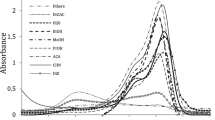
Summary
Membrane fusion induced by ions and its associated membrane property, surface dielectric constant, were studied with the use of acidic and neutral phospholipid vesicles. The fusion of vesicles was monitored by utilizing two fluorescence fusion assays: fluorescence content mixing method and fluorescence labelled membrane component dilution method. For the surface dielectric constant measurements, a fluorescence method was used which detected the environmental effect on the membrane surface upon the addition of various fusogenic cations. Also, the effects of poly-(ethylene glycol) on both fusion and surface dielectric properties were examined. It was found that the extent of fusion correlated well with the degree of lowering in the dielectric constant of the surface membrane, which corresponds to the increase in hydrophobicity of the membrane surface. This agrees with the previously obtained experimental results that the increase in interfacial tension of the membrane, which also corresponds to the increase in surface hydrophobicity, correlates with the extent of membrane fusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnold, K., Herrmann, A., Gawrisch, K., Pratsch, L. 1988. Water-mediated effects of PEG on membrane properties and fusion.”In: Molecular Mechanisms of Membrane Fusion. S. Ohki, D. Doyle, T.D. Flanagan, S.W. Hui, and E. Mayhew, editors. pp 255–272. Plenum, New York
Arnold, K., Herrmann, A., Pratsch, L., Gawrisch, K. 1985. The dielectric properties of aqueous solution of poly-(ethylene glycol) and their influence on membrane structure.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 815:515–518
Arnold, K., Zschornig, O., Herold, W., Barthel, D. 1987. Effect of PEG on the electrophoretic mobility of liposomes.Mol. Cryst. Liq. Cryst. 152:357–362
Duzgunes, N., Ohki, S. 1977. Calcium-induced interaction of phospholipid vesicles and bilayer lipid membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 467:301–308
Ekerdt, R., Papahadjopoulos, D. 1980. Intermembrane contact affects calcium binding to phospholipid vesicles.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 79:2273–2277
Feigenson, G.W. 1986. On the nature of calcium ion binding between phosphatidylserine lamellae.Biochemistry 25:5819–5825
Hauser, H., Finer, G.E., Darke, A. 1977. Crystalline anhydrous Ca-phosphatidylserine bilayers.Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 76:267–274
Hiemenz, P.C. 1977. Principles of Colloid and Surface Chemistry. Marcel Dekker, New York
Hoekstra, D. 1982. Role of lipid phase separation and membrane hydration in phospholipid vesicle fusion.Biochemistry 21:2833–3840
Kimura, Y., Ikegami, A. 1985. Local dielectric properties around polar region of lipid bilayers membranes.J. Membrane Biol. 85:225–231
LeNeveu, D.M., Rand, P., Parsegian, A. 1976. Measurement of forces between lecithin bilayers.Nature (London) 259:601–603
Lippert, E. von 1957. Spektroskopische Bestimmung des Dipolmoments Aromatischer Verbindungen im ersten Angeregten Singulettzustand.Z. Electrochem. 61:962–975
MacDonald, R.I. 1985. Membrane Fusion Due to Dehydration by Polyethylene Glycol, Dextran or Sucrose.Biochemistry 24:4058–4066
Marcelja, S., Radic, N. 1976. Repulsion of interfaces due to bound water.Chem. Phys. Lett. 42:129–130
Mataga, N., Kaifu, Y., Koizumi, M. 1955. The solvent effect on fluorescence spectrum. Changes of solute-solvent interaction during the life time of excited solute molecule.Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 28:690–691
Ohki, S. 1982. A mechanism of divalent ion-induced phosphatidylserine membrane fusion.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 689:1–11
Ohki, S. 1985. Membrane fusion: Theory and experiments.Studia Biophys. 111:95–104
Ohki, S. 1988. Surface tension, hydration energy and membrane fusion.In: Molecular Mechanism of Membrane Fusion. S. Ohki, D. Doyle, T.D. Flanagan, S.W. Hui, and E. Mayhew, editors. pp. 123–138. Plenum, New York
Ohki, S., Doyle, D., Flanagan, T.D., Hui, S.W., Mayhew, E. (editors) 1988. Molecular Mechanisms of Membrane Fusion, Plenum, New York
Ohki, S., Duax, J. 1986. Effects of cations and polyamines on the aggregation and fusion of phosphatidylserine membranes.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 861:177–186
Ohki, S., Ohshima, H. 1984. Divalent cation-induced surface tension increase in acidic phospholipid membranes: Ion binding and membrane fusion.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 776:177–182
Parente, T.A., Lentz, B.R. 1986. Rate and extent of poly-(ethylene glycol)-induced large vesicle fusion monitored by bilayer and internal content mixing.Biochemistry 25:6678–6688
Portis, A., Newton, C., Pangborn, W., Papahadjopoulos, D. 1979. Studies on the mechanism of membrane fusion: Evidence for an intermembrane Ca2+-phospholipid complex synergism with Mg2+ and inhibition by spectrin.Biochemistry 18:780–790
Poste, G., Allison, A.C. 1973. Membrane Fusion.Biochim. Biophys. Acta 300:421–465
Poste, G., Nicolson, G.L. (editors) 1978. Membrane Fusion. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Rasmussen, H. 1970. Cell communication, calcium ion, and cyclic adenosine monophosphate.Science 170:404–412
Sowers, A.E. (editor) 1987. Membrane Fusion. Plenum, New York
Struck, D.K., Hoekstra, D., Pagano, R.E. 1981. Use of resonance energy transfer to monitor membrane fusion.Biochemistry 20:4093–4099
Waggoner, A.S., Stryer, L. 1970. Fluorescent probes of biological membranes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 67:579–589
Weast, R.C. (editor). 1968. Handbook of Chemistry and Physics. The Chemical Rubber Co., Cleveland (OH)
Wilshut, J., Papahadjopoulos, D. 1979. Ca2+-induced fusion of phospholipid vesicles monitored by mixing of aqueous contents.Nature (London) 281:690–692
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohki, S., Arnold, K. Surface dielectric constant, surface hydrophobicity and membrane fusion. J. Membrain Biol. 114, 195–203 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869214
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01869214