Abstract
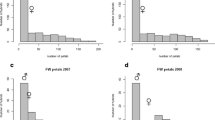
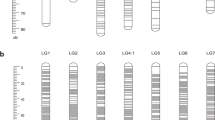
We have constructed the first integrated consensus map (ICM) for rose, based on the information of four diploid populations and more than 1,000 initial markers. The single population maps are linked via 59 bridge markers, on average 8.4 per linkage group (LG). The integrated map comprises 597 markers, 206 of which are sequence-based, distributed over a length of 530 cM on seven LGs. By using a larger effective population size and therefore higher marker density, the marker order in the ICM is more reliable than in the single population maps. This is supported by a more even marker distribution and a decrease in gap sizes in the consensus map as compared to the single population maps. This unified map establishes a standard nomenclature for rose LGs, and presents the location of important ornamental traits, such as self-incompatibility, black spot resistance (Rdr1), scent production and recurrent blooming. In total, the consensus map includes locations for 10 phenotypic single loci, QTLs for 7 different traits and 51 ESTs or gene-based molecular markers. This consensus map combines for the first time the information for traits with high relevance for rose variety development. It will serve as a tool for selective breeding and marker assisted selection. It will benefit future efforts of the rose community to sequence the whole rose genome and will be useful for synteny studies in the Rosaceae family and especially in the section Rosoideae.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biber A, Kaufmann H, Linde M, Spiller M, Terefe D, Debener T (2010) Microsatellite markers from a BAC contig spanning the Rdr1 locus: a tool for marker assisted selection in roses. Theor Appl Genet 120:765–773
Brondani RPV, Williams ER, Brondani C, Grattapaglia D (2006) A microsatellite-based consensus linkage map for species of Eucalyptus and a novel set of 230 microsatellite markers for the genus. BMC Plant Biol 6:20
Byrne DH (2009) Genetics and genomics of Rosaceae, rose structural genomics. In: Folta KM, Gardiner SE (eds) Plant genetics and genomics: crops and models. Springer, Berlin, pp 357–383
Cregan PB, Jarvik T, Bush AL, Shoemaker RC, Lark KG, Kahler AL, Kaya N, VanToai TT, Lohnes DG, Chung L, Specht JE (1999) An integrated genetic linkage map of the soybean genome. Crop Sci 39:1464–1490
Crespel L, Chirollet M, Durel CE, Zhang D, Meynet J, Gudin S (2002) Mapping of qualitative and quantitative phenotypic traits in Rosa using AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:1207–1214
Debener T, Mattiesch L (1999) Construction of a genetic linkage map for roses using RAPD and AFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 99:891–899
Debener T, Linde M (2009) Exploring complex ornamental genomes: the rose as a model plant. Crit Rev Plant Sci 28:267–280
Debener T, Mattiesch L, Vosman B (2001) A molecular marker map for roses. Acta Hortic 547:582–587
Debener T, Bretzke M, Spiller M, Linde M, Kaufmann H, Berger RG, Krings U (2010) Genetic and molecular analyses of key loci involved in self incompatibility and floral scent in roses. Acta Hortic 870:183–190
Dirlewanger E, Graziano E, Joobeur T, Garriga-Caldere F, Cosson P, Howad W, Arus P (2004) Comparative mapping and marker-assisted selection in Rosaceae fruit crops. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9891–9896
Doligez A, Adam-Blondon AF, Cipriani G, Laucou V, Merdinoglu D, Meredith CP, Riaz S, Roux C, This P, Di Gaspero G (2006) An integrated SSR map of grapevine based on five mapping populations. Theor Appl Genet 113:369–382
Dugo ML, Satovic Z, Millan T, Cubero JI, Rubiales D, Cabrera A, Torres AM (2005) Genetic mapping of QTLs controlling horticultural traits in diploid roses. Theor Appl Genet 111:511–520
Ferreira A, da Silva MF, Silva LDCE, Cruz CD (2006) Estimating the effects of population size and type on the accuracy of genetic maps. Gen Mol Biol 29:187–192
Hattendorf A, Linde M, Kaufmann H, Debener T (2004) Genetic analysis of rose resistance genes and their localisation in the rose genome. Acta Hortic 651:123–130
Hess G, Scheuring D, Byrne D, Zhang D (2007) Towards positional cloning of the everblooming gene in plants: a BAC library of Rosa chinensis cv. Old Blush. Acta Hortic 751:169–174
Hibrand-Saint Oyant L, Crespel L, Rajapakse S, Zhang L, Foucher F (2008) Genetic linkage maps of rose constructed with new microsatellite markers and locating QTL controlling flowering traits. Tree Genet Genomes 4:11–23
Huhn M, Piepho HP (2008) A note on the bias of genetic distances in linkage maps based on small samples for backcrosses and intercrosses with complete dominance. Genome 51:1054–1061
Isobe S, Kolliker R, Hisano H, Sasamoto S, Wada T, Klimenko I, Okumura K, Tabata S (2009) Construction of a consensus linkage map for red clover (Trifolium pratense L.). BMC Plant Biol 9:57
Kaufmann H, Mattiesch L, Lorz H, Debener T (2003) Construction of a BAC library of Rosa rugosa Thunb. and assembly of a contig spanning Rdr1, a gene that confers resistance to black spot. Mol Genet Genomics 268:666–674
Kiani M, Zamani Z, Khalighi A, Fatahi R, Byrne DH (2008) Wide genetic diversity of Rosa damascena Mill. germplasm in Iran as revealed by RAPD analysis. Sci Hortic 115:386–392
Kitahara K, Matsumoto S (2000) Rose MADS-box genes ‘MASAKO C1 and D1’ homologous to class C floral identity genes. Plant Sci 151:121–134
Koning-Boucoiran CFS, Dolstra O, van der Linden CG, Van der Schoot J, Gitonga VW, Verlinden K, Maliepaard CA, Krens FA (2009) Specific mapping of disease resistance genes in tetraploid cut roses. Acta Hortic 836:137–142
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Linde M, Hattendorf A, Kaufmann H, Debener T (2006) Powdery mildew resistance in roses: QTL mapping in different environments using selective genotyping. Theor Appl Genet 113:1081–1092
Lombard V, Delourme R (2001) A consensus linkage map for rapeseed (Brassica napus L.): construction and integration of three individual maps from DH populations. Theor Appl Genet 103:491–507
Mace ES, Rami JF, Bouchet S, Klein PE, Klein RR, Kilian A, Wenzl P, Xia L, Halloran K, Jordan DR (2009) A consensus genetic map of sorghum that integrates multiple component maps and high-throughput Diversity Array Technology (DArT) markers. BMC Plant Biol 9:13
Mantovani P, van der Linden CG, Maccaferri M, Sanguineti MC, Tuberosa R (2006) Nucleotide-binding site (NBS) profiling of genetic diversity in durum wheat. Genome 49:1473–1480
Meynet J, Barrade R, Duclos A, Siadous R (1994) Dihaploid plants of roses (Rosa × hybrida, Cv Sonia) obtained by parthenogenesis induced using irradiated pollen and in vitro culture of immature seeds. Agronomie 14:169–175
Mibus H, Serek M (2005) An easy PCR method to isolate unknown ACC synthase genes in ornamental plant species. Acta Hortic 682:307–312
N’Diaye A, Van de Weg WE, Kodde LP, Koller B, Dunemann F, Thiermann M, Tartarini S, Gennari F, Durel CE (2008) Construction of an integrated consensus map of the apple genome based on four mapping populations. Tree Genet Genomes 4:727–743
Orita M, Suzuki Y, Sekiya T, Hayashi K (1989) Rapid and sensitive detection of point mutations and DNA polymorphisms using the polymerase chain-reaction. Genomics 5:874–879
Pelgas B, Beauseigle S, Achere V, Jeandroz S, Bousquet J, Isabel N (2006) Comparative genome mapping among Picea glauca, P. mariana × P. rubens and P. abies, and correspondence with other Pinaceae. Theor Appl Genet 113:1371–1393
Rajapakse S, Byrne DH, Zhang L, Anderson N, Arumuganathan K, Ballard RE (2001) Two genetic linkage maps of tetraploid roses. Theor Appl Genet 103:575–583
Remay A, Lalanne D, Thouroude T, Le CF, Hibrand-Saint Oyant L, Foucher F (2009) A survey of flowering genes reveals the role of gibberellins in floral control in rose. Theor Appl Genet 119:767–781
Saal B, Wricke G (2002) Clustering of amplified fragment length polymorphism markers in a linkage map of rye. Plant Breed 121:117–123
Sargent DJ, Cipriani G, Vilanova S, Gil-Ariza D, Arús P, Simpson DW, Tobutt KR, Monfort A (2008) The development of a bin mapping population and the selective mapping of 103 markers in the diploid Fragaria reference mapping population FV×FN. Genome 51:120–127
Sargent DJ, Marchese A, Simpson DW, Howad W, Fernandez-Fernandez F, Monfort A, Arus P, Evans KM, Tobutt KR (2009) Development of “universal” gene-specific markers from Malus spp. cDNA sequences, their mapping and use in synteny studies within Rosaceae. Tree Genet Genomes 5:133–145
Schuelke M (2000) An economic method for the fluorescent labeling of PCR fragments. Nat Biotechnol 18:233–234
Sewell MM, Sherman BK, Neale DB (1999) A consensus map for loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). I. Construction and integration of individual linkage maps from two outbred three-generation pedigrees. Genetics 151:321–330
Shupert DA, Byrne DH, Pemberton HB (2007) Inheritance of flower traits, leaflet number and prickles in roses. Acta Hortic 751:331–335
Spiller M, Berger RG, Debener T (2010) Genetic dissection of scent metabolic profiles in diploid rose populations. Theor Appl Genet 120:1461–1471
Stam P (1993) Construction of integrated genetic-linkage maps by means of a new computer package—Joinmap. Plant J 3:739–744
Terefe D, Debener T (2010) An SSR from the LRR region of the rose Rdr1 gene family is a useful RGA marker for roses and other Rosaceae. Plant Breed. doi:10.1111/j.1439-0523.2010.01780
Van der Linden CG, Wouters DCAE, Mihalka V, Kochieva EZ, Smulders MJM, Vosman B (2004) Efficient targeting of plant disease resistance loci using NBS profiling. Theor Appl Genet 109:384–393
Van Ooijen JW (2006) JoinMap 4, Software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps in experimental populations. Kyazma B. V, Wageningen
Vezzulli S, Troggio M, Coppola G, Jermakow A, Cartwright D, Zharkikh A, Stefanini M, Grando MS, Viola R, Adam-Blondon AF, Thomas M, This P, Velasco R (2008) A reference integrated map for cultivated grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) from three crosses, based on 283 SSR and 501 SNP-based markers. Theor Appl Genet 117:499–511
Vilanova S, Sargent DJ, Arús P, Monfort A (2008) Synteny conservation between two distantly-related Rosaceae genomes: Prunus (the stone fruits) and Fragaria (the strawberry). BMC Plant Biol 8:67
Von Malek B, Debener T (1998) Genetic analysis of resistance to black spot (Diplocarpon rosae) in tetraploid roses. Theor Appl Genet 96:228–231
Voorrips RE (2002) MapChart: software for the graphical presentation of linkage maps and QTLs. J Hered 93:77–78
Wenzl P, Li HB, Carling J, Zhou MX, Raman H, Paul E, Hearnden P, Maier C, Xia L, Caig V, Ovesna J, Cakir M, Poulsen D, Wang JP, Raman R, Smith KP, Muehlbauer GJ, Chalmers KJ, Kleinhofs A, Huttner E, Kilian A (2006) A high-density consensus map of barley linking DArT markers to SSR, RFLP and STS loci and agricultural traits. BMC Genomics 7:206
Whitaker VM, Bradeen JM, Debener T, Biber A, Hokanson SC (2010) Rdr3, a novel locus conferring black spot disease resistance in tetraploid rose: genetic analysis, LRR profiling, and SCAR marker development. Theor Appl Genet 120:573–585
Yan Z, Denneboom C, Hattendorf A, Dolstra O, Debener T, Stam P, Visser PB (2005) Construction of an integrated map of rose with AFLP, SSR, PK, RGA, RFLP, SCAR and morphological markers. Theor Appl Genet 110:766–777
Zhang LH, Byrne DH, Ballard RE, Rajapakse S (2006) Microsatellite marker development in rose and its application in tetraploid mapping. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 131:380–387
Acknowledgments
This study has been carried out in part with financial support from the Netherlands Ministry of Agriculture, Nature and Food Safety (KB-01) and from the Commission of the European Community [QLRT-2001-01278, Genetic evaluation of European rose resources for conservation and horticultural use (Generose)]. This study does not necessarily reflect the Commission’s views and in no way anticipates the Commission’s future policy in this area. Additionally the Basye Endowment for Rose Genetics and the TDA-BARD funded by the Texas-Israel Exchange Fund supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Nybom.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spiller, M., Linde, M., Hibrand-Saint Oyant, L. et al. Towards a unified genetic map for diploid roses. Theor Appl Genet 122, 489–500 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1463-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1463-x