Abstract
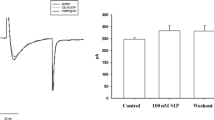
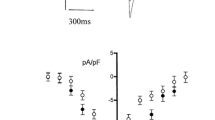
Rise in free cytosolic calcium concentrations [Ca2+]i in response to bradykinin and guanosine 5′-O-thiotriphosphate (GTPτS) was related to the action of phospholipase A2 (arachidonic acid release). At 900 μM extracellular CaCl2, bradykinin induced a typical Ca2+ movement consisting of an initial [Ca2+]i peak at approximately 400 nM followed by a sustained increase in the steady-state cytosolic Ca2+ level at approximately 290 nM. As the extracellular CaCl2 concentration was reduced to 100 μM, the bradykinin induced initial spike was reduced followed by only a marginal increase in steady-state cytosolic Ca2+ levels. Treatment of endothelial cells with saponin (0.002% w/w) did not increase [Ca2+]i and saponin treated cells exhibited a very similar pattern of Ca2+ mobilization in response to bradykinin. However, with saponin treatment, GTPτS (100 μM) increased [Ca2+]i at an almost identical tracing exhibited with 50 nM bradykinin stimulation (in either the presence or absence of 0.002% saponin). No additive increase in [Ca2+]i was observed in cells stimulated with both 100 μM GTPτS and 50 nM bradykinin or in bradykinin stimulated cells subsequently exposed to GTPτS. Pertussis toxin (PTX) did not affect the bradykinin induced Ca2+ mobilization. However, as we showed previously [1], PTX inhibited bradykinin stimulated arachidonic acid release. These results indicate transduction of the bradykinin signal by G-protein for both phospholipase A2 (PLA2) activation and Ca2+ mobilization but likely by different Gα subunits, a PTX sensitive and an insensitive subunit. Furthermore, the bradykinin and GTPτS stimulated release of arachidonic acid appears to be only partially dependent on [Ca2+]i. For example, 10 μM ionomycin, a calcium ionophore, did not release arachidonic acid at extracellular CaCl2 concentrations below 300 μM while GTPτS stimulated a greater release of arachidonic acid at 300 and 100 μM CaCl2 than at 900 μM CaCl2. However, at 100 μM CaCl2, ionomycin increased [Ca2+]i to the same level as bradykinin or GTPτS stimulated cells incubated in 900 μM CaCl2.
In previously published experiments [1], we showed that phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (TPA) augments bradykinin activated arachidonic acid release in endothelial cells. In the absence of bradykinin, TPA had little effect on arachidonic acid release by endothelial cells. However, in the saponin treated cells, TPA alone (in the absence of bradykinin) caused a marked release of arachidonic acid. The bradykinin and TPA activated arachidonic acid releases were additive. The TPA activated release did not require an increase in [Ca2+]i and occurred in the absence of any added extracellular CaCl2. TPA did not induce an increase in [Ca2+]i in either saponin treated or untreated endothelial cells. This TPA stimulated release of arachidonic acid was totally down-regulated by an 18 h preincubation of the cells in 500 nM TPA but was not inhibited by protein kinase C inhibitor H7.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
D. A. Ricupero, L. Taylor, A. Tlucko, J. Navarro and P. Polgar, Mediat. Inflammation1, 133 (1992).
A. R. Whorton, S. L. Yong, J. L. Data, A. Barachowsky and R. S. Kent, Biochim. Biophys. Acta712, 79 (1982).
W. P. Schilling, L. Rajan and E. Strobl-Jager, J. Biol. Chem.264, 12838 (1989).
R. J. Flower and G. J. Blackwell, Biochem. Pharmacol.25, 285 (1976).
S. L. Hong and D. Deykin, J. Biol. Chem.257, 7151 (1982).
S. L. Hong, N. J. McLaughlin, C. Tzeng and G. Patton, Thrombin Res.38, 1 (1985).
E. A. Jaffe, J. Grulich, B. B. Weksler, G. Hampel and K. Watanabe, J. Biol. Chem.263 8557 (1987).
H. Kaya, G. M. Patton and S. L. Hong, J. Biol. Chem.264, 4972 (1989).
S. Kremer, P. Harper, R. Hegele and K. Skorecki, Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol.66, 43 (1987).
M. Colden-Stanfield, W. P. Schilling, A. K. Ritchie, S. G. Eskin, L. T. Navarro and D. L. Kunze, Circ. Res.61, 632 (1987).
R. Morgan-Boyd, J. M. Stewart, F. J. Vavrek and A. Hassid, Am. J. Phys.253, c588 (1987).
P. C. Sternweis and I. Pang, Trends Neurosci.13, 122 (1990).
L. Birnbaumer, J. Abramowitz and A. M. Brown, Biochem. Biophys. Acta1031, 163 (1990).
B. J. Buckley, A. Barachowsky, R. J. Dolor and A. R. Whorton, Biochem. J.280, 281 (1991).
A. Lückhoff, U. Pohl, A. Mülsch and R. Busse, Br. J. Pharmacol.95, 189 (1988).
A. R. Whorton, C. E. Willis, R. S. Kent and S. L. Young, Lipids19, 17 (1984).
R. A. Voyno-Yasenetskaya, V. A. Tkachuk, E. G. Cheknyova, M. P. Panchenko, G. Y. Grigorian, R. J. Vavrek, J. M. Stewart and U. S. Ryan, FASEB J.3, 44 (1989).
T. L. Lambert, R. S. Kent and A. R. Worton, J. Biol. Chem.261, 15288 (1986).
C. K. Derian and M. A. Moskowitz, J. Biol. Chem.261, 3831 (1986).
A. Lückhoff, R. Zeh and R. Busse, Pfleüegers Arch.412, 654 (1988).
M. Menconi, G. Hahn and P. Polgar, J. Cell. Physiol.120, 163 (1984).
G. Fiskum, Cell Calcium6, 25 (1985).
S. Chueh and D. L. Gill, J. Biol. Chem.261, 13883 (1986).
S. Nakashima, T. Tohmatsu, H. Hattori, A. Suganuma and Y. Nozawa, J. Biochem.101, 1055 (1987).
G. Grynkiewicz, M. Poenie and R. Y. Tsien, J. Biol. Chem.260, 3440 (1985).
S. Levy and A. Fein, J. Gen. Physiol.85, 805 (1985).
A. Jones, T. W. Lategan, N. J. Lodge, U. S. Ryan, C. van Breeman and D. J. Adams, Tissue and Cell19, 733 (1987).
K. W. Buchan and W. Martin, Br. J. Pharmacol.102, 35 (1991).
W. P. Schilling and S. J. Elliott, Am. J. Physiol.262, H1617 (1992).
T. A. Voyno-Yasenetskaya, M. P. Panchenko, E. V. Nupenko, V. O. Rybin and V. A. Thachuk, FEBS Lett.259, 67 (1989).
S. Gutowski, A. Smrcka, L. Nowak, D. Wu, M. Simon and P. C. Sternweis, J. Biol. Chem.266, 20519 (1991).
S. L. Hong and D. Deykin, J. Biol. Chem.254, 11463 (1979).
S. L. Hong, Prog. Allergy44, 99 (1988).
J. D. Sharp, D. L. White, X. G. Chiou, T. Goodson, G. C. Gamboa, D. McClure, S. Burgett, J. Hoskin, P. L. Skatrud, L. H. Kang, E. F. Robert and R. M. Kramer, J. Biol. Chem.266, 1480 (1991).
J. D. Clark, L.-L. Lin, R. W. Kriz, C. S. Ramesha, L. A. Sultzman, A. Y. Lin and J. L. Knopf, Cell65, 1043 (1991).
A. E. McEachern, E. R. Shelton, S. Bhakta, R. Obernolte, B. Chinh, P. Zuppan, J. Fujisaki, R. W. Aldrich and K. Jarnagin, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA88, 7724 (1991).
C. L. Jelsema and J. Axelrod, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA84, 3623 (1987).
D. Kim, D. L. Lewis, L. Graziadei, E. J. Neer, D. Bar-Sagi and D. E. Clapman, Nature337, 557 (1989).
R. M. Burch, Mol. Neurobiol.3, 155 (1989).
R. L. Bell, D. A. Kennedy, N. Stanford and P. W. Majerus, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA76, 3238 (1979).
Y. Nishizuka, J. Am. Assoc.262, 1826 (1989).
M. J. Berridge, J. Am. Med. Assoc.262, 1834 (1989).
P. J. Parker, G. Kour, R. M. Marais, F. Mitchell, C. Pears, D. Schaap, S. Stabel and C. Webster, Mol. Cell. Endocrinol.65, 1 (1989).
D. Schaap, P. J. Parker, A. Bristol, R. Kriz and J. Knopf, FEBS Lett.243, 351 (1989).
K. Sekiguchi, M. Tsukuda, K. Ogita, U. Kikkawa and Y. Nishizuka, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun.145, 797 (1987).
S. Paglin, R. Roy and P. Polgar, J. Biol. Chem.268, 11697 (1993).
K. S. Ha and J. H. Exton, J. Biol. Chem.268, 10534 (1993).
J. Noireaud, C. M. Bright and D. Ellis, J. Mol. Cardiol.21, 291–298 (1989).
A. Y. Lin, M. Wartman, L. Y. Lin, J. L. Kopf, A. Seth and R. J. Davis, Cell72, 269–278 (1993).
K. Ha-Soo and J. H. Exton, J. Biol. Chem.268, 10534 (1989).
F. L. Haddy, T. E. Emerson, J. B. Scott and R. M. Dougherty, Handbook Exp. Pharmacol.25, 362 (1970).
D. Regoli, N. Rhaleb, G. Drapeau, S. Dion, C. Tousignant and P. D'Orleans-Juste, Adv. Exp. Med. Biol.236, 399 (1990).
T. Griesbacher and F. Lembeck, Br. J. Pharmacol.92, 333 (1987).
T. S. Chao, K. L. Byron, K. M. Lee, M. Villereal and M. R. Rosner, J. Biol. Chem.267, 19876 (1992).
G. S. Campbell, L. Pang, T. Miyasaka, A. R. Saltiel and C. Charter-Su, J. Biol. Chem.267, 6074 (1992).
L. L. Lin, M. Wartman, A. Y. Lin and J. L. Knopf, Cell72, 269 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ricupero, D., Taylor, L. & Polgar, P. Interactions of bradykinin, calcium, G-protein and protein kinase in the activation of phospholipase A2 in bovine pulmonary artery endothelial cells. Agents and Actions 40, 110–118 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976759
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01976759