Abstract
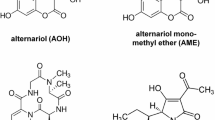
The Alternaria mycotoxins alternariol (AOH) and alternariol methyl ether (AME) are potential carcinogens. As planar compounds, AOH and AME are preferentially metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP) 1A1 and 1A2. The most prominent regulator of CYP1A1 is the dimeric transcription factor complex AhR/ARNT, which is activated by planar ligands. Therefore, we studied the activation of AhR/ARNT by AOH and AME and monitored CYP1A1 induction in murine hepatoma cells (Hepa-1c1c7). Indeed, AOH and AME enhanced the levels of CYP1A1 in Hepa-1c1c7 cells but not in cells with inactivated AhR (Hepa-1c1c12) or ARNT (Hepa-1c1c4). AOH and AME did not increase the production of reactive oxygen species but reduced cell counts in Hepa-1c1c7 cells after 24 and 48 h. This effect, however, was independent of AhR/ARNT. At 48 h, AOH and AME increased apoptosis dependent on AhR and ARNT. In conclusion, AOH and AME are novel inducers of the AhR/ARNT pathway, which mediates induction of CYP1A1 and apoptosis and might thereby contribute to the toxicity of these mycotoxins.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bock KW, Kohle C (2005) Ah receptor- and TCDD-mediated liver tumor promotion: clonal selection and expansion of cells evading growth arrest and apoptosis. Biochem Pharmacol 69:1403–1408
Bock KW, Kohle C (2006) Ah receptor: dioxin-mediated toxic responses as hints to deregulated physiologic functions. Biochem Pharmacol 72:393–404
Burkhardt B, Pfeiffer E, Metzler M (2009) Absorption and metabolism of the mycotoxins alternariol and alternariol-9-methyl ether in Caco-2 cells in vitro. Mycotoxin Res 25:149–157
Burkhardt B, Jung SA, Pfeiffer E et al (2011) Mouse hepatoma cell lines differing in aryl hydrocarbon receptor-mediated signaling have different activities for glucuronidation. Arch Toxicol (Accompanying manuscript)
Denison MS, Nagy SR (2003) Activation of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor by structurally diverse exogenous and endogenous chemicals. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 43:309–334
Donauer J, Schreck I, Liebel U et al (2011) Role and interaction of p53, BAX and the stress-activated protein kinases p38 and JNK in benzo(a)pyrene-diolepoxide induced apoptosis in human colon carcinoma cells. Arch Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-011-0757-3
EFSA (2011) European food safety authority: scientific opinion on the risks for animal and public health related to the presence of Alternaria toxins in feed and food. EFSA J 9:2407–2503. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2011.2407
Fehr M, Pahlke G, Fritz J et al (2009) Alternariol acts as a topoisomerase poison, preferentially affecting the IIalpha isoform. Mol Nutr Food Res 53:441–451
Hankinson O (1979) Single-step selection of clones of a mouse hepatoma line deficient in aryl hydrocarbon hydroxylase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76:373–376
Kolluri SK, Weiss C, Koff A, Gottlicher M (1999) p27(Kip1) induction and inhibition of proliferation by the intracellular Ah receptor in developing thymus and hepatoma cells. Genes Dev 13:1742–1753
Lehmann L, Wagner J, Metzler M (2006) Estrogenic and clastogenic potential of the mycotoxin alternariol in cultured mammalian cells. Food Chem Toxicol 44:398–408
Liu GT, Qian YZ, Zhang P et al (1991) Relationships between Alternaria alternata and oesophageal cancer. IARC scientific publications, Lyon, pp 258–262
Nguyen LP, Bradfield CA (2008) The search for endogenous activators of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Chem Res Toxicol 21:102–116
Oesch-Bartlomowicz B, Huelster A, Wiss O et al (2005) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor activation by cAMP vs. dioxin: divergent signaling pathways. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9218–9223
Pfeiffer E, Schebb NH, Podlech J, Metzler M (2007a) Novel oxidative in vitro metabolites of the mycotoxins alternariol and alternariol methyl ether. Mol Nutr Food Res 51:307–316
Pfeiffer E, Eschbach S, Metzler M (2007b) Alternaria toxins: DNA strand-breaking activity in mammalian cells in vitro. Mycotoxin Res 23:152–157
Pfeiffer E, Burkhardt B, Altemöller M, Podlech J, Metzler M (2008) Activities of human recombinant cytochrome P450 isoforms and human hepatic microsomes for the hydroxylation of Alternaria toxins. Mycotoxin Res 24:117–123
Schreck I, Chudziak D, Schneider S et al (2009) Influence of aryl hydrocarbon- (Ah) receptor and genotoxins on DNA repair gene expression and cell survival of mouse hepatoma cells. Toxicology 259:91–96
Wahl M, Guenther R, Yang L et al (2010) Polybrominated diphenyl ethers and arylhydrocarbon receptor agonists: Different toxicity and target gene expression. Toxicol Lett 198:119–126
Weiss C, Kolluri SK, Kiefer F, Gottlicher M (1996) Complementation of Ah receptor deficiency in hepatoma cells: negative feedback regulation and cell cycle control by the Ah receptor. Exp Cell Res 226:154–163
Weiss C, Faust D, Durk H et al (2005) TCDD induces c-jun expression via a novel Ah (dioxin) receptor-mediated p38-MAPK-dependent pathway. Oncogene 24:4975–4983
Weiss C, Faust D, Schreck I et al (2008) TCDD deregulates contact inhibition in rat liver oval cells via Ah receptor, JunD and cyclin A. Oncogene 27:2198–2207
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schreck, I., Deigendesch, U., Burkhardt, B. et al. The Alternaria mycotoxins alternariol and alternariol methyl ether induce cytochrome P450 1A1 and apoptosis in murine hepatoma cells dependent on the aryl hydrocarbon receptor. Arch Toxicol 86, 625–632 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0781-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-011-0781-3