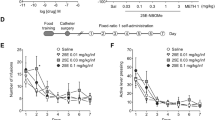
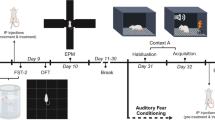
Abstract
One month (but not 1–3 days) after intermittent morphine administration, the hyperresponsiveness of rats toward the locomotor effects of morphine and amphetamine was associated with an increase in dopamine (DA) D-1 receptor-stimulated adenylyl cyclase activity and enhanced steady state levels of preprodynorphin gene expression in slices of the caudate/putamen and nucleus accumbens. Such an enduring increase in postsynaptic D-1 receptor efficacy also occurred in cultured γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA) neurons of the striatum obtained from rats prenatally treated with morphine. Interestingly, in vitro glucocorticoid receptor activation in these cultured striatal neurons by corticosterone potentiated this neuroadaptive effect of prior in vivo morphine exposure. Since activation of glucocorticoid receptors by corticosterone did not affect D-1 receptor functioning in cultured neurons of saline-pretreated rats, prior intermittent exposure to morphine (somehow) appears to induce a long-lasting state of corticosterone hyperresponsiveness in striatal neurons. Therefore, DA-sensitive striatal GABA neurons may represent common neuronal substrates acted upon by morphine and corticosterone. We hypothesize that the delayed occurrence of these long-lasting morphine-induced neuroadaptive effects in GABA/dynorphin neurons of the striatum is involved in the enduring nature of behavioral sensitization to drugs of abuse and cross-sensitization to stressors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Piazza, P. V., Deminiere, J. M., Le Moal, M., and Simon, H. 1990. Stress- and pharmacologically-induced behavioral sensitization increases vulnerability to acquisition of amphetamine self-administration. Brain Res. 514:22–26.
Kalivas, P. W., and Stewart, J. 1991. Dopamine transmission in the initiation and expression of drug- and stress-induced sensitization of motor activity. Brain Res. Rev. 16:223–244.
Robinson, T. E., and Berridge, K. C. 1993. The neural basis of drug craving: an incentive-sensitization theory of addiction. Brain Res. Rev. 18:247–291.
Valadez, A. and Schenk, S. 1994. Persistence of the ability of amphetamine preexposure to facilitate acquisition of cocaine self-administration. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 47:203–205.
Liu, J. L., Nickolenko, J., and Sharp, F. R. 1994. Morphine induces c-fos and junB in striatum and nucleus accumbens via D1 and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91:8537–8541.
Simpson, J. N., Wang, J. Q., and McGinty, J. F. 1995. Repeated amphetamine administration induces a prolonged augmentation of phosphorylated cyclase response element-binding protein and Fos-related antigen immunoreactivity in rat striatum. Neuroscience 69: 441–457.
Hope, B. T., Nye, H. E., Kelz, M. B., Self, D. W., Iadarola, Y. N., Duman, R. S., and Nestler, E. J. 1994. Induction of a long-lasting AP-1 complex composed of altered Fos-like proteins in brain by chronic cocaine and other chronic treatments. Neuron 13: 1235–1244.
Konradi, C., Cole, R. L., Heckers, S., and Hyman, S. E. 1994. Amphetamine regulates gene expression in rat striatum via transcription factor CREB. J. Neurosci. 14:5623–5634.
Cole, R. L., Konradi, C., Douglass, J., and Hyman, S. E. 1995. Neuronal adaptation to amphetamine and dopamine: Molecular mechanisms of prodynorphin gene regulation in rat striatum. Neuron 14:813–823.
Henry, D. J., and White, F. J. 1991. Repeated cocaine administration causes persistent enhancement of D1 dopamine receptor sensitivity within the rat nucleus accumbens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 258:882–890.
Wolf, M. E., White, F. J., and Hu, X-T. 1994. MK-801 prevents alterations in the mesoaccumbens dopamine system associated with behavioral sensitization to amphetamine. J. Neurosci. 14: 1735–1745.
Tjon, G. H. K., De Vries, T. J., Ronken, E., Hogenboom, F., Wardeh, G., Mulder, A. H., and Schoffelmeer, A. N. M. 1994. Repeated and chronic morphine administration causes differential long-lasting changes in dopaminergic neurotransmission in rat striatum without changing its δ- and κ-opioid receptor regulation. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 252:205–212.
Pfeiffer, A., and Herz, A. 1984. Endocrine actions of opioids. Horm. Metab. Res. 16:386–397.
Rivier, C., and Vale, W. 1987. Cocaine stimulates adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) secretion through a corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF)-mediated mechanism. Brain Res. 422:403–406.
Roberts, A. J., Lessov, C. N., and Phillips, T. J. 1995. Critical role for glucocorticoid receptors in stress- and ethanol-induced locomotor sensitization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 275:790–797.
Swerdlow, N. R., Koob, G. F., Cador, M., Lorang, M., and Hauger, R. L. 1993. Pituitary-adrenal axis responses to acute amphetamine in the rat. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 45:629–637.
Evans, R. M., and Arriza, J. L. 1989. A molecular framework for the action of glucocorticoid hormones in the central nervous system. Neuron 2:1105–1112.
Cador, M., Dulluc, J. and Mormede, P. 1993. Modulation of the locomotor response to amphetamine by corticosterone. Neuroscience 56:981–988.
Deroche, V., Piazza, P. V., Casolini, P., Le Moal, M., and Simon, H. 1993. Sensitization to the psychomotor effects of amphetamine and morphine induced by food restriction depend on corticosterone secretion. Brain Res. 611:352–356.
Deroche, V., Marinelli, M., Maccari, S., Le Moal, M., Simon, H., and Piazza, P. V. 1995. Stress-induced sensitization and glucocorticoids. I. Sensitization of dopamine-dependent locomotor effects of amphetamine and morphine depends on stress-induced corticosterone secretion. J. Neurosci. 15:7181–7188.
Piazza, P. V., Marinelli, M., Jodogne, C., Deroche, V., Rouge-Pont, F., Maccari, S., Le Moal, M., and Simon, H. 1994. Inhibition of corticosterone synthesis by metyrapone decreases cocaine-induced locomotion and relapse of cocaine self-administration. Brain Res. 658:259–264.
Rouge-Pont, F., Marinelli, M., Le Moal, M., Simon, H., And Piazza, P. V. 1995. Stress-induced sensitization and glucocorticoids. II. Sensitization of the increase in extracellular dopamine by cocaine depends on stress-induced corticosterone secretion. J. Neurosci. 15:7189–7195.
Schoffelmeer, A. N. M., De Vries, T. J., Vanderschuren, L. J. M. J., Tjon, G. H. K., Nestby, P., Wardeh, G., and Mulder, A. H. 1995. Glucocorticoid receptor activation potentiates the morphine-induced adaptive increase in dopamine D-1 receptor efficacy in γ-aminobutyric acid neurons of rat striatum/nucleus accumbens. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 274:1154–1160.
Paxinos, G., and Watson, C. 1986. The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. 2nd ed. Sydney, Academic Press.
Voorn, P., and Docter, G. J. 1992. A rostrocaudal gradient in the synthesis of enkephalin in nucleus accumbens. Neuroreport 3: 161–164.
Angulo, J. A., and McEwen, B. 1994. Molecular aspects of neuropeptide regulation and function in the corpus striatum and nucleus accumbens. Brain Res. Rev. 19:1–28.
Klitenick, M. A., DeWitte, P., and Kalivas, P. W. 1992. Regulation of somatodendritic dopamine release in the ventral tegmental area by opioids and GABA: an in vivo microdialysis study. J. Neurosci. 12:2623–2632.
Ronken, E., Mulder, A. H., and Schoffelmeer, A. N. M. 1993. Interacting presynaptic kappa-opioid and GABAa receptors modulate dopamine release from striatal synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 61:1634–1639.
Pickel, V. M., Chan, J., and Sesack, S. R. 1993. Cellular substrates for interactions between dynorphin terminals and dopamine dendrites in rat ventral tegmental area and substantia nigra. Brain Res. 602:275–289.
Schoffelmeer, A. N. M., De Vries, T. J., Hogenboom, F., and Mulder, A. H. 1993. Mu- and delta-opioid receptors inhibitorily linked to dopamine-sensitive adenylate cyclase in rat striatum display a selectivity profile towards endogenous opioid peptides different from that of presynaptic mu, delta and kappa receptors. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 267:205–210.
Spanagel, R., Herz, A., and Shippenberg, T. S. 1990. The effects of opioid peptides on dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens: an in vivo microdialysis study. J. Neurochem. 55:1734–1740.
Van Vliet, B. J., Wardeh, G., Mulder, A. H., and Schoffelmeer, A. N. M. 1991. Reciprocal effects of chronic morphine administration on stimulatory and inhibitory G-protein α subunits in primary cultures of rat striatal neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 208:341–342.
Van Vliet, B. J., Van Rijswijk, A. L. C. T., Wardeh, G., Mulder, A. H., and Schoffelmeer, A. N. M. 1993. Adaptive changes in the number of Gs- and Gi-proteins underlie adenylyl cyclase sensitization in morphine-treated rat striatal neurons. Eur. J. Pharmacol. Mol. Pharmacol. 245:23–29.
Kalivas, P. W., and Duffy, P. 1993. Time course of extracellular dopamine and behavioral sensitization to cocaine. I. Dopamine axon terminals. J. Neurosci. 13:266–275.
Kalivas, P. W., and Duffy, P. 1993. Time course of extracellular dopamine and behavioral sensitization to cocaine. II. Dopamine perikarya. J. Neurosci. 13:276–284.
McDougall, S. A., Duke, M. A., Bolanos, C. A., and Crawford, C. A. 1994. Ontogeny of behavioral sensitization in the rat: effects of direct and indirect dopamine agonists. Psychopharmacology 116:483–490.
Ronken, E., Mulder, A. H., and Schoffelmeer, A. N. M. 1994. Chronic activation of mu- and kappa-opioid receptors in cultured catecholaminergic neurons from rat brain causes neuronal supersensitivity without receptor desensitization. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 268:595–599.
Saito, N., Guitart, X., Hayward, M., Tallman, J. F., Duman, R. S., and Nestler, E. J. 1989. Corticosterone differentially regulates the expression of Gsα and Giα messenger RNA and protein in rat cerebral cortex. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., USA 86:3906–3910.
De Vries, T. J., Schoffelmeer, A. N. M., Tjon, G. H. K., Nestby, P., Mulder, A. H., and Vanderschuren, L. J. M. J. 1996. Mifepristone prevents the expression of long-term behavioural sensitization to amphetamine. Eur. J. Pharmacol., 307:R3-R4.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Special issue dedicated to Dr. Eric J. Simon.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schoffelmeer, A.N.M., Voorn, P., Jonker, A.J. et al. Morphine-induced increase in D-1 receptor regulated signal transduction in rat striatal neurons and its facilitation by glucocorticoid receptor activation: Possible role in behavioral sensitization. Neurochem Res 21, 1417–1423 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02532383
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02532383