Abstract
Background
We have previously shown that single doses of serotonin-selective and noradrenaline-selective antidepressant agents produce positive biases in measures of emotional processing in healthy volunteers. The aim of the present study was to confirm and extend this finding by studying the effects of a single dose of the selective serotonin and noradrenaline re-uptake inhibitor, duloxetine.
Materials and methods
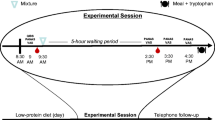
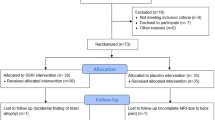
Healthy volunteers were randomly allocated to double-blind administration of either duloxetine 60 mg orally or placebo. Participants then completed a battery of emotional-processing tasks measuring facial expression recognition, emotional memory and emotion-potentiated startle. Subjective state was measured using visual analogue scales throughout the test period.
Results
Duloxetine enhanced the recognition of both disgusted and happy facial expressions and increased memory intrusions for positive personality characteristics in the free recall test. There were no significant effects on startle responses. However, duloxetine was not well tolerated and was associated with a high level of negative subjective effects.
Conclusions
Despite the induction of negative subjective effects after duloxetine administration, some positive effects on emotional processing were seen in line with acute administration of serotonin-selective and noradrenaline-selective antidepressant agents. These results confirm the induction of fast changes in emotional processing in healthy volunteer groups and suggest a mechanism by which antidepressants may act in depression. Further studies are required to assess whether positive effects on emotional processing are more selective at a lower dose of duloxetine.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson NH (1968) Likableness ratings of 555 personality trait words. J Pers Soc Psychol 9:272–279
Bradley B, Mathews A (1983) Negative self-schemata in clinical depression. Br J Clin Psychol 22(Pt 3):173–181
Browning M, Reid C, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM, Harmer C (2007) A single dose of citalopram increases fear recognition in healthy subjects. J Psychopharmacol 21:684–690
Burghardt NS, Bush DE, McEwen BS, LeDoux JE (2007) Acute selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors increase conditioned fear expression: blockade with a 5-HT(2C) receptor antagonist. Biol Psychiatry 62(10):1111–1118
Cahill L (1997) The neurobiology of emotionally influenced memory. Implications for understanding traumatic memory. Ann NY Acad Sci 821:238–246
Calder AJ, Lawrence AD, Young AW (2001) Neuropsychology of fear and loathing. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(5):352–363
Chan SW, Goodwin GM, Harmer CJ (2007) Highly neurotic never-depressed students have negative biases in information processing. Psychol Med 37:1281–1291
Damasio AR (1996) The somatic marker hypothesis and the possible functions of the prefrontal cortex. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 351(1346):1413–1420
Ekman P, Friesen WV (1976) Pictures of facial affect. Consulting Psychologists, Palo Alto, CA
Eysenck HJ, Eysenck SBG, Barrett P (1985) A revised version of the psychoticism scale. Pers Individ Differ 6:21–29
Frampton JE, Plosker GL (2007) Duloxetine: a review of its use in the treatment of major depressive disorder. CNS Drugs 21:581–609
Grier JB (1971) Nonparametric indexes for sensitivity and bias: computing formulas. Psychol Bull 75(6):424–429
Grillon C, Levenson J, Pine DS (2007) A single dose of the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor citalopram exacerbates anxiety in humans: a fear-potentiated startle study. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:225–231
Gupta S, Nihalani N, Masand P (2007) Duloxetine: review of its pharmacology, and therapeutic use in depression and other psychiatric disorders. Ann Clin Psychiatry 19:125–132
Gur RC, Erwin RJ, Gur RE, Zwil AS, Heimberg C, Kraemer HC (1992) Facial emotion discrimination: II. Behavioral findings in depression. Psychiatry Res 42:241–251
Harmer CJ, Bhagwagar Z, Perrett DI, Vollm BA, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2003a) Acute SSRI administration affects the processing of social cues in healthy volunteers. Neuropsychopharmacology 28:148–152
Harmer CJ, Hill SA, Taylor MJ, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2003b) Toward a neuropsychological theory of antidepressant drug action: increase in positive emotional bias after potentiation of norepinephrine activity. Am J Psychiatry 160:990–992
Harmer CJ, Shelley NC, Cowen PJ, Goodwin GM (2004) Increased positive versus negative affective perception and memory in healthy volunteers following selective serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibition. Am J Psychiatry 161:1256–1263
Hayward G, Goodwin GM, Cowen PJ, Harmer CJ (2005) Low-dose tryptophan depletion in recovered depressed patients induces changes in cognitive processing without depressive symptoms. Biol Psychiatry 57:517–524
Johnson-Laird PN, Mancini F, Gangemi A (2006) A hyper-emotion theory of psychological illnesses. Psychol Rev 113:822–841
Lang PJ, Bradley MM, Cuthbert BN (1998) International Affective Picture System (IAPS): technical manual and affective ratings. The Center for Research in Psychophysiology, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL (Pamphlet)
Larson CL, Ruffalo D, Nietert JY, Davidson RJ (2000) Temporal stability of the emotion-modulated startle response. Psychophysiology 37:92–101
Murphy SE, Norbury R, Cowen PJ, Harmer CJ (2006) Imaging the acute effects of citalopram. J Psychopharmacol (S) 20, A11
Surguladze SA, Young AW, Senior C, Brebion G, Travis MJ, Phillips ML (2004) Recognition accuracy and response bias to happy and sad facial expressions in patients with major depression. Neuropsychology 18:212–218
Tremblay P, Blier P (2006) Catecholaminergic strategies for the treatment of major depression. Curr Drug Targets 7:149–158
Turcotte JE, Debonnel G, de Montigny C, Hébert C, Blier P (2001) Assessment of the serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake blocking properties of duloxetine in healthy subjects. Neuropsychopharmacology 24(5):511–521
von Zerrsen D, Strian F, Schwarz D (1974) Evaluation of depressive states, especially in longitudinal studies. In: Pichot P (ed) Psychological measurements in psychopharmacology. Karger, Basel, Switzerland, pp 189–202
Young AW, Rowland D, Calder AJ, Etcoff NL, Seth A, Perrett DI (1997) Facial expression megamix: tests of dimensional and category accounts of emotion recognition. Cognition 63:271–313
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by the MRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harmer, C.J., Heinzen, J., O’Sullivan, U. et al. Dissociable effects of acute antidepressant drug administration on subjective and emotional processing measures in healthy volunteers. Psychopharmacology 199, 495–502 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1058-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-007-1058-7