Abstract
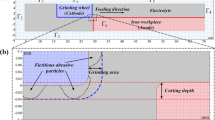
Surface quality of workpiece could be significantly improved by ELID grinding. However, ELID grinding bearing outer ring raceway with small inner diameter has small space, which limits installation of electrode. In this work, ELID grinding bearing outer ring raceway acting as cathode is proposed. But electric spark discharge will occur in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode, which affects grinding quality. The purpose of this work is to investigate formation mechanism of electric spark discharge and influence of oxide layer on grinding quality. A novel experimental method is proposed to study state of oxide layer (mainly thickness and compactness) in ELID grinding bearing outer ring raceway with workpiece-cathode. Experimental results show that electric spark discharge occurs with thick oxide layer (characterized by control current), resulting in corroded pits on surface of oxide layer and workpiece in ELID grinding with workpiece-cathode. With increased control current, surface of oxide layer becomes smooth. Moreover, grinding force increases with increased control current. When control current is 0.5 A, surface roughness of workpiece is the largest. And surface roughness of workpiece increases with increased control current, as control current is greater than or equal to 1 A. The results are helpful to apply ELID to grind bearing outer ring raceway and improve ELID grinding performance.















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- E :
-
Voltage of power supply
- R p :
-
Resistance of protective resistance
- R s :
-
Resistance of matrix of wheel
- R o :
-
Resistance of oxide layer
- R w :
-
Resistance of workpiece
- I :
-
Current
- R :
-
Resistance of material
- E 1 :
-
Electric field intensity
- φ :
-
Scalar potential
- ρ :
-
Resistivity of material
- L :
-
Length of material
- S :
-
Sectional area of material
- ρ o :
-
Resistivity of oxide layer
- h :
-
Thickness of oxide layer
- S o :
-
Sectional area of oxide layer
- d :
-
Gap between anode and cathode
- ρ 1 :
-
Density of the charge body
- ε :
-
Dielectric constant of medium
References
Kim H-G, Lee J-Y, Jin Kim H (2018) Look angle constrained impact angle control guidance law for homing missiles with bearings-only measurements. IEEE T Aero Elec Syst 54(6):3096–3107
Wu MY, Gao H (2016) Experimental study on large size bearing ring raceways’ precision polishing with abrasive flowing machine (AFM) method. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 83(9-12):1927–1935
Ohmori H, Nakagawa T (1990) Mirror surface grinding of silicon wafer with electrolytic in-process dressing. Ann CIRP 39(1):329–332
Ding WF, Li HN, Zhang LC et al (2017) Diamond wheel dressing: a comprehensive review. J Manuf Sci E-T ASME 139(12):1–25
Li J (2005) Mechanisms of sawing of Bk7 glass by electrolytic in-process dressing. J Mater Process Technol 168(3):377–389
Ohmori H, Marinescu ID, Katahira K (2011) Electrolytic in-process dressing (Elid) technologies: Fundamentals and Applications. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Kuai JC, Ardashev DV, Zhang HL (2017) Study of alpha-Fe2O3 formation and its measurement in oxide films of wheel surface during ELID grinding process. Mod Phys Lett B 31(4):1–9
Biswas I, Kumar AS, Rahman M (2010) A study on the equilibrium condition of the oxide layer in ELID grinding. Int J Abras Technol 3(1):25–36
Kim HY, Ahn JH, Seo YH, Paik IH (2001) In-process measurement of ELID grinding status thickness of insulating layer. KSME Int J 15(9):1268–1273
Wang ZQ, Ren CZ, Chen G et al (2018) A comparative study on state of oxide layer in ELID grinding with tool-cathode and workpiece-cathode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(1-4):1299–1307
Yang LJ, Ren CZ, Jin XM (2010) Experimental study of ELID grinding based on the active control of oxide layer. J Mater Process Technol 210:1748–1753
Zhang KF, Ren CZ, Yang LJ, Jin XM, Li QF (2013) Precision grinding of bearing steel based on active control of oxide layer state with electrolytic interval dressing. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 65:411–419
Yuan LW, Ren CZ, Shu Z (2006) Research on state change of passivation layer in ELID ultraprecision mirror grinding. Aviat Precis Manuf Technol 42(1):5–8
Zhou H, Ding W, Liu C (2019) Material removal mechanism of PTMCs in high-speed grinding when considering consecutive action of two abrasive grains. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 100:153–165
Xi X, Yu T, Ding W et al (2018) Grinding of Ti2AlNb intermetallics using silicon carbide and alumina abrasive wheels: tool surface topology effect on grinding force and ground surface quality. Precis Eng 53:134–145
Tang H, Deng ZH, Guo YS et al (2015) Depth-of-cut errors in ELID surface grinding of zirconia-based ceramics (Article). Int J Mach Tool Manu 88:34–41
Zhang CH, Ohmori H, Kato T et al (2001) Evaluation of surface characteristics of ground CVD-SiC using cast iron bond diamond wheels. Precis Eng 25:56–62
Huang ST, Yu XL (2018) A study of grinding forces of SiCp/Al composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 94(9-12):3633–3639
Yu XL, Huang ST, Xu LF (2016) ELID grinding characteristics of SiCp/Al composites. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 86(5-8):1165–1171
Zhao QL, Guo B (2015) Ultra-precision grinding of optical glasses using mono-layer nickel electroplated coarse-grained diamond wheels. Part 1: ELID assisted precision conditioning of grinding wheels. Precis Eng 39:56–56
Wu ML, Ren CZ, Zhang KF (2018) Wear life characterization of the grinding wheel for electrolytic in-process dressing (ELID) grinding of ball bearing raceways: a new perspective based on a moving normal distribution curve of the grit state variation. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 96(5-8):1919–1928
Wu ML, Ren CZ, Zhang KF (2015) ELID groove grinding of ball-bearing raceway and the accuracy durability of the grinding wheel. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 79:1721–1731
Wu ML, Zhang KF, Ren CZ (2015) Study on the non-uniform contact during ELID groove grinding. Precis Eng 39:116–124
Qian J, Li W, Ohmori H (2000) Cylindrical grinding of bearing steel with electrolytic in-process dressing. Precis Eng 24(2):153–159
Qian J, Ohmori H, Lin W (2001) Internal mirror grinding with a metal/metal–resin bonded abrasive wheel. Int J Mach Tool Manu 41(2):193–208
Biswas I (2009) Fundamental studies on wheel wear in Elid grinding. Doctorate dissertation, National university of Singapore
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge to the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Contract no. 51675377) and Tianjin application foundation and advanced technology research project (Contract No.15JCZDJC39500 & No.18JCZDJC10050) for providing the financial support to complete this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Ren, C., Chen, G. et al. Influence of oxide layer on grinding quality in ELID grinding bearing outer ring raceway with workpiece-cathode. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 105, 3045–3056 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04475-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-019-04475-7