Abstract
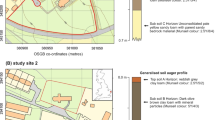
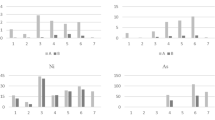
Chemical, mineralogical and isotopic composition (34S/32S) analyses were carried out on “black crusts” developed on the old buildings of Palermo (Sicily) with the aim to distinguish between natural and anthropogenic sulphur sources. Furthermore individual samples of total suspended particulate (TSP) were collected and analysed in order to estimate the influence of air pollution on the decay process of calcareous stones in a typical southern Mediterranean coastal environment. SEM/EDS analysis, X-ray diffractometry, IR spectroscopy and liquid chromatography led to the compositional characterization of “black crusts” and airborne particulate matter in the city. Sulphur isotopic compositions of gypsum-bearing crusts showed a prevailing contribution of anthropogenic sources (vehicle exhaust and other combustion processes). Natural sulphur and/or sulphate sources (biogenic and/or sea-spray) were shown to play a secondary role. These data can be considered a starting point for the determination of the rate of growth of “black crusts” in a coastal Mediterranean urban environment like Palermo. In the future, they might be useful to local authorities for planning more efficient maintenance action in order to slow as much as possible the rate of decay of the monumental heritage of the city.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abate B, Catalano R, Renda P (1982) I monti di Palermo. Guida alla geologia della Sicilia Occidentale. Soc Geol It (Guide geologiche regionali)
Aires-Barros L, Alves L (1988) Geochemistry and origin of “black crusts” of portals of Jeronimos. In: The engineering ecology of ancient works, monuments and historical sites. Balkemo, Rotterdam, p 793
Alaimo R, Deganello S, Di Franco L, Montana G (1989) Caratteristiche composizionali del particolato solido atmosferico e chimismo delle acque di precipitazione nell’area urbana di Palermo. In: Proceedings of the international symposium. The Conservation of Monuments in The Mediterranean Basin, Bari
Alaimo MG, Dongarrà G, Melati MR, Monna F, Varrica D (1999) Recognition of environmental trace metal contamination using pine needles as bioindicators. The urban area of Palermo (Italy). Environ Geol 39:914–923
Ausset P, Crovisier JL, Del Monte M, Furlan V, Girardet F, Hammecker C, Jeannette D, Lefevre R (1996) Experimental study of limestone and sandstone sulphation in polluted realistic conditions: the Lausanne Atmospheric Simulation Chamber (LASC). Atmos Environ 30(18):3197–3207
Ausset P, Del Monte M, Lefevre RA (1999) Embryonic sulphated black crusts on carbonate in atmospheric simulation chamber and in the field: role of carbonaceous fly-ash. Atmos Environ 33:1525–1534
Badalamenti F, Carapezza M, Dongarrà G, Hauser S, Macaluso A, Parello F (1984) Precipitazioni atmosferiche in Sicilia. 1) L’area urbana di Palermo. Rend Soc It Min e Petr 39(1):81–92
Bugini R, Tabasso LM, Realini M (2000) Rate of formation of black crusts on marble. A case study. J Cult Herit 1(2):111–116
Buzek F, Sramek J (1985) Sulphur isotopes in the study of stone monument conservation. Stud Conserv 30:171–176
Camuffo D (1986) Deterioration processes of historical buildings. In: Schneider T (ed) Acidification and its policy Implications. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 189–221
Camuffo D, Del Monte M, Sabbioni C, Vittori O (1982) Wetting, deterioration and visual features of stone surfaces in a urban area. Atmos Environ 16:2253–2259
Camuffo D, Del Monte M, Sabbioni C (1983) Origin and growth mechanisms of the sulfated crusts on urban limestone. Water Air Soil Pollut 19:351–359
Carrol D (1970) Rock weathering. Plenum, New York
Coleman ML, Moore MP (1978) Direct reduction of sulphates to sulphur dioxide for isotopic analysis. Anal Chem 50:1594–1595
Colombo C, Fabbri B, Negrotti R, Toniolo L (1996) The Ca’ Granda in Milan: the ceramic materials and the oxalate films. In: Proceeding of the IInd international symposium of works of arts, Milano
Cortecci G, Longinelli A (1970) Isotopic composition of sulphate in rain water, Pisa, Italy. Earth Planet Sci Lett 8:36–40
Cusimano G, Di Cara A, Nastasi P (1981) Analisi degli elementi principali del clima della Piana di Palermo. Il Naturalista Siciliano, Supplemento Società Siciliana Scienze Naturali, vol 5
Delalieux F, Cardell C, Todorov V, Dekov V, Van Grieken R (2001) Environmental conditions controlling the chemical weathering of the Madara Horseman Monument, N.E Bulgaria. J Cult Herit 2:43–54
Esbert RM, Díaz-Pache F, Grossi CM, Alonso FJ, Ordaz J (2000) Airborne particulate matter around the Cathedral of Burgos (Castilla y Léon, Spain). Atmos Environ 35:441–452
Fassina V, Amoroso G (1983) Stone decay and conservation. Elsevier Science Inc., Amsterdam
Fassina V, Lazzarini L, Biscontin G (1976) Effects of atmospheric pollutants on the composition of black crust deposited on ventian marbles and stones. 2e Colloque sur la Deterioration des Pierres en Oeuvre. Athens, pp 201–210
Franzini M, Gratziu C, Wicks E (1984) Patine ad ossalati di calcio su elementi marmorei. Rend Soc It Min e Petr 39:47–58
Grinenko VA (1962) The preparation of sulphur dioxide for isotopic analysis. Zh Neorgan Khim 7:2478–2483
Honeyborne DB, Harris PB (1958) The structure of porous building stone and its relation to weathering behaviour. In: Proceedings of the 10th symposium of the Colston Research Society. Butterworths Scientific Publications, London, pp 343–359
Johnson JB, Haneef SJ, Dickenson C, Thompson GE, Wood GC (1991) Laboratory exposure chamber studies: pollutant and acid rain preservation rates and stone degradation. In: Baer NS, Sabbioni C, Sors AI (eds) Science, technology and European cultural heritage. Butterworth-Heineman, Oxford, pp 474–477
Lazzarini L, Laurenzi Tabasso M (1986) Il restauro della pietra. CEDAM, Padova
Lokman T (1999) Laboratory experiments on the investigation of the effects of sulphuric acid on the deterioration of carbonate stones and surface corrosion. Water, Air Soil Pollut 114:1–12
Longinelli A, Bartelloni M (1978) Atmospheric pollution in Venice, Italy, as indicated by stable isotope measurements. Water Air Soil Pollut 10:335–341
Montana G, Gagliardo Briuccia V (1998) I marmi e i diaspri del Barocco siciliano. S.F. Flaccovio Editore, Palermo
Montana G, Scaduto R (1999) La pietra d’Aspra. Storia ed utilizzo. Il recupero delle ville barocche di Bagheria. Flaccovio Editore, Palermo
Paoletti L, De Berardis B, Arizza L (2003) Inquinamento da polveri e da particolato fino, in siti con differenti caratteristiche ambientali. Annali Istituto Superiore di Sanità, 39(03):381–385
Punturo R, Russo LG, Lo Giudice A, Mazzoleni P, Pezzino A (2006) Building stone employed in the historical monuments of Eastern Sicily (Italy). An example: the ancient city centre of Catania. Environ Geol 50:156–169
Realini M, Negrotti R, Appollonia L, Vaudan D (1995) Deposition of particulate matter on stone surfaces: an experimental verification of its effects on Carrara marble. Sci Total Environ 167:67–72
Realini M, Negrotti R, Colombo C, Toniolo L (1997) The decay of Saltrio stone exposed in polluted area. A quantitative approach. In: Proceeding of 4th international symposium on the conservation of monuments in the mediterranean. Rodhes, vol 1, pp 253–262
Ress CE, Jenkins WJ, Monster J (1978) The sulphur isotopic composition of ocean water sulphate. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 42:377–381
Robinson G, Baker MC (1975) Wind—driven rain and building. Technical paper no. 445 of the Division of Building Research, National Research Council of Canada
Thorfs KM, Van Grieken RE (1997) Use of stable isotope measurements to evaluate the origin of sulphur in gypsum layers on limestone building. Environ Sci Technol 31:2650–2655
UNI 11182:2006 (2006) Beni culturali—Materiali lapidei naturali ed artificiali—Descrizione della forma di alterazione—Termini e definizioni
Varrica D, Dongarrà G, Sabatino G, Monna F (2003) Inorganic geochemistry of roadway dust from the metropolitan area of Palermo, Italy. Environ Geol 44:222–230
Winkler EM (1982) Decay of stone monuments and buildings: the role of acid rain. Technology and conservation (Spring 1982), pp 32–36
Zappia G, Sabbioni C, Riontino C, Gobbi G, Favoni O (1998) Exposure tests of building materials in urban atmosphere. Sci Total Environ 224:235–244
Zezza F, Macrì F (1995) Marine aerosol and stone decay. Sci Total Environ 167:123–143
Zhao FJ, Spiro B, Poulton N, Mcgrath SP (1998) Use of sulphur isotope ratios to determine the anthropogenic sulphur signals in a grassland ecosystem. Environ Sci Technol 32:2288–2291
Acknowledgments
The authors are pleased to thank the anonymous reviewers for their constructive comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montana, G., Randazzo, L., Oddo, I.A. et al. The growth of “black crusts” on calcareous building stones in Palermo (Sicily): a first appraisal of anthropogenic and natural sulphur sources. Environ Geol 56, 367–380 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1175-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1175-y