Summary
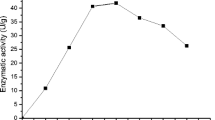
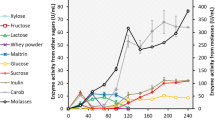
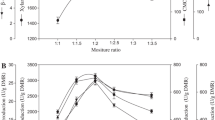
Clostridium thermocellum is well known for its ability to convert cellulose into ethanol and to hydrolyse hemicellulose. The present work shows its ability to hydrolyse model pectins and to use them for growth. The main products on these substrates as well as on sugar beet pulps were as follows: acetate, ethanol and methanol. Galacturonase and lyase activities were measured in the fermentation broths. As shown by the accumulation of methanol in the medium, there is a pectin esterase activity but this one seems to be very low.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avrova NP, Zubko IK, Alekseeva EG (1981) Fermentation products and pectolytic enzyme activity ofCl. felsineum strains having different rates of spore germination. Microbiologiya 3:318–325
Barbier M, Thibault JF (1981) Pectic substances of cherry fruits. Phytochemistry 1, 21:111–115
Goel SC, Ramachandran KB (1983) Studies on the adsorption of cellulase on lignocellulose. J Ferment Technol 61:281–286
Gordon J (1981) Ph. D. Thesis. M.I.T. (Mass.) (1979)
Kapitonova LS, Rodionova NA, Feniskova RV (1972) Pectolytic enzymes ofCl. felsineum. Prikl Biokhim Mikrobiol 8:456–461
Lund BM, Brocklehurst JF (1978) Pectic enzymes of pigmentated strains ofClostridium. J Gen Microbiol 104:59–66
Miller GL (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugars. Anal Chem 31:426–428
NG TK, Weimer PJ, Zeikus JG (1977) Cellulolytic and physiological properties ofCl. thermocellum. Arch Microbiol 114:1–7
Obi SKC (1981) Pectinase activity of anaerobic and facultatively anaerobic bacteria associated with soft rot of Yam (Diascorea rotundata). Appl Env Microbiol 41:563–567
Park WS, Ryu DDY (1983) Cellulolytic activities ofCl. thermocellum and its carbohydrate metabolism. J Ferment Technol 61:563–571
Patni MJ, Alexander JK (1971) Utilization of glucose byCl. thermocellum: presence of glucokinase and other glycolytic enzymes in cell extracts. J Bacteriol 105:220–225
Popova I, Angelova S, Roshkova Z, Slyvsarencot T (1981) Possible utilization of enzyme hydrolyzate from sugar beet pulp for production of fodder yeast. Nauchni Tr, Vissh Inst Khranit Ukusova Prom ST, Plovdiv 27:179–187
Saddler JM, Chan MKH (1982) Optimization ofCl. thermocellum growth on cellulose and pretreated wood substrates. Eur J Appl Microbiol 16:99–104
Schink B, Zeikus JG (1980) Microbial methanol formation: a major end product of pectin metabolism. Current Microbiol 4:387–389
Schink B, Zeikus JG (1983) Characterization of pectinolitic enzymes ofCl. thermosulfurogenes. FEMS Microbiol Letters 17:295–298
Sheiman MI, MacMillan JO, Miller L, Chase JR (1976) Coordinated action of pectinesterase and polygalacturonase lyase complex ofCl. multifermentans. Eur J Biochem 64:565–572
Szymanski PT (1981) A note on the fermentation of pectins by pure strains and combined cultures of rumen bacteria. Acta Microbiologica Polonica 30:159–163
Thibault JF (1979) Automatisation du dosage des substances pectiques par la methode au meta-hydroxy diphenyl. Lebensm-Wiss and Technol 12:247–251
Wang DIC, Biocic I, Fang HY, Wang SD (1979) Direct microbiological conversion of cellulosic biomass to ethanol. “3rd Annual Biomass Energy Systems Conference” Golden,
Zertuche L, Zall RR (1982) A study of producing ethanol from cellulose usingCl. thermocellum. Biotechnol Bioeng 24:57–68
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Spinnler, H.E., Lavigne, B. & Blachere, H. Pectinolytic activity ofClostridium thermocellum: Its use for anaerobic fermentation of sugar beet pulp. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 23, 434–437 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02346055
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02346055