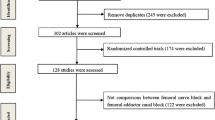
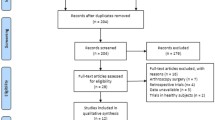
Abstract
Purpose
Femoral nerve blocks (FNBs) provide effective analgesia after total knee arthroplasty, but have been associated with quadriceps weakness. Adductor canal block (ACB) is a promising alternative option that delivers a primarily sensory blockade. The aim of this study was to determine whether ACB provides superior quadriceps strength and similar pain control than FNB.
Methods
A systematic search of PubMed, the Cochrane Library, EMBASE and Web of Science was conducted without publication data or language restriction. Comparative studies comparing ACB with FNB were included. Two authors independently assessed data extraction and quality of the studies.
Results
Nine studies with 639 patients were identified. Results of meta-analysis showed that compared with FNB, ACB preserved quadriceps muscle strength better than FNB [MD24h = 1.14, 95 % CI (0.38, 1.91), p < 0.01; MD48h = 0.40, 95 % CI (0.16, 0.64), p < 0.01], while there were no significant differences in pain score during rest at 24 h [SMD = − 0.04, 95 % CI (−0.17, 0.26); n.s] or 48 h [SMD = − 0.10, 95 % CI (−0.27, 0.08); n.s], pain score during activity at 24 h [SMD = 0.13, 95 % CI (−0.36, 0.62); n.s] or 48 h [SMD = − 0.13, 95 % CI (−0.37, 0.12); n.s], opioid consumption at 24 h [SMD = − 0.01, 95 % CI (−1.68, 1.66); n.s] or 48 h [SMD = − 0.92, 95 % CI (−6.86, 5.01); n.s], length of hospital stay [MD = 0.05, 95 % CI (−0.91, 1.00); n.s] and nausea or vomiting [RR = 1.17, 95 % CI (0.62, 2.20); n.s] between ACB and FNB.
Conclusions
ACB preserved the strength of quadriceps more than FNB and achieves similar analgesic effects in post-operative pain.
Level of evidence
Level III.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Feibel RJ, Dervin GF, Kim PR, Beaule PE (2009) Major complications associated with femoral nerve catheters for knee arthroplasty: a word of caution. J Arthroplasty 24:132–137
Fowler SJ, Symons J, Sabato S, Myles PS (2008) Epidural analgesia compared with peripheral nerve blockade after major knee surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized trials. Br J Anaesth 100:154–164
Grevstad U, Mathiesen O, Valentiner LS, Jaeger P, Hilsted KL, Dahl JB (2015) Effect of adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block on quadriceps strength, mobilization, and pain after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, blinded study. Reg Anesth Pain Med 40:3–10
Grosu I, Lavand’homme P, Thienpont E (2014) Pain after knee arthroplasty: an unresolved issue. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 22:1744–1758
Jaeger P, Nielsen ZJ, Henningsen MH, Hilsted KL, Mathiesen O, Dahl JB (2013) Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block and quadriceps strength: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study in healthy volunteers. Anesthesiology 118:409–415
Jaeger P, Zaric D, Fomsgaard JS, Hilsted KL, Bjerregaard J, Gyrn J, Mathiesen O, Larsen TK, Dahl JB (2013) Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block for analgesia after total knee arthroplasty: a randomized, double-blind study. Reg Anesth Pain Med 38:526–532
Jiang J, Teng Y, Fan Z, Khan MS, Cui Z, Xia Y (2013) The efficacy of periarticular multimodal drug injection for postoperative pain management in total knee or hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 28:1882–1887
Johnson RL, Kopp SL, Hebl JR, Erwin PJ, Mantilla CB (2013) Falls and major orthopaedic surgery with peripheral nerve blockade: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Anaesth 110:518–528
Kim DH, Lin Y, Goytizolo EA, Kahn RL, Maalouf DB, Manohar A, Patt ML, Goon AK, Lee YY, Ma Y, Yadeau JT (2014) Adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block for total knee arthroplasty: a prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Anesthesiology 120:540–550
Liu Y, Zhang YZ, Tan Z, Liao R, Shen B (2014) Comparison of postoperative analgesia between ultrasound guided adductor canal block and femoral nerve block in patients after total knee arthroplasty. West China Med J 29:2231–2235
Lund J, Jenstrup MT, Jaeger P, Sorensen AM, Dahl JB (2011) Continuous adductor-canal-blockade for adjuvant post-operative analgesia after major knee surgery: preliminary results. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 55:14–19
Manickam B, Perlas A, Duggan E, Brull R, Chan VW, Ramlogan R (2009) Feasibility and efficacy of ultrasound-guided block of the saphenous nerve in the adductor canal. Reg Anesth Pain Med 34:578–580
Memtsoudis SG, Dy CJ, Ma Y, Chiu YL, Della Valle AG, Mazumdar M (2012) In-hospital patient falls after total joint arthroplasty: incidence, demographics, and risk factors in the United States. J Arthroplasty 27(823–828):e821
Memtsoudis SG, Yoo D, Stundner O, Danninger T, Ma Y, Poultsides L, Kim D, Chisholm M, Jules-Elysee K, Valle AG, Sculco TP (2015) Subsartorial adductor canal vs femoral nerve block for analgesia after total knee replacement. Int Orthop 39:673–680
Mudumbai SC, Kim TE, Howard SK, Workman JJ, Giori N, Woolson S, Ganaway T, King R, Mariano ER (2014) Continuous adductor canal blocks are superior to continuous femoral nerve blocks in promoting early ambulation after TKA. Clin Orthop Relat Res 472:1377–1383
Oxford Center for Evidence-Based Medicine, Oxford. www.cebm.net
Patterson ME, Bland KS, Thomas LC, Elliott CE, Soberon JR Jr, Nossaman BD, Osteen K (2015) The adductor canal block provides effective analgesia similar to a femoral nerve block in patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective study. J Clin Anesth 27:39–44
Paul JE, Arya A, Hurlburt L, Cheng J, Thabane L, Tidy A, Murthy Y (2010) Femoral nerve block improves analgesia outcomes after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology 113:1144–1162
Pelt CE, Anderson AW, Anderson MB, Van Dine C, Peters CL (2014) Postoperative falls after total knee arthroplasty in patients with a femoral nerve catheter: can we reduce the incidence? J Arthroplasty 29:1154–1157
Shah NA, Jain NP (2014) Is continuous adductor canal block better than continuous femoral nerve block after total knee arthroplasty? Effect on ambulation ability, early functional recovery and pain control: a randomized controlled trial. J Arthroplasty 29:2224–2229
Zhang W, Hu Y, Tao Y, Liu X, Wang G (2014) Ultrasound-guided continuous adductor canal block for analgesia after total knee replacement. Chin Med J (Engl) 127:4077–4081
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, D., Ma, Gg. Analgesic efficacy and quadriceps strength of adductor canal block versus femoral nerve block following total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 24, 2614–2619 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3874-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3874-3