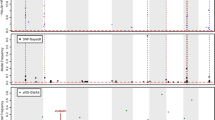
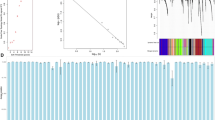
Abstract
Heterosis is a well-known phenomenon but the underlying molecular mechanisms are not yet established. To contribute to the understanding of heterosis at the molecular level, we analyzed genome-wide gene expression profile data of Arabidopsis thaliana in a systems biological approach. We used partial correlations to estimate the global interaction structure of regulatory networks. Our hypothesis states that heterosis comes with an increased number of partial correlations which we interpret as increased numbers of regulatory interactions leading to enlarged adaptability of the hybrids. This hypothesis is true for mid-parent heterosis for our dataset of gene expression in two homozygous parental lines and their reciprocal crosses. For the case of best-parent heterosis just one hybrid is significant regarding our hypothesis based on a resampling analysis. Summarizing, both metabolome and gene expression level of our illustrative dataset support our proposal of a systems biological approach towards a molecular basis of heterosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agilent Technologies Inc. (2008) Agilent feature extraction software: reference guide, 6th edn. USA, G4460-90020
Andorf S, Gärtner T, Steinfath M, Witucka-Wall H, Altmann T, Repsilber D (2009) Towards systems biology of heterosis: a hypothesis about molecular network structure applied for the arabidopsis metabolome. EURASIP J Bioinform Syst Biol 147157
Backes C, Keller A, Kuentzer J, Kneissl B, Comtesse N, Elnakady YA, Müller R, Meese E, Lenhof HP (2007) Genetrail—advanced gene set enrichment analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 35(Web Server issue):W186–W192
Barabási AL, Oltvai ZN (2004) Network biology: understanding the cell’s functional organization. Nat Rev Genet 5(2):101–113
Benjamini Y, Hochberg Y (1995) Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J R Stat Soc Series B Stat Methodol 57(1):289–300
Birchler JA, Auger DL, Riddle NC (2003) In search of the molecular basis of heterosis. Plant Cell 15:2236–2239
Bruce AB (1910) The mendelian theory of heredity and the augmentation of vigor. Science 32(827):627–628
Butte AJ, Tamayo P, Slonim D, Golub TR, Kohane IS (2000) Discovering functional relationships between RNA expression and chemotherapeutic susceptibility using relevance networks. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97(22):12182–12186
Crow JF (1952) Heterosis. In: Dominance and overdominance. Iowa State College Press, Ames, pp 282–297
Draghici S, Khatri P, Martins RP, Ostermeier GC, Krawetz SA (2003) Global functional profiling of gene expression. Genomics 81(2):98–104
East EM (1936) Heterosis. Genetics 21(4):375–397
Frisch M, Thiemann A, Fu J, Schrag TA, Scholten S, Melchinger AE (2010) Transcriptome-based distance measures for grouping of germplasm and prediction of hybrid performance in maize. Theor Appl Genet (accepted)
Gärtner T, Steinfath M, Andorf S, Lisec J, Meyer RC, Altmann T, Willmitzer L, Selbig J (2009) Improved heterosis prediction by combining information on DNA- and metabolic markers. PLoS One 4(4):e5220
Genoud T, Métraux JP (1999) Crosstalk in plant cell signaling: structure and function of the genetic network. Trends Plant Sci 4(12):503–507
Gentleman RC, Carey VJ, Bates DM, Bolstad B, Dettling M, Dudoit S, Ellis B, Gautier L, Ge Y, Gentry J, Hornik K, Hothorn T, Huber W, Iacus S, Irizarry R, Leisch F, Li C, Maechler M, Rossini AJ, Sawitzki G, Smith C, Smyth G, Tierney L, Yang JY, Zhang J (2004) Bioconductor: open software development for computational biology and bioinformatics. Genome Biol 5:R80
Guo M, Rupe MA, Yang X, Crasta O, Zinselmeier C, Smith OS, Bowen B (2006) Genome-wide transcript analysis of maize hybrids: allelic additive gene expression and yield heterosis. Theor Appl Genet 113(5):831–845
Harrison GA (1962) Heterosis and adaptability in the heat tolerance of mice. Genetics 47(4):427–434
Hartwell LH, Hopfield JJ, Leibler S, Murray AW (1999) From molecular to modular cell biology. Nature 402(SUPP):C47–C52
Kerr MK, Churchill GA (2001) Experimental design for gene expression microarrays. Biostatistics 2(2):183–201
Kerr MK, Martin M, Churchill GA (2000) Analysis of variance for gene expression microarray data. J Comput Biol 7(6):819–837
Lamkey KR, Edwards JW (1999) The quantitative genetics of heterosis. In: Coors JG, Pandey S (eds) The genetics and exploitation of heterosis in crops. ASA, CSSA, and SSSA, Madison, pp 31–48
Lee TI, Rinaldi NJ, Robert F, Odom DT, Bar-Joseph Z, Gerber GK, Hannett NM, Harbison CT, Thompson CM, Simon I, Zeitlinger J, Jennings EG, Murray HL, Gordon DB, Ren B, Wyrick JJ, Tagne JB, Volkert TL, Fraenkel E, Gifford DK, Young RA (2002) Transcriptional regulatory networks in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Science 298(5594):799–804
Li ZK, Luo LJ, Mei HW, Wang DL, Shu QY, Tabien R, Zhong DB, Ying CS, Stansel JW, Khush GS, Paterson AH (2001) Overdominant epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of inbreeding depression and heterosis in rice. I. Biomass and grain yield. Genetics 158:1737–1753
Luo LJ, Li ZK, Mei HW, Shu QY, Tabien R, Zhong DB, Ying CS, Stansel JW, Khush GS, Paterson AH (2001) Overdominant epistatic loci are the primary genetic basis of inbreeding depression and heterosis in rice. II. Grain yield components. Genetics 158:1755–1771
Ma L, Sun N (2005) Organ-specific expression of Arabidopsis genome during development. Plant Physiol 138:80–91
Maynard Smith J (1956) Acclimatization to high temperatures in inbred and outbred Drosophila subobscura. J Genet 54(1):497–505
Melchinger AE, Utz HF, Piepho HP, Zeng ZB, Schön CC (2007) The role of epistasis in the manifestation of heterosis: a systems-orientated approach. Genetics 177:1815–1825
Meyer RC, Törjék O, Becher M, Altmann T (2004) Heterosis of biomass production in arabidopsis. Establsiment during early development. Plant Physiol 134:1813–1823
Milo R, Shen-Orr S, Itzkovitz S, Kashtan N, Chklovskii D, Alon U (2002) Network motifs: simple building blocks of complex networks. Science 298(5594):824–827
Opgen-Rhein R, Strimmer K (2007) From correlation to causation networks: a simple approximate learning algorithm and its application to high-dimensional plant gene expression data. BMC Syst Biol 1:37
Opgen-Rhein R, Schäfer J, Strimmer K (2007) GeneNet: Modeling and Inferring Gene Networks. http://strimmerlab.org/software/genenet/
Parrish RS, Spencer III HJ, Xu P (2009) Distribution modeling and simulation of gene expression data. Comput Stat Data Anal 53(5):1650–1660
R Development Core Team (2008) R: a language and environment for statistical computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. ISBN 3-900051-07-0. http://www.R-project.org
Ritchie ME, Silver J, Oshlack A, Holmes M, Diyagama D, Holloway A, Smyth GK (2007) A comparison of background correction methods for two-colour microarrays. Bioinformatics 23:2700–2707
Robertson FW, Reeve EC (1952) Heterozygosity, environmental variation and heterosis. Nature 170(4320):286
Schäfer J, Strimmer K (2005a) An empirical Bayes approach to inferring large-scale gene association networks. Bioinformatics 21(6):754–764
Schäfer J, Strimmer K (2005b) A shrinkage approach to large-scale covariance matrix estimation and implications for functional genomics. Stat Appl Genet Mol Biol 4:32
Schnell FW, Cockerham CC (1992) Multiplicative vs. arbitrary gene action in heterosis. Genetics 131(2):461–469
Shubik M (1996) Simulations, models and simplicity. Complexity 2(1):60
Shull GH (1908) The composition of a field of maize. Am Breeders Assoc Rep 4:296–301
Shull GH (1952) Beginnings of the heterosis concept. In: Gowen JW (ed) Heterosis: a record of researches directed toward explaining and utilizing the vigor of hybrids. Iowa State College Press, Ames, pp 14–48
Smyth GK (2005) Limma: linear models for microarray data. In: Gentleman R, Carey V, Dudoit S, Irizarry R, Huber W (eds) Bioinformatics and computational biology solutions using R and bioconductor. Springer, New York, pp 397–420
Smyth GK, Speed T (2003) Normalization of cDNA microarray data. Methods 31:265–273
Somogyi R, Sniegoski CA (1996) Modeling the complexity of genetic networks: understanding multigenic and pleiotropic regulation. Complexity 1:45–63
Song R, Messing J (2003) Gene expression of a gene family in maize based on noncollinear haplotypes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:9055–9060
Steinfath M, Gärtner T, Lisec J, Meyer RC, Altmann T, Willmitzer L, Selbig J (2010) Prediction of hybrid biomass in Arabidopsis thaliana by selected parental SNP and metabolic markers. Theor Appl Genet (accepted)
Strimmer K (2008) A unified approach to false discovery rate estimation. BMC Bioinformatics 9:303
Swanson-Wagner RA, Jia Y, DeCook R, Borsuk LA, Nettleton D, Schnable PS (2006) All possible modes of gene action are observed in a global comparison of gene expression in a maize F1 hybrid and its inbred parents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(18):6805–6810
Swarbreck D, Wilks C, Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Garcia-Hernandez M, Foerster H, Li D, Meyer T, Muller R, Ploetz L, Radenbaugh A, Singh S, Swing V, Tissier C, Zhang P, Huala E (2008) The Arabidopsis information resource (TAIR): gene structure and function annotation. Nucleic Acids Res 36(Database issue):D1009–D1014. http://www.arabidopsis.org
The Plant Ontology Consortium (2002) The plant ontology consortium and plant ontologies. Comp Funct Genomics 3:137–142. http://www.plantontology.org
Thiemann A, Fu J, Schrag TA, Melchinger AE, Frisch M, Scholten S (2010) Correlation between parental transcriptome and field data for the characterization of heterosis in Zea mays L. Theor Appl Genet (accepted)
Thimm O, Bläsing O, Gibon Y, Nagel A, Meyer S, Krüger P, Selbig J, Müller LA, Rhee SY, Stitt M (2004) MAPMAN: a user-driven tool to display genomics data sets onto diagrams of metabolic pathways and other biological processes. Plant J 37(6):914–939
Usadel B, Poree F, Nagel A, Lohse M, Czedik-Eysenberg A, Stitt M (2009) A guide to using MapMan to visualize and compare omics data in plants: a case study in the crop species, Maize. Plant Cell Environ 32(9):1211–1229
Vuylsteke M, van Eeuwijk F, Van Hummelen P, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (2005) Genetic analysis of variation in gene expression in Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 171(3):1267–1275
Wei G, Tao Y, Liu G, Chen C, Luo R, Xia H, Gan Q, Zeng H, Lu Z, Han Y, Li X, Song G, Zhai H, Peng Y, Li D, Xu H, Wei X, Cao M, Deng H, Xin Y, Fu X, Yuan L, Yu J, Zhu Z, Zhu L (2009) A transcriptomic analysis of superhybrid rice LYP9 and its parents. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(19):7695–7701
Werhli AV, Grzegorczyk M, Husmeier D (2006) Comparative evaluation of reverse engineering gene regulatory networks with relevance networks, graphical gaussian models and bayesian networks. Bioinformatics 22(20):2523–2531
Xiao J, Li J, Yuan L, Tanksley SD (1995) Dominance is the major genetic basis of heterosis in rice as revealed by QTL analysis using molecular markers. Genetics 140:745–754
Yang YH, Dudoit S, Luu P, Lin DM, Peng V, Ngai J, Speed TP (2002) Normalization for cDNA microarray data: a robust composite method addressing single and multiple slide systematic variation. Nucleic Acids Res 30(4):e15
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the German Research Council (DFG) under Grants RE 1654/2-1 and SE 611/3-1. We want to thank Dirk Hincha (MPIMP-Golm) and his lab for supporting our gene expression experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. van Eeuwijk.
Contribution to the special issue “Heterosis in Plants”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andorf, S., Selbig, J., Altmann, T. et al. Enriched partial correlations in genome-wide gene expression profiles of hybrids (A. thaliana): a systems biological approach towards the molecular basis of heterosis. Theor Appl Genet 120, 249–259 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1214-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1214-z