Abstract
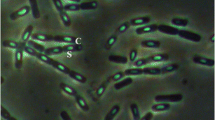
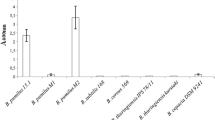
Parasporin, a Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal protein, is unique in having a strong cytocidal activity preferential for human cancer cells. In this study, we characterized parasporin activities associated with three novel geographical isolates of B. thuringiensis. Parasporal inclusion proteins of the three isolates were highly toxic to human uterus cervix cancer cells (HeLa), but not to non-cancer uterine smooth muscle cells (UtSMC). Inclusions of the isolates lacked insect toxicity and hemolytic activity against sheep erythrocytes. Ouchterlony immunodiffusion tests revealed that the proteins of the three isolates are immunologically closely related to parasporin-1 (Cry31A), but dissimilar to the three other existing parasporin groups. Our results provide evidence that the parasporin-1-producing organism is a common member in B. thuringiensis populations occurring in natural environments of Japan.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Behl C, Davis J, Cole GM, Schubert D (1992) Vitamin E protect nerve cells from amyloid β protein toxicity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 186:944–950
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Craigie J (1931) Studies on the serological reactions of the flagella of B. typhos. J Immunol 21:417–511
Glare TR, O’Callaghan M (2000) Bacillus thuringiensis: biology, ecology and safety. Wiley, Chichester
Heiss P, Bernatz C, Burchelt G, Senekowitsch-Schimidtke R (1997) Cytotoxic effect of immunoconjugate composed of glucose-oxidase coupled to an anti-ganglioside (GD2) antibody on spheroids. Anticancer Res 17:3177–3178
Ishii T, Ohba M (1993) Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis environmental isolates showing larvicidal activity specific for mosquitoes. J Gen Microbiol 139:2849–2854
Ishiwata S (1901) On a kind of severe flacherie (sotto disease). Dainihon Sanshi Kaiho 114:1–5
Katayama H, Yokota H, Akao T, Nakamura O, Ohba M, Mekada E, Mizuki E (2005) Parasporin-1, a novel cytotoxic protein to human cells from non-insecticidal parasporal inclusions of Bacillus thuringiensis. J Biochem 137:17–25
Mizuki E, Ohba M, Akao T, Yamashita S, Saitoh H, Park YS (1999) Unique activity associated with non-insecticidal Bacillus thuringiensis parasporal inclusions: in vitro cell-killing action on human cancer cells. J Appl Microbiol 86:477–486
Mizuki E, Park YS, Saitoh H, Yamashita S, Akao T, Higuchi K, Ohba M (2000) Parasporin, a human leukemic cell-recognizing parasporal protein of Bacillus thuringiensis. Clin Diagn Lab Immunol 7:625–634
Ohba M, Aizawa K (1978) Serological identification of Bacillus thuringiensis and related bacteria isolated in Japan. J Invertebr Pathol 32:303–309
Ohba M, Aizawa K (1986) Insect toxicity of Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from soils of Japan. J Invertebr Pathol 47:12–20
Ohba M, Wasano N, Mizuki E (2000) Bacillus thuringiensis soil populations naturally occurring in the Ryukyus, a subtropic region of Japan. Microbiol Res 155:17–22
Shisa N, Wasano N, Ohgushi A, Lee D-H, Ohba M (2002) Extremely high frequency of common flagellar antigens between Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiol Lett 213:93–96
Yasutake K, Binh DN, Kagoshima K, Uemori A, Ohgushi A, Maeda M, Mizuki E, Yu YM, Ohba M (2006) Occurrence of parasporin-producing Bacillus thuringiensis in Vietnam. Can J Microbiol 52:365–372
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Miyamoto for providing the silkworm, Bombyx mori. We also thank S. Kitada for advices on experimental techniques of in vitro cytotoxicity tests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Uemori, A., Maeda, M., Yasutake, K. et al. Ubiquity of parasporin-1 producers in Bacillus thuringiensis natural populations of Japan. Naturwissenschaften 94, 34–38 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-006-0153-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00114-006-0153-7