Abstract
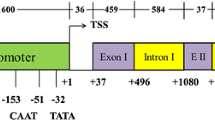
A set of plasmids has been constructed utilizing the promoter, 5′ untranslated exon, and first intron of the maize ubiquitin (Ubi-1) gene to drive expression of protein coding sequences of choice. Plasmids containing chimaeric genes for ubiquitin-luciferase (Ubi-Luc), ubiquitin-β-glucuronidase (Ubi-GUS), and ubiquitin-phosphinothricin acetyl transferase (Ubi-bar) have been generated, as well as a construct containing chimaeric genes for bothUbi-GUS andUbi-bar in a single plasmid. Another construct was generated to allow cloning of protein coding sequences of choice onBam HI andBam HI-compatible restriction fragments downstream of theUbi-1 gene fragment. Because theUbi-1 promotor has been shown to be highly active in monocots, these constructs may be useful for generating high-level gene expression of selectable markers to facilitate efficient transformation of monocots, to drive expression of reference reporter genes in studies of gene expression, and to provide expression of biotechnologically important protein products in transgenic plants.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. (1989)Current Protocols in Molecular Biology, Vols. 1 and 2 New York: Wiley.
Block, M. de, Botterman, J., Vandewiele, M., Dockx, J., Thoen, C., Goosele, V., Movva, N.R., Thompson, C., Montagu, M. Van and Lemmans, J. (1987) Engineering herbicide resistance in plants by expression of a detoxifying enzyme.EMBO J. 6, 2513–8.
Bruce, W.B., and Quail, P.H. (1990)Cis-acting elements involved in photoregulation of an oat phytochrome promoter in rice.Plant Cell 2, 1081–9.
Bruce, W.B., Christensen, A.H., Klein, T., Fromm, M. and Quail, P.H. (1989) Photoregulation of a phytochrome gene promoter from oat transferred into rice by particle bombardment.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 86, 9692–6.
Callis, J., Fromm, M. and Walbot, V. (1988) Heat inducible expression of a chimeric maize hsp70CAT gene in maize protoplasts.Plant Physiol. 88, 965–8.
Christensen, A.H., Sharrock, R.A. and Quail, P.H. (1992) Maize polyubiquitin genes: structure, thermal perturbation of expression and transcript splicing, and promoter activity following transfer to protoplasts by electroporations.Plant Mol. Biol. 18, 675–89.
Cornejo, M.J., Luth, D., Blankenship, K.M., Anderson, O.D. and Blechl, A.E. (1993) Activity of a maize ubiquitin promoter in transgenic rice.Plant Mol. Biol. 23, 567–81.
Devereux, J., Haeberli, P. and Smithies, O. (1984) A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX.Nucl. Acids Res. 12, 387–95.
Fromm, M.E., Morrish, F., Armstrong, C., Williams, R., Thomas, J. and Klein, T.M. (1990) Inheritance and expression of chimeric genes in the progeny of transgenic maize plants.Biol/Technology 8, 833–9.
Gallo-Meagher, M. and Irvine, J.E. (1993) Effects of tissue type and promoter strength on transient GUS expression in sugarcane following particle bombardment.Plant Cell Rep. 11, 567–70.
Goff, S.A., Cone, K.C. and Fromm, M.E. (1991) Identification of functional domains in the maize transcriptional activator C1: comparison of wild-type and dominant inhibitor proteins.Gen. Dev. 5, 298–309.
Jefferson, R.A., Kavanagh, T.A. and Bevan, M.W. (1987) GUS fusions: β-glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants.EMBO J. 6, 3901–7.
Kyozuka, J., Fujimoto, H., Izawa, T. and Shimamoto, K. (1991) Anaerobic induction and tissue-specific expression of maizeAdh1 promoter in transgenic rice plants and their progeny.Mol. Gen. Genet. 228, 40–8.
McElroy, D. and Brettell, R.I.S., (1994) Foreign gene expression in transgenic cereals.Trends Biotech. 12, 62–8.
McElroy, D., Zhang, W. and Wu, R. (1990) Isolation of an efficient actin promotor for use in rice transformation.Plant Cell 2, 163–71.
Ow, D., Wood, K.V., DeLuca, M., Wet, J.R. de, Helinski, D.R. and Howell, S.P. (1986) Transient and stable expression of the firefly luciferase gene in plant cells and transgenic plants.Science 234, 856–9.
Rolfe, S.A. and Tobin, E.M. (1991) Deletion analysis of a phytochrome-regulated monocotrbcS promoter in a transient assay system.Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 88, 2683–6.
Schledzewski, K. and Mendel, R. (1994) Quantitative transient gene expression: comparison of the promoters for maize polyubiquitin 1 rice actin 1, maize derivedEmu and CaMV 35S in cells of barley, maize and tobacco.Transgenic Res. 3 249–55.
Takimoto, I., Christensen, A.H., Quail, P.H., Uchimiya, H. and Toki, S. (1994) Non-systemic expression of a stress-responsive maize polyubiquitin gene (Ubi-1) in transgenic rice plants.Plant Mol. Biol. 26, 1007–12.
Taylor, M.G., Vasil, V. and Vasil, I.K. (1993) Enhanced GUS gene expression in cereal/grass cell suspensions and immature embryos using the maize ubiquitin-based plasmid pAHC25.Plant Cell Rep. 12, 491–5.
Toki, S., Takamatsu, S., Ooba, S., Anzai, H., Iwata, M., Christensen, A.H., Quail, P.H. and Uchimiya, H., (1992) Expression of maize ubiquitin gene promoter-bar chimeric gene in transgenic rice plants.Plant Physiol. 100, 1503–7.
Uchimiya, H., Iwata, M., Nojiri, C., Smarajeewa, P.K., Takamatsu, S., Ooba, S., Anzai, H., Christensen, A.H., Quail, P.H. and Toki, S. (1993) Bialaphos treatment of transgenic rice plants expressing a bar gene prevents infection by the sheath blight pathogen (Rhizoctonia solani).Bio/Technology 11, 835–36.
Vasil, V., Srivastava, V., Castillo, A.M., Fromm, M.E. and Vasil, I.K. (1993) Rapid production of transgenic wheat plants by direct bombardment of cultured immature embryos.Biol/Technology 11, 1553–8.
Wan, Y. and Lemaux, P.G. (1994) Generation of large numbers of independently transformed fertile barley plants.Plant Physiol. 104, 37–48.
Weeks, T.J., Anderson, O.D. and Blechl, A.E. (1993) Rapid production of multiple independent lines of fertile transgenic wheat (Triticum aestivum).Plant Physiol. 102, 1077–84.
Wilmink, A., van de Ven, B.C.E. and Dons, J.J.M. (1995) Activity of constitutive promoters in various species from the Lilaceae.Plant Mol. Biol. 28, 949–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Christensen, A.H., Quail, P.H. Ubiquitin promoter-based vectors for high-level expression of selectable and/or screenable marker genes in monocotyledonous plants. Transgenic Research 5, 213–218 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01969712
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01969712