Abstract
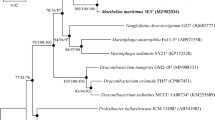
An aerobic, Gram-stain-negative, rod-shaped bacterium with flagellum, designated L22T, was isolated from sediment of Hulun Lake, Inner Mongolia, China. The organism was found to grow optimally at 30° C in a medium containing 0–0.75% (w/v) NaCl at pH 7.5. The major fatty acid identified was summed feature 8 (C18:1ω7c). The dominant polar lipids were phosphomonoester, phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylglycerol and phosphatidylcholine. The main respiratory quinone was Q-10. The draft genome sequence of strain L22T consisted of 4354,788 bp. The G + C content of genomic DNA was 69.8 mol %. The 16S rRNA gene sequences indicated that strain L22T was affiliated with the genus Methylobrevis within the family Pleomorphomonadaceae, being most closely related to Methylobrevis pamukkalensis JCM 30229T with 95.9% 16S rRNA gene sequences similarity. The AAI, ANI and dDDH values between strain L22T and M. pamukkalensis JCM 30229T were 72.5%, 80.7% and 22.7%. Based on taxonomic results in this study, we proposed that strain L22T a novel species in the genus Methylobrevis of the family Pleomorphomonadaceae, for which the name Methylobrevis albus sp. nov. is proposed. The type strain is L22T (=KCTC 72858T=MCCC 1H00432T).


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- KCTC :
-
Korean Collection for Type Cultures
- MCCC :
-
Marine Culture Collection of China
- MEGA :
-
Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis
- HPLC :
-
High-performance liquid chromatography
- TLC :
-
Thin-layer chromatography
- JCM :
-
Japan Collection of Microorganisms
References
Athalye M, Noble WC, Minnikin DE (2010) Analysis of cellular fatty acids by gas chromatography as a tool in the identification of medically important coryneform bacteria. J Appl Bacteriol 58:507–512
Aziz RK, Bartels D, Best AA, DeJongh M, Disz T, Edwards RA, Formsma K, Gerdes S, Glass EM, Kubal M, Meyer F, Olsen GJ, Olson R, Osterman AL, Overbeek RA, McNeil LK, Paarmann D, Paczian T, Parrello B, Pusch GD, Reich C, Stevens R, Vassieva O, Vonstein V, Wilke A, Zagnitko O (2008) The RAST server: rapid annotations using subsystems technology. BMC Genomics 9:75
Bowman JP (2000) Description of Cellulophaga algicola sp. nov., isolated from the surfaces of Antarctic algae, and reclassification of Cytophaga uliginosa (ZoBell and Upham 1944) Reichenbach 1989 as Cellulophaga uliginosa comb. nov. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 50:1861–1868
Chun J, Lee I, Kim YO, Park SC (2015) OrthoANI: an improved algorithm and software for calculating average nucleotide identity. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 66:1100
CLSI (2018) Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing, 28th edn. Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Wayne, PA
Cowan ST, Steel KJ (1974) Bacterial Characters and Characterization, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK
Cowan ST, Steel KJ, Mccoy E (1966) Manual for the identification of medical bacteria. Proc R Soc Med 59:468
Felsenstein J (1981) Evolutionary trees from DNA sequences: a maximum likelihood approach. J Mol Evol 17:368–376
Goris J, Konstantinidis KT, Klappenbach JA, Coenye T, Vandamme P, Tiedje JM (2007) DNA-DNA hybridization values and their relationship to whole-genome sequence similarities. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57:81–91
Hördt A, López MG, Meier-Kolthoff JP, Schleuning M, Lisa-Maria W, Tindall BJ, Gronow S, Kyrpides NC, Woyke T, Göker M (2020) Analysis of 1,000+ type-strain genomes substantially improves taxonomic classification of Alphaproteobacteria. Front Microbiol 11:468
Ivica L, Peer B (2019) Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res 47(W1):W256–W259. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz239
Kanehisa M, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M (2016) KEGG as a reference resource for gene and protein annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 44(1):457–462
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2012) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–772. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.038075-0
Kim D, Kang K, Tae-Young A (2017) Chthonobacter albigriseus gen. nov. sp. nov., Isolated from Grass-field Soil in Korea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(4):883–888
Letunic I, Bork P (2019) Interactive Tree Of Life (iTOL) v4: recent updates and new developments. Nucleic Acids Res 47(1):256–259
Li R, Yu C, Li Y, Lam TW, Yiu SM, Kristiansen K, Wang J (2009) SOAP2: an improved ultrafast tool for short read alignment. Bioinformatics 25:1966–1967
Liu QQ, Li XL, Rooney AP, Du ZJ, Chen GJ (2014) Tangfeifania diversioriginum gen. nov., sp. nov., a representative of the family Draconibacteriaceae. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3473–3477
Luke S (2002) Two fast tree-creation algorithms for genetic programming. IEEE Trans Evol Comput 4:274–283
Lv H, Masuda S, Fujitani Y, Sahin N, Tani A (2017) Oharaeibacter diazotrophicus gen. nov., sp. nov., a diazotrophic and facultatively methylotrophic bacterium, isolated from rice rhizosphere. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67(3):576–582
Meier-Kolthoff JP, Auch AF, Klenk HP, Göker M (2013) Genome sequence-based species delimitation with confidence intervals and improved distance functions. BMC Bioinformatics 14:60
Minnikin DE, Donnell AGO, Goodfellow M, Alderson G, Athalye M, Schaal A, Parlett JH (1984) An integrated procedure for the extraction of bacterial isoprenoid quinones and polar lipids. J Microbiol Methods 2:233–241
Ok-Sun K, Yong-Joon C, Lee K, Seok-Hwan Y, Kim M, Na H, Sang-Cheol P, Jeon YS, Jae-Hak L, Yi H, Won S, Chun J (2011) Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 62:716–721
Poroshina MN, Trotsenko YA, Doronina NV (2015) Methylobrevis pamukkalensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a halotolerant restricted facultative methylotroph isolated from saline water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 65:1321–1327
Robert C (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32(5):1792–1797
Rodriguez-R LM, Konstantinidis KT (2014) Bypassing cultivation to identify bacterial species. Microbe 9:111–118
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol BiolEvol 4:406–425
Schäfer H (2007) Isolation of Methylophaga spp. from marine dimethylsulfide-degrading enrichment cultures and identification of polypeptides induced during growth on dimethylsulfide. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:2580–2591
Suarez C, Ratering S, Geissler-Plaum R, Schnell S (2014) Hartmannibacter diazotrophicus gen. nov., sp. nov., a phosphate-solubilizing and nitrogen-fixing alphaproteobacterium isolated from the rhizosphere of a natural salt-meadow plant. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 64:3160–3167
Sudhir K, Glen S, Koichiro T (2016) MEGA7: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version for bigger datasets. Mol Biol Evol 33(7):e1887
Trifinopoulos J, Nguyen LT, vonHaeseler A, Minh BQ (2016) W-IQ-TREE: a fast online phylogenetic tool for maximum likelihood analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 44(1):232–235
Xi J, Wang Y, Yang X et al (2017) Mongoliimonas terrestris gen. nov., sp. nov., isolated from desert soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 67:3010–3014
Xie CH, Yokota A (2005) Pleomorphomonas oryzae gen. nov., sp. nov., a nitrogen-fixing bacterium isolated from paddy soil of Oryza sativa. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 55:1233–1237
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 32070002 and Grant No. 31770002) and the National Science and Technology Fundamental Resources Investigation Program of China (Grant No. 2019FY100700).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
The GenBank accession number for the 16S rRNA gene sequence of Methylobrevis albus L22T is MW195049 and the draft genome has been deposited in GenBank under the accession number JADZLT000000000.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zou, QH., Feng, X., Wang, TJ. et al. Methylobrevis albus sp. nov., isolated from freshwater lake sediment. Arch Microbiol 203, 4549–4556 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02442-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02442-z