Abstract
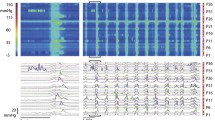
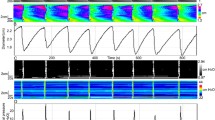
To investigate the mechanisms for elicitation of peristaltic activity in the human colon, we studied the effect of balloon distension of the transverse, descending, and sigmoid colon and the rectum. Fifteen healthy subjects were studied by means of a colonoscopically positioned probe carrying a 5-cm latex balloon. After positioning of the probe, stepwise distension was performed for each colonic segment (transverse, descending, sigmoid, rectum), and the onset of large (>50 mm Hg) and small (<50 mm Hg) propagated waves was observed. Analysis of the tracings showed: (1) In 8/15 subjects (53.3%), balloon distension elicited propagated contractions, but these contractions were qualitatively different from the spontaneously occurring high-amplitude propagated contractions previously found to occur in association with defecation. Therefore, intraluminal distension is probably not the cause of defecation-associated high-amplitude propagated contractions. (2) Pain reports were poorly correlated with propagated contractions elicited by balloon distension, suggesting that these contractions are not the cause of the pain produced by balloon distension. (3) The transverse colon shows lower pressures, fewer pain reports, and fewer large propagated contractions in response to balloon distension as compared to the descending and the sigmoid colon.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cherbut C, Achard F, Denavit M, Roche M: Relationships between electromyographic ileal and colonic motility patterns in cats during fasting and feeding. Can J Vet Res 50:106–110, 1986
Schuurkes JAJ, Tukker JJ: The interdigestive colonic motor complex of the dog. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 247:329–334, 1980
Fioramonti J, Bueno L: Diurnal changes in colonic motor profile in conscious dogs. Dig Dis Sci 28:257–264, 1983
Sarna SK, Condon R, Cowles V: Colonic migrating and nonmigrating motor complexes in dogs. Am J Physiol 246:G355-G360, 1984
Ferré JP, Ruckebusch Y: Myoelectrical activity and propulsion in the large intestine of fed and fasted rats. J Physiol (London) 362:93–106, 1985
Narducci F, Bassotti G, Gaburri M, Morelli A: Twenty four hour manometric recording of colonic motor activity in man. Gut 28:17–25, 1987
Bassotti G, Imbimbo BP, Gaburri M, Daniotti S, Morelli A: Transverse and sigmoid colon motility in healthy humans: Effect of eating and of cimetropium bromide. Digestion 37:59–64, 1987
Bassotti G, Bucaneve G, Pelli MA, Morelli A: Regular contractile patterns of the human colon. J Gastrointest Motil 2:73–78, 1990
Sarna SK: Physiology and pathophysiology of colonic motor activity. Part one. Dig Dis Sci 36:827–862, 1991
Huizinga JD, Daniel EE: Motor functions of the colon.In The Large Intestine: Physiology, Pathophysiology, and Disease. SF Phillips, JH Pemberton, RG Shorter (eds). New York, Raven Press, 1991, pp 93–114
Hertz AF: The passage of food along the human alimentary canal. Guy's Hosp Rep 61:389–427, 1907
Holzknecht G: Die normale Peristaltik des Colon. Munch Med Wochenschr 56:2401–2403, 1909
Ritchie JA: Colonic motor activity and bowel function. I. Normal movement of contents. Gut 9:442–456, 1968
Holdstock DJ, Misiewicz JJ, Smith T, Rowlands EN: Propulsion (mass movements) in the human colon and its relationship to meals and somatic activity. Gut 11:91–99, 1970
Ritchie JA: Mass peristalsis of the human colon after contact with oxyphenisatin. Gut 13:211–219, 1972
Karaus M, Sarna SK: Giant migrating contractions during defecation in the dog colon. Gastroenterology 92:925–933, 1987
Bassotti G, Gaburri M: Manometric investigation of high-amplitude propagated contractile activity of the human colon. Am J Physiol 255:G660-G664, 1988
Crowell MD, Bassotti G, Cheskin LJ, Schuster MM, Whitehead WE: Method for prolonged monitoring of high-amplitude propagated contractions from colon. Am J Physiol 261:G263-G268, 1991
Hardcastle JD, Mann CV: Study of large bowel peristalsis. Gut 9:412–420, 1968
Hardcastle JD, Mann CV: Physical factors in the stimulation of colonic peristalsis. Gut 11:41–46, 1970
Torsoli A, Ramorino ML, Ammaturo MV, Capurso L, Paoluzi P, Anzini F: Mass movements and intracolonic pressures. Am J Dig Dis 16:693–696, 1971
Bassotti G, Bucaneve G, Betti C, Morelli A: Sudden awakening from sleep: effects on proximal and distal colonic contractile activity in humans. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2:475–478, 1990
Bassotti G, Imbimbo BP, Betti C, Erbella GS, Pelli MA, Morelli A: Edrophonium chloride for testing colonic contractile activity in man. Acta Physiol Scand 141:289–293, 1990
Costa M, Furness JB: The peristaltic reflex: an analysis of the nerve pathways and their pharmacology. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 294:47–60, 1976
Christensen J, Lund GF: Esophageal responses to distention and electrical stimulation. J Clin Invest 48:408–419, 1969
Waldron DJ, Gill RC, Bowes KL: Pressure response of human colon to intraluminal distension. Dig Dis Sci 34:1163–1167, 1989
Preston DM, Lennard-Jones JE, Thomas BM: Towards a radiologic definition of idiopathic megacolon. Gastrointest Radiol 10:167–169, 1985
Richter JE, Dalton CB, Buice RG, Castell DO: Nifedipine: A potent inhibitor of contractions in the body of the human esophagus. Gastroenterology 89:549–554, 1985
Richter JE, Hackshaw BT, Wu WC, Castell DO: Edrophonium: A useful provocative test for esophageal chest pain. Ann Intern Med 103:14–21, 1985
Devroede G: Storage and propulsion along the large intestine.In Colon Structure and Function. L Bustos-Fernandez (ed). New York, Plenum, 1983, pp 121–139
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassotti, G., Gaburri, M., Imbimbo, B.P. et al. Distension-stimulated propagated contractions in human colon. Digest Dis Sci 39, 1955–1960 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088131
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02088131