Abstract
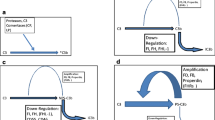
The split product of the complement protein, C5, is C5a and is an extremely potent pro-inflammatory peptide that interacts with two C5a receptors, C5aR and C5L2, present on surfaces of phagocytes as well as other cell types. The former is a well-established receptor that initiates G-protein-coupled signaling via mitogen-activated protein kinase pathways. Its in vivo blockade greatly reduces inflammatory injury. Much less is known about C5L2, occupancy of which by C5a does not initiate increased intracellular Ca2+. There are numerous conflicting reports suggesting that C5L2 is a “default receptor” that attenuates C5a-dependent biological responses by competing with C5aR for binding of C5a. However, there are other reports suggesting that C5L2 plays an active, positive role in inflammatory responses. Better definition of C5L2 is needed if its in vivo blockade, along with C5aR, is to be considered in complement-dependent inflammatory diseases.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gerard NP, Gerard C (1991) The chemotactic receptor for human C5a anaphylatoxin. Nature 349:614–617
Boulay F, Tardif M, Brouchon L, Vignais P (1990) Synthesis and use of a novel N-formyl peptide derivative to isolate a human N-formyl peptide receptor cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 168:1103–1109
Strainic MG, Liu J, Huang D, An F, Lalli PN, Muqim N, Shapiro VS, Dubyak GR, Heeger PS, Medof ME (2008) Locally produced complement fragments C5a and C3a provide both costimulatory and survival signals to naïve CD4+ T cells. Immunity 28:425–435
Hawlisch H, Wills-Karp M, Karp CL, Köhl J (2004) The anaphylatoxins bridge innate and adaptive immune responses in allergic asthma. Mol Immunol 41:123–131
Lee H, Whitfeld PL, Mackay CR (2008) Receptors for complement C5a. The importance of C5aR and the enigmatic role of C5L2. Immunol Cell Biol 86:153–160
Okinaga S, Slattery D, Humbles A, Zsengeller Z, Morteau O, Kinrade MB, Brodbeck RM, Krause JE, Choe HR, Gerard NP, Gerard C (2003) C5L2, a nonsignaling C5a binding protein. Biochemistry 42:9406–9415
Gerard N, Lu B, Liu P, Craig S, Fujiwara Y, Okinaga S, Gerard C (2005) An anti-inflammatory function for the complement anaphylatoxin C5a-binding protein, C5L2. JBC 280:39677–39680
Kalant D, Cain SA, Maslowska M, Sniderman AD, Cianflone K, Monk PN (2003) The chemoattractant receptor-like protein C5L2 binds the C3a des-arg77/acylation-stimulating protein. J Biol Chem 278:11123–11129
Kalant D, MacLaren, Cui W, Samanta R, Monk PN, Laporte SA, Cianflone K (2005) C5L2 is a functional receptor for acylation-stimulating protein. J Biol Chem 280:23936–23944
Cain SA, Monk PN (2002) The orphan receptor C5L2 has high affinity binding sites for complement fragments C5a and C5a des-arg74. J Biol Chem 277:7165–7169
Johswich K, Martin M, Thalmann J, Rheinheimer C, Monk PN, Klos A (2006) Ligand specificity of the anaphylatoxin C5L2 receptor and its regulation on myeloid and epithelial cell lines. J Biol Chem 281:39088–39095
Hopken UE, Lu B, Gerard NP, Gerard C (1997) Impaired inflammatory responses in the reverse Arthus reaction through genetic deletion of the C5a receptor. J Exp Med 186:749–756
Gao H, Neff TA, Guo TA, Speyer CL, Sarma JV, Tomlins S, Man Y, Riedemann NC, Hoesel LM, Younkin E, Zetoune FS, Ward PA (2005) Evidence for a functional role of the second C5a receptor C5L2. FASEB J 19:1003–1005
Chen NJ, Mirtsos C, Suh D, Lu YC, Lin WJ, McKerlie C, Lee T, Baribault H, Tian H, Yeh WC (2007) C5L2 is critical for the biological activities of the anaphylatoxins C5a and C3a. Nat Lett 446:203–207
Karp CL, Grupe A, Schadt E, Ewart SL, Keane-Moore M, Cuomo PJ, Köhl J, Wahl L, Kuperman D, Germer S, Aud D, Peltz G, Wills-Karp (2000) Identification of complement factor 5 as a susceptibility locus for experimental allergic asthma. Nat Immunol 1:221–226
Köhl J, Baelder R, Lewkowich IP, Pandey MK, Hawlisch H, Wang L, Best J, Herman NS, Sproles AA, Zwirner J, Whitsett JA, Gerard C, Sfyroera G, Lambris JD, Wills-Karp M (2006) A regulatory role for the C5a anaphylatoxin in type 2 immunity in asthma. J Clin Invest 116:628–632
Rittirsch D, Flierl MA, Nadeau BA, Day DE, Huber-Lang M, Mackay CR, Zetoune FS, Gerard NP, Cianflone K, Koehl J, Gerard C, Sarma JV, Ward PA (2008) Functional roles for C5a receptors in sepsis. Nat Med 14:551–557
Yang H, Wang H, Czura CJ, Tracey KJ (2005) The cytokine activity of HMGB1. J Leuk Biol 78:1–8
Huber-Lang M, Sarma JV, Rittirsch D, Schreiber H, Weiss M, Flierl M, Younkin E, Schneider M, Suger-Wiedeck H, Gebhard F, McClintock SD, Neff T, Zetoune F, Bruckner U, Guo RF, Monk PN, Ward PA (2005) Changes in the novel orphan, C5a receptor (C5L2), during experimental sepsis and sepsis in humans. J Immunol 174:1104–1110
Gavrilyuk V, Kalinin S, Hilbush BS, Middlecamp A, McGuire S, Pelligrino D, Weinberg G, Feinstien DL (2005) Identification of complement 5a-like receptor (C5L2) from astrocytes: characterization of anti-inflammatory properties. J Neurochem 92:1140–1149
Johswich K, Kos A (2007) C5L2 – an anti-inflammatory molecule or a receptor for acylation stimulating protein (C3a-desArg)? Review. Advances in experimental medicines and biology. In: Lambris JD (ed) Current topics in innate immunity. Springer, New York, pp 159–180
Scola A-M et al (2008) The human complement fragment receptor, C5L2, is a recycling decoy receptor. Mol Immunol. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2008.11.001
Acknowledgment
We thank Professor Craig Gerard (Dept. Pediatrics, Children’s Hospital of Boston, MA) for helpful suggestions for the manuscript. This work is supported in part by National Institute of Health grants: HL-31963, GM-61656 and GM-029507.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ward, P.A. Functions of C5a receptors. J Mol Med 87, 375–378 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0442-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-009-0442-7