Future national results on adolescent drug use: overview of key findings. National Institute on Drug Abuse, Bethesda
Jones E, Sigall H (1971) The bogus pipeline: a new paradigm for measuring affect and attitude. Psychol Bull 76:349–364
Kim JH, Kim HJ, Noh HS, Roh GS, Kang SS, Cho GJ, Park SK, Lee BJ, Choi WS (2003) Suppression by ethanol of male reproductive activity. Brain Res 989:91–98
Kuperberg GR, Broome MR, McGuire PK, David AS, Eddy M, Ozawa F, Goff D, West WC, Williams SC, van der Kouwe AJ, Salat DH, Dale AM, Fischl B (2003) Regionally localized thinning of the cerebral cortex in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60:878–888
Lenroot RK, Giedd JN (2006) Brain development in children and adolescents: insights from anatomical magnetic resonance imaging. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 30:718–729
Lopez-Larson MP, Bogorodzki P, Rogowska J, McGlade E, King JB, Terry J, Yurgelun-Todd D (2011) Altered prefrontal and insular cortical thickness in adolescent marijuana users. Behav Brain Res 220:164–172
Loring DW, Meador KJ (2003) The Medical College of Georgia (MCG) complex figures: four forms for follow-up. In: Knight J, Kaplan E (eds) Rey–Osterrieth handbook. Psychological Assessment Resources, Odessa
Lucas CP, Zhang H, Fisher PW, Shaffer D, Regier DA, Narrow WE, Bourdon K, Dulcan MK, Canino G, Rubio-Stipec M, Lahey BB, Friman P (2001) The DISC Predictive Scales (DPS): efficiently screening for diagnoses. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 40:443–449
Mann K, Batra A, Gunthner A, Schroth G (1992) Do women develop alcoholic brain damage more readily than men? Alcohol Clin Exp Res 16:1052–1056
McQueeny T, Schweinsburg BC, Schweinsburg AD, Jacobus J, Bava S, Frank LR, Tapert SF (2009) Altered white matter integrity in adolescent binge drinkers. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1278–1285
Meador KJ, Moore EE, Nichols ME, Abney OL, Taylor HS, Zamrini EY, Loring DW (1993) The role of cholinergic systems in visuospatial processing and memory. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 15:832–842
Medina KL, McQueeny T, Nagel BJ, Hanson KL, Schweinsburg AD, Tapert SF (2008) Prefrontal cortex volumes in adolescents with alcohol use disorders: unique gender effects. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 32:386–394
Miller JW, Naimi TS, Brewer RD, Jones SE (2007) Binge drinking and associated health risk behaviors among high school students. Pediatrics 119:76–85
NIAAA (2004) NIAAA Council approves definition of binge drinking, vol 3. NIAAA Newsletter, Bethesda
Pakkenberg B, Gundersen HJ (1997) Neocortical neuron number in humans: effect of sex and age. J Comp Neurol 384:312–320
Petersen AC, Crockett L, Richards M, Boxer A (1988) A self-report measure of pubertal status: reliability, validity, and initial norms. J Youth Adolescence 17
Rey A, Osterrieth PA (1993) Translations of excerpts from Andre Rey’s “Psychological examination of traumatic encephalopathy” and P.A. Osterrieth’s “The complex figure copy test” (J. Corwin & F. W. Bylsma, Trans.). Clin Neuropsychol 7:3–21
Rice JP, Reich T, Bucholz KK, Neuman RJ, Fishman R, Rochberg N, Hesselbrock VM, Nurnberger JIJ, Schuckit MA, Begleiter H (1995) Comparison of direct interview and family history diagnoses of alcohol dependence. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 19:1018–1023
Rosas HD, Liu AK, Hersch S, Glessner M, Ferrante RJ, Salat DH, van der Kouwe A, Jenkins BG, Dale AM, Fischl B (2002) Regional and progressive thinning of the cortical ribbon in Huntington’s disease. Neurology 58:695–701
Salat DH, Buckner RL, Snyder AZ, Greve DN, Desikan RS, Busa E, Morris JC, Dale AM, Fischl B (2004) Thinning of the cerebral cortex in aging. Cereb Cortex 14:721–730
SAMHSA (2008) Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration, Office of Applied Studies (2008). Results from the 2007 National Survey on Drug Use and Health: National Findings, Rockville, NSDUH Series H-34, DHHS Publication No. SMA 08–4343
Scheff SW, Price DA, Sparks DL (2001) Quantitative assessment of possible age-related change in synaptic numbers in the human frontal cortex. Neurobiol Aging 22:355–365
Schweinsburg BC, Alhassoon OM, Taylor MJ, Gonzalez R, Videen JS, Brown GG, Patterson TL, Grant I (2003) Effects of alcoholism and gender on brain metabolism. Am J Psychiatry 160:1180–1183
Silk TJ, Wood AG (2011) Lessons about neurodevelopment from anatomical magnetic resonance imaging. J Dev Behav Pediatr 32:158–168
Sobell LC, Sobell MB (1992) Timeline follow-back: a technique for assessing self-reported ethanol consumption. In: Allen J, Litten RZ (eds) Measuring alcohol consumption: psychosocial and biological methods. Humana, Totowa, pp 41–72
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Tessner K, Toga AW (2001) Mapping continued brain growth and gray matter density reduction in dorsal frontal cortex: inverse relationships during postadolescent brain maturation. J Neurosci 21:8819–8829
Sowell ER, Thompson PM, Leonard CM, Welcome SE, Kan E, Toga AW (2004) Longitudinal mapping of cortical thickness and brain growth in normal children. J Neurosci 24:8223–8231
Spear LP (2009) The behavioral neuroscience of adolescence, 1st edn. W. W. Norton & Co Inc, New York
Spielberger CD, Gorsuch RL, Lushene RE (1970) Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory. Consulting Psychologists Press, Palo Alto
Squeglia LM, Jacobus J, Tapert SF (2009a) The influence of substance use on adolescent brain development. J Clin EEG Neurosci 40:31–38
Squeglia LM, Spadoni AD, Infante MA, Myers MG, Tapert SF (2009b) Initiating moderate to heavy alcohol use predicts changes in neuropsychological functioning for adolescent girls and boys. Psychol Addict Behav 23:715–722
Squeglia LM, Dager Schweinsburg A, Pulido C, Tapert SF (2011) Adolescent binge drinking linked to abnormal spatial working memory brain activation: differential gender effects. Alcoholism: Clin Experiment Res (in press)
Stoneham ET, Sanders EM, Sanyal M, Dumas TC (2010) Rules of engagement: factors that regulate activity-dependent synaptic plasticity during neural network development. Biol Bull 219:81–99
Tapert SF, Brown SA (1999) Neuropsychological correlates of adolescent substance abuse: four-year outcomes. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 5:481–493
Tapert SF, Granholm E, Leedy NG, Brown SA (2002) Substance use and withdrawal: neuropsychological functioning over 8 years in youth. J Int Neuropsychol Soc 8:873–883
Tapert SF, Schweinsburg AD, Drummond SPA, Paulus MP, Brown SA, Yang TT, Frank LR (2007) Functional MRI of inhibitory processing in abstinent adolescent marijuana users. Psychopharmacology 194:173–184
Taylor LB (1969) Localisation of cerebral lesions by psychological testing. Clin Neurosurg 16:269–287
Wechsler D (1997) Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale, 3rd edn. The Psychological Corporation, San Antonio
Wechsler H, Isaac N (1992) ‘Binge’ drinkers at Massachusetts colleges. Prevalence, drinking style, time trends, and associated problems. J Am Med Assoc 267:2929–2931
Wechsler H, Davenport A, Dowdall G, Moeykens B, Castillo S (1994) Health and behavioral consequences of binge drinking in college. A national survey of students at 140 campuses. J Am Med Assoc 272:1672–1677
Wechsler H, Dowdall GW, Davenport A, Rimm EB (1995) A gender-specific measure of binge drinking among college students. Am J Public Health 85:982–985
Widmark E (1922) A micromethod for the estimation of alcohol in blood. Biochemistry 131:473–484
Wilkinson GS (1993) WRAT-3: Wide Range Achievement Test administration manual, 3rd edn. Western Psychological Services, Wilmington
Zucker RA, Ellis DA, Fitzgerald HE (1994) Developmental evidence for at least two alcoholisms: I. Biopyschosocial variation among pathways into symptomatic difficulty. In: Babor TF, Hesselbrock V, Meyer RE, Shoemaker W (eds) Types of alcoholics: evidence from clinical, experimental and genetic research. The New York Academy of Sciences, New York, pp 134–146
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (R01 AA13419, PI: Tapert; F31 AA018940, PI: Squeglia, F32 AA018597; R21 AA019748, PI: Pulido) and the National Institute on Drug Abuse (R01 DA021182, P20 DA024194, P20 DA027834).
The authors thank Veronique Boucquey, Norma Castro, Sonja Eberson, Diane Goldenberg, Joanna Jacobus, Anthony Scarlett, Rachel Thayer, Dr. Sunita Bava, Dr. Sandra Brown, Dr. Karen Hanson, Dr. Omar Mahmood, Dr. M.J. Meloy, and the participating families and schools.
Conflicts of interest and financial disclosures
The authors report no conflicts of interest or financial disclosures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Squeglia, L.M., Sorg, S.F., Schweinsburg, A.D. et al. Binge drinking differentially affects adolescent male and female brain morphometry. Psychopharmacology 220, 529–539 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2500-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2500-4