Abstract
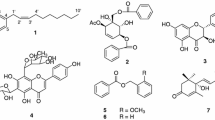
In a bioassay-guided search for acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from Korean natural resources, four isoquinoline alkaloids, corynoxidine (1), protopine (2), palmatine (3), and berberine (4) have been isolated from the methanolic extract of the aerial parts ofCorydalis speciosa. Structures of these compounds were elucidated on the basis of spectroscopic techniques. These compounds inhibited acetylcholinesterase activity in a dose-dependent manner, and the IC50 values of compounds1-4 were 89.0, 16.1, 5.8, and 3.3 μM, respectively.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn, D. K.,Illustrated Book of Korean Medicinal Herbs. Kyohaksa, Seoul, p. 488. (2001).
Bartus, R. T., On neurodegenerative diseases, models, and treatment strategies: lessons learned and lessons forgotten a generation following the cholinergic hypothesis.Exp. Neurol., 163, 495–529 (2000).
Bartus, R. T., Dean, R. L., Beer, B., and Lippa, A. S., The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction.Science, 217, 408–414 (1982).
Chung, Y. K., Heo, H. J., Kim, E. K., Kim, H. K., Huh, T. L., Lim, Y., Kim, S. K., and Shin, D. H., Inhibitory effect of ursolic acid purified fromOriganum majorana L. on the acetylcholinesterse.Mol. Cells, 11, 137–143 (2001).
Ellman, G. L., Courtney, D., Valentino, A., and Featherstone, R. M., A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetyl-cholinesterase activity.Biochem. Pharmacol, 7, 88–95 (1961).
Hussain, R. A., Kim, J., Beecher, C. W. W., and Kinghorn, A. D., Unambiguous carbon-13 NMR assignments of some biologically active protoberberine alkaloids.Heterocycles, 29, 2257–2260 (1989).
Hwang, S. Y., Chang, Y. P., Byun, S. J., Jeon, M. H., and Kim, Y. C., An acetylcholinesterase inhibitor isolated from Corydalis Tuber and its mode of action.Kor. J. Pharmacogn., 27, 91–95 (1996).
Jewers, K. and Manchanda, A. H., The proton magnetic resonances spectra of protoberberium salts.J. Chem. Soc. Perkin II. 1393–1396 (1972).
Kalauni, S. K., Choudhary, M. I., Khalid, A., Manandhar, M. D., Shaheen, F., Atta-ur-Rahman, and Gewali, M. B., New cholinesterase inhibiting steroidal alkaloids from the leaves ofSarcococca coriacea of Nepalese origin.Chem. Pharm. Bull., 50, 1423–1426 (2002).
Kim, D. K., Inhibitory effect of corynoline isolated from the aerial parts ofCorydalis incisa on the acetylcholinesterase.Arch. Pharm. Res., 25, 817–819 (2002).
Kim, D. K. and Lee, K., Inhibitory effect oftrans-N-coumaroyl tyramine from the twigs ofCeltis chinensis on acetylcholinesterase.Arch. Pharm. Res., 26, 735–738 (2003).
Kim, D. K., Lim, J. P., Yang, J. H., Eom, D. O., Eun, J. S., and Leem, K. H., Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the roots ofAngelica dahurica.Arch. Pharm. Res., 25, 856–859 (2002).
Lee, J. H., Lee, K. T., Yang, J. H., Baek, N. I., and Kim, D. K., Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the twigs ofVaccinium oldhami Miquel.Arch. Pharm. Res., 27, 53–56 (2004).
Mortensen, S. R., Chanda, S. M., Hooper, M. J., and Padilla, S., Maturational differences in chlorpyrifos-oxonase activity may contribute to age-related sensitivity to chlorpyrifos.J. Biochem. Toxicol, 11, 279–287 (1996).
Park, C. H., Kim, S. H., Choi, W., Lee, Y. J., Kim, J. S., Kang, S. S., and Suh, Y. H., Novel anticholinesterase and antiamnesic activities of dehydroevodiamine, a constituent ofEvodia rutaecarpa.Planta Med., 62, 405–409 (1996).
Perry, E. K., The cholinergic hypothesis-ten years on.Br. Med. Bull., 42, 63–69 (1986).
Riger, F., Shelanski, M. L., and Greene, L. A., The effects of nerve growh factor on acetylcholinesterase and its multiple forms in cultures of rat PC12 pheochromocytoma cells; increased total specific activity and appearance of the 16 S molecular form.Dev. Biol., 76, 238–243 (1980).
Tani, C., Nagakura, N., and Sugiyama, N., Studies on the alkaloids of Papaveraceous plants. XXI. Alkaloids ofCorydalis speciosa Maxim. (1). The isolation of the tertiary bases by the multi-buffered D.C.C.C.Yakugaku Zasshi, 95(7), 838–842 (1975a).
Tani, C., Nagakura, N., and Hattori, S., Structures of corynoxidine and epicorynoxidine, new alkaloids fromCorydalis koidzumiana. Chem. Lett., 1081–1084 (1975b).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, D.K., Lee, K.T., Baek, NI. et al. Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors from the aerial parts ofCorydalis speciosa . Arch Pharm Res 27, 1127–1131 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975117
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02975117