Abstract
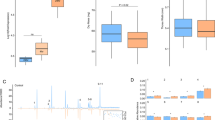
Differences in the number of sexual partners (i.e., mating system) have the potential to exert a strong influence on the bacterial communities present in reproductive structures like the vagina. Because this structure serves as a conduit for gametes, bacteria present there may have a pronounced, direct effect on host reproductive success. As a first step towards the identification of the relationship between sexual behavior and potentially pathogenic bacterial communities inhabiting vital reproductive structures, as well as their potential effects on fitness, I sought to quantify differences in bacterial diversity in a promiscuous and monogamous mammal species. To accomplish this, I used two sympatric species of Peromyscus rodents—Peromyscus californicus and Peromyscus maniculatus that differ with regard to the number of sexual partners per individual to test the hypothesis that bacterial diversity should be greater in the promiscuous P. maniculatus relative to the monogamous P. californicus. As predicted, phylogenetically controlled and operational taxonomic unit-based indices of bacterial diversity indicated that diversity is greater in the promiscuous species. These results provide important new insights into the effects of mating system on bacterial diversity in free-living vertebrates, and may suggest a potential cost of promiscuity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ (1990) Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403–410
Benson DA, Karsch-Mizrachi I, Lipman DJ, Ostell J, Wheeler DL (2007) GenBank. Nucl Acids Res 36:D25–D30
Bik EM et al (2010) Bacterial diversity in the oral cavity of 10 healthy individuals. The ISME Journal 4:962–974
Birdsall D, Nash D (1973) Occurrence of successful multiple insemination of females in natural populations of deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). Evolution 27:106–110
Boneh S, Boneh A, Caron R (1998) Estimating the prediction function and the number of unseen species in sampling with replacement. J Am Stat Assoc 93:372–379
Brook I (2005) The role of bacterial interference in otitis, sinusitis and tonsillitis. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 133:139–146
Brown CJ et al (2007) Preliminary characterization of the normal microbiota of the human vulva using cultivation-independent methods. J Med Microbiol 56:271–276
Burnham K, Overton W (1979) Robust estimation of population-size when capture probabilities vary among animals. Ecology 60:927–936
Calisi RM, Bentley GE (2009) Lab and field experiments: are they the same animal? Horm Behav 56:1–10
Camacho C et al (2009) BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC Bioinforma 10:421
Chao A (1984) Nonparametric estimation of the number of classes in a population. Scand J Statist 11:265–270
Chao A (1992) Estimating the number of classes via sample coverage. J Am Stat Assoc 87:210–217
Chao A (1993) Stopping rules and estimation for recapture debugging with unequal failure rates. Biometrika 80:193–201
Coolen M, Post E, Davis C, Forney L (2005) Characterization of microbial communities found in the human vagina by analysis of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms of 16S rRNA genes. Appl Environ Microb 71:8729–8737
De P, Singh A, Wong T, Yacoub W, Jolly A (2004) Sexual network analysis of a gonorrhoea outbreak. Sex Transm Infect 80:280–285
DeSantis TZ et al (2006) NAST: a multiple sequence alignment server for comparative analysis of 16S rRNA genes. Nucl Acids Res 34:W394–W399
Dethlefsen L, Huse S, Sogin ML, Relman DA (2008) The pervasive effects of an antibiotic on the human gut microbiota, as revealed by deep 16S rRNA sequencing. PLoS Biol 6:2383–2400
Dionne M, Miller KM, Dodson JJ, Caron F, Bernatchez L (2007) Clinical variation in MHC diversity with temperature: evidence for the role of host–pathogen interaction on local adaptation in Atlantic salmon. Evolution 61:2154–2164
Drummond AJ, Ashton B, Buxton S, Cheung M, Cooper A, Duran C, Field M, Heled J, Kearse M, Markowitz S, Moir R, Stones-Havas S, Sturrock S, Thierer T, Wilson A (2011) Geneious v5.4. Available from http://www.geneious.com/. Accessed 1 July 2011
Erb-Downward JR et al (2011) Analysis of the lung microbiome in the “healthy” smoker and in COPD. PLoS ONE 6:e16384
Faith D (1992) Conservation evaluation and phylogenetic diversity. Biol Conserv 61:1–10
Flanagan JL et al (2007) Loss of bacterial diversity during antibiotic treatment of intubated patients colonized with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Clin Microbiol 45:1954–1962
Foltz D (1981) Genetic evidence for long-term monogamy in a small rodent, Peromyscus polionotus. Am Nat 117:665–675
Fredricks D, Fiedler T, Marrazzo J (2005) Molecular identification of bacteria associated with bacterial vaginosis. New Engl J Med 353:1899–1911
Fuller C, Blaustein A (1996) Effects of the parasite Eimeria arizonensis on survival of deer mice (Peromyscus maniculatus). Ecology 77:2196–2202
Gibernick D, Teferi T (2000) Adaptive significance of male parental care in a monogamous mammal. P Roy Soc Lond B Bio 267:147–150
Good I (1953) The population frequencies of species and the estimation of population parameters. Biometrika 40:237–264
Gray R et al (2001) Probability of HIV-1 transmission per coital act in monogamous, heterosexual, HIV-1-discordant couples in Rakai, Uganda. Lancet 357:1149–1153
Green TJ, Barnes AC (2010) Bacterial diversity of the digestive gland of Sydney rock oysters, Saccostrea glomerata infected with the paramyxean parasite, Marteilia sydneyi. J Appl Microbiol 109:613–622
Gregson S et al (2002) Sexual mixing patterns and sex-differentials in teenage exposure to HIV infection in rural Zimbabwe. Lancet 359:1896–1903
Handelsman J (2004) Metagenomics: application of genomics to uncultured microorganisms. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 68:669–685
Hattori M, Taylor TD (2009) The human intestinal microbiome: a new frontier of human biology. DNA Res 16:1–12
Hill JE et al (2010) Improvement of the representation of bifidobacteria in fecal microbiota metagenomic libraries by application of the cpn60 universal primer cocktail. Appl Environ Microb 76:4550–4552
Huber T, Faulkner G, Hugenholtz P (2004) Bellerophon: a program to detect chimeric sequences in multiple sequence alignments. Bioinformatics 20:2317–2319
Hugenholtz P, Tyson GW (2008) Microbiology—metagenomics. Nature 455:481–483
Hupton G, Portocarrero S, Newman M, Westneat D (2003) Bacteria in the reproductive tracts of red-winged blackbirds. Condor 105:453–464
Jin L et al (2007) Species diversity and relative abundance of vaginal lactic acid bacteria from women in Uganda and Korea. J Appl Microbiol 102:1107–1115
Kelly CP, Pothoulakis C, LaMont JT (1994) Clostridium difficile colitis. N Engl J Med 330:257–262
Kim TK et al (2009) Heterogeneity of vaginal microbial communities within individuals. J Clin Microbiol 47:1181–1189
Kleiman D (1977) Monogamy in mammals. Q Rev Biol 52:39–69
Kraut-Becher J, Aral S (2003) Gap length: an important factor in sexually transmitted disease transmission. Sex Transm Dis 30:221–225
Kvennefors ECE, Sampayo E, Ridgway T, Barnes AC, Hoegh-Guldberg O (2010) Bacterial communities of two ubiquitous great barrier reef corals reveals both site- and species-specificity of common bacterial associates. PLoS ONE 5:e10401
Lozupone C, Knight R (2005) UniFrac: a new phylogenetic method for comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 71:8228–8235
Manhart L, Aral S, Holmes K, Foxman B (2002) Sex partner concurrency—measurement, prevalence, and correlates among urban 18–39-year-olds. Sex Transm Dis 29:133–143
Martin A (2002) Phylogenetic approaches for describing and comparing the diversity of microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 68:3673–3682
Miller S, Dykes D, Polesky H (1988) A simple salting out procedure for extracting DNA from human nucleated cells. Nucl Acids Res 16:1215
Mitsunaga T, Powell A, Heard N, Larsen U (2005) Extramarital sex among Nigerian men—polygyny and other risk factors. Jaids-J Acq Imm Def 39:478–488
Myer L, Kuhn L, Stein ZA, Wright TC, Denny L (2005) Intravaginal practices, bacterial vaginosis, and women’s susceptibility to HIV infection: epidemiological evidence and biological mechanisms. Lancet Infect Dis 5:786–794
Padian N, Shiboski S, Glass S, Vittinghoff E (1997) Heterosexual transmission of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in Northern California: results from a ten-year study. Am J Epidemiol 146:350–357
Paster B et al (2001) Bacterial diversity in human subgingival plaque. J Bacteriol 183:3770–3783
Poiani A, Gwozdz J (2002) Cloacal microorganisms and mating systems of four Australian bird species. Emu 102:291–296
Pontes DS, Lima-Bittencourt CI, Chartone-Souza E, Amaral Nascimento AM (2007) Molecular approaches: advantages and artifacts in assessing bacterial diversity. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 34:463–473
Potterat J et al (1999) Chlamydia transmission: concurrency, reproduction number, and the epidemic trajectory. Am J Epidemiol 150:1331–1339
Pruesse E et al (2007) SILVA: a comprehensive online resource for quality checked and aligned ribosomal RNA sequence data compatible with ARB. Nucl Acids Res 35:7188–7196
Ravel J et al (2011) Vaginal microbiome of reproductive-age women. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108(Suppl 1):4680–4687
Ribble D (1991) The monogamous mating system of Peromyscus californicus as revealed by DNA fingerprinting. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 29:161–166
Ribble D (1992) Dispersal in a monogamous rodent, Peromyscus californicus. Ecology 73:859–866
Ribble D, Millar J (1996) The mating system of northern populations of Peromyscus maniculatus as revealed by radiotelemetry and DNA fingerprinting. Ecoscience 3:423–428
Rivera AJ, Stumpf RM, Wilson B, Leigh S, Salyers AA (2010a) Baboon vaginal microbiota: an overlooked aspect of primate physiology. Am J Primatol 72(6):467–474
Rivera AJ, Frank JA et al (2010b) Differences between the normal vaginal bacterial community of baboons and that of humans. Am J Primatol 73:119–126
Schloss PD (2008) Evaluating different approaches that test whether microbial communities have the same structure. Isme J 2:265–275
Schloss PD et al (2009) Introducing mothur: open-source, platform-independent, community-supported software for describing and comparing microbial communities. Appl Environ Microb 75:7537–7541
Schwanz LE (2008) Chronic parasitic infection alters reproductive output in deer mice. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 62:1351–1358
Servin AL (2004) Antagonistic activities of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria against microbial pathogens. FEMS Microbiol Rev 28:405–440
Shannon C (1948) A mathematical theory of communication. The Bell Sys Tech J 27:379–423
Shurtliff Q, Pearse D, Rogers D (2005) Parentage analysis of the canyon mouse (Peromyscus crinitus): evidence for multiple paternity. J Mammal 86:531–540
Sikes RS, Gannon WL (2011) Guidelines of the American Society of Mammalogists for the use of wild mammals in research. J Mammal 92:235–253
Simpson E (1949) Measurement of diversity. Nature 163:688–688
Smith M, Patton J (1993) The diversification of South American murid rodents: evidence from mitochondrial DNA sequence data for the akodontine tribe. Biol J Linn Soc 50:149–177
Smith E, VanBelle G (1984) Nonparametric estimation of species richness. Biometrics 40:119–129
Spear GT et al (2010) Identification of rhesus macaque genital microbiota by 16S pyrosequencing shows similarities to human bacterial vaginosis: implications for use as an animal model for HIV vaginal infection. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses 26:193–200
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22(21):2688–2690
Suerbaum S, Michetti P (2002) Helicobacter pylori infection. N Engl J Med 347:1175–1186
Turnbaugh PJ et al (2009) A core gut microbiome in obese and lean twins. Nature 457:480–U7
Vandegrift KJ, Raffel TR, Hudson PJ (2008) Parasites prevent summer breeding in white-footed mice, Peromyscus leucopus. Ecology 89:2251–2258
Wang Y, Qian P-Y (2009) Conservative fragments in bacterial 16S rRNA genes and primer design for 16S ribosomal DNA amplicons in metagenomic studies. PLoS ONE 4:e7401
Wawer M et al (2005) Rates of HIV-1 transmission per coital act, by stage of HIV-1 infection, in Rakai, Uganda. J Infect Dis 191:1403–1409
Webberley K, Hurst G, Buszko J, Majerus M (2002) Lack of parasite-mediated sexual selection in a ladybird/sexually transmitted disease system. Anim Behav 63:131–141
Weigler BJ et al (1988) Aspects of the epidemiology of Chlamydia psittaci infection in a population of koalas (Phascolarctos cinereus) in southeastern Queensland, Australia. J Wildlife Dis 24:282–291
Weisburg W, Barns S, Pelletier D, Lane D (1991) 16S ribosomal DNA amplification for phylogenetic study. J Bacteriol 173:697–703
Wienemann T et al (2011) The bacterial microbiota in the ceca of Capercaillie (Tetrao urogallus) differs between wild and captive birds. Syst Appl Microbiol doi:10.1016/j.syapm.2011.06.003
Witkin SS, Linhares IM, Giraldo P (2007) Bacterial flora of the female genital tract: function and immune regulation. Best Pract Res Cl Ob 21:347–354
Yarza P et al (2008) The All-Species Living Tree project: a 16S rRNA-based phylogenetic tree of all sequenced type strains. Syst Appl Microbiol 31:241–250
Zambrano-Nava S, Boscán-Ocando J, Nava J (2010) Normal bacterial flora from vaginas of Criollo Limonero cows. Trop Anim Health Prod 43:291–294
Zhou X et al (2007) Differences in the composition of vaginal microbial communities found in healthy Caucasian and black women. Isme J 1:121–133
Acknowledgments
The research was supported generously by the Museum of Vertebrate Zoology (University of California, Berkeley) and the NSF (IOS0909798). Computational resources were supported in part by the National Science Foundation through TeraGrid resources provided by The Texas Advanced Computing Center under grant number TG-IBN100014. Thanks are owed to Eileen Lacey and the Lacey Lab as well as to Rodrigo Almeida for help during all stages of this work. Lastly, I would like to thank my wife and kids, whose support has been unwavering.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by: Sven Thatje
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
MacManes, M.D. Promiscuity in mice is associated with increased vaginal bacterial diversity. Naturwissenschaften 98, 951 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-011-0848-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-011-0848-2