Abstract.
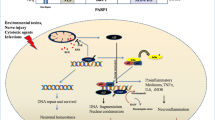
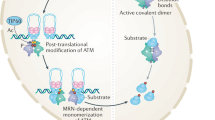
Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation is required by multicellular eukaryotes to ensure genomic integrity under conditions of mild to moderate genotoxic stress. However, severe stress following acute neuronal injury causes overactivation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1, which results in unregulated poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) synthesis and widespread neuronal cell death. Once thought to be a necrotic cell death resulting from energy failure, PARP-1 activation is now known to induce the nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor, which results in caspase-independent cell death. Conversely, poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase, once thought to contribute to neuronal injury, now appears to have a protective role as demonstrated by recent studies utilizing gene disruption technology. Thus, the emerging mechanism dictating the fate of neurons appears to involve the regulation of PAR levels in neurons. Therefore, therapies targeting poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation in the treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as stroke and Parkinson’s disease are required to inhibit PAR synthesis and/or facilitate its degradation.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Koh, D.W., Dawson, T.M. & Dawson, V.L. Poly-ADP-ribosylation in health and disease. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 760–768 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4508-y
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-004-4508-y