Abstract
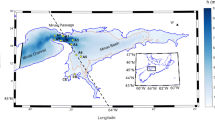
Horizontal variation of seston concentration in the shallow, eutrophic Loosdrecht Lakes (A=9.8 km2;\(\overline z \)=1.9 m) was studied in relation to windspeed and effective fetch. Simple wave theory was applied in order to predict resuspension using wind data from a nearby meteorological station. Most results were consistent with the theory, but a clear limit for the occurrence of resuspension could not be established. Generally, changes in epipelon—the particles at the sediment-water interface — were not directly related to computed frequency of resuspension at the sampling station. The frequency was estimated for 37 grid points over the entire lake. Resuspension was computed to affect high percentages of the lake area in winter. In summer the frequency was much lower, but in June and July 1984 there were days with nearly 50% of the lake area subject to resuspension. The resulting input of particulate organic carbon into the water column during these days was estimated to equal 12–25 times the daytime phytoplankton carbon fixation. Most of the resuspended matter appeared to be redeposited rapidly. The computed frequency of resuspension for the 37 locations of the lake varied between 7 and 48 days in 1984.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BEST, E.P.H., D. DE VRIES and A. REINS, 1984. The macrophytes in the Loosdrecht Lakes: a story of their decline in the course of eutrophication. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol., 22: 868–875.
BOERS, P.C.M., 1986. Studying the phosphorus release from the Loosdrecht Lake sediments using a continuous flow system. Hydrobiol. Bull.
CARPER, G.L. and R.W. BACHMANN, 1984. Wind resuspension of sediments in a prairie lake. Can. J. Fish. Aquat. Sci., 41: 1763–1767.
COASTAL ENGINEERING RESEARCH CENTER (C.E.R.C.), 1977, 1984. Shore protection manual. Vol. I. U.S. Army Engineer Waterways Experiment Station Coastal Engineering Research Center, Vicksburg, Miss.
DE GROOT, W.T., 1981. Phosphate and wind in a shallow lake. Arch. Hydrobiol., 91: 475–489.
GONS, H.J., 1982. Structural and functional characteristics of epiphyton and epipelon in relation to their distribution in Lake Vechten. Hydrobiologia, 95: 79–114.
GONS, H.J., R.D. GULATI and L. VAN LIERE, 1986. The eutrophic Loosdrecht Lakes: current ecological research and restoration perspectives. Hydrobiol. Bull. 20: 61–75.
GULATI, R.D., K. SIEWERTSEN and G. POSTEMA, 1985. Zooplankton structure and grazing activities in relation to food quality and concentration in Dutch lakes. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol., 21: 91–102.
HÅKANSON, L., 1977. The influence of wind, fetch, and water depth on the distribution of sediments in Lake Vänern, Sweden. Can. J. Earth Sci., 14: 397–412.
HÅKANSON, L., 1981. A manual of lake morphometry. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York.
JÓNASSON, P.M. and C. LINDEGAARD, 1979. Zoobenthos and its contribution to the metabolism of shallow lakes. Arch. Hydrobiol. Beih. Ergebn. Limnol., 13: 162–180.
KAL, B.F.M., G.B. ENGELEN and Th.E. CAPPENBERG, 1984. Loosdrecht Lakes restoration project: hydrology and physico-chemical characteristics of the lakes. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol., 22: 835–841.
KROMKAMP, J.C. and H.J. GONS, 1984. Seston-epipelon interrelationships in the shallow, eutrophic Loosdrecht Lakes. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol., 22: 853–857.
RIEGMAN, R., 1985. Phosphate-phytoplankton interactions., Thesis, University of Amsterdam, 143 pp.
RIJKEBOER, M., W.A. DE KLOET and H.J. GONS, 1986. A comparison of primary production measurements using two laboratory systems with differences in light quality. Hydrobiol. Bull. 20: 93–99
SMITH, I.R., 1979. Hydraulic conditions in isothermal lakes. Freshwater Biol., 9: 119–145.
SWEERTS, J-P.R.A., H.J. GONS and M. RIJKEBOER, 1986. Phosphate uptake capacity of Summer phytoplankton of the Loosdrecht Lakes in relation to phosphorus loading and irradiance. Hydrobiol. Bull.
VAN LIERE, L., 1986. Loosdrecht Lakes, origin, eutrophication, restoration and research programme. Hydrobiol. Bull. 20: 101–107.
VAN LIERE, L., T. ALDENBERG, L. VAN BALLEGOOIJEN, W.A. DE KLOET and K. SIEWERTSEN, 1986. Primary production in the various parts of Loosdrecht Lakes. Hydrobiol. Bull. 20: 77–85.
VAN LIERE, L., S. PARMA, L.R. MUR, P. LEENTVAAR and G.B. ENGELEN, 1984. Loosdrecht Lakes restoration project, an introduction. Verh. Internat. Verein. Limnol., 22: 829–834.
VEENINGEN, R. (in preparation). Significance of wind-induced resuspension for internal loading in a shallow eutrophic lake.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gons, H.J., Veeningen, R. & Van Keulen, R. Effects of wind on a shallow lake ecosystem: Resuspension of particles in the Loosdrecht Lakes. Hydrobiological Bulletin 20, 109–120 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291156
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02291156