Abstract
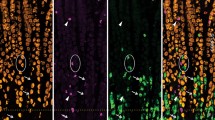
The distribution of nerve fibres immunoreactive for vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), substance P (SP), methionine-enkephalin (ENK), calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and neuropeptide Y (NPY) within the circular muscle layer was examined histochemically in the human pylorus, adjacent antrum and duodenum. Longitudinal cryostat sections of the pyloric and surrounding regions were stained by an indirect immunofluorescence method, and the total length of each type of peptidecontaining fibre per unit sectional area (µm/mm2) was measured using an image-analysing system. The narrow region of the circular muscle layer bordering the submucosa in the pylorus contained a rich supply of VIP, SP, ENK and CGRP immunoreactive fibres; VIP fibres were most prominent with less SP and ENK fibres and moderate amounts of CGRP. These peptide-containing nerve fibres were more dense than in the pyloric circular muscle, the longitudinal muscle layer and also the adjacent muscle layer. NPY-immunoreactive fibres were sparsely distributed throughout the pyloric region. These results suggest that the inner edge of the circular muscle, lying adjacent to the submucosa and densely innervated with peptidecontaining fibres, may be a characteristic feature of the human pyloric sphincter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Edin R, Lundberg J, Ahlman H, Dahlstrom A, Kahrenkrug J, Hokfelt T, Kewenter J. On the VIPergic innervation of the feline pylorus.Acta Physiol Scand 1979;107: 185–187.
Edin R, Lundberg J, Terenius L, Dahlstrom A, Hokfelt T, Kewenter J, Ahlman H. Evidence for vagal enkephalinergic neural control of the feline pylorus and stomach.Gastroenterology 1980;78: 492–497.
Alumets J, Fahrenkrug J, Håkanson R, Shafflitzky de Muckadell OB, Sundler F, Uddman R. A rich VIP nerve supply is characteristic of sphincters.Nature 1979;280: 155–156.
Lidberg P, Dahlstrom A, Lundberg JM, Ahlman H. Different modes of action of substance P in the motor control of the feline stomach and pylorus.Regulatory Peptides 1983;7: 41–52.
Daniel EE, Berezin I, Allescher HD, Manaka H, Posey-Daniel V. Morphology of the canine pyloric sphincter in relation to function.Can J Physiol Pharmacol 1989;67: 1560–1573.
McGregor GP, Bishop AE, Blank MA, Christofides ND, Yiangou Y, Plak JM, Bloom SR. Comparative distribution of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, substance P and PHI in the enteric sphincters of the cat.Experientia 1984;40: 469–471.
Wattchow DA, Furness JB, Costa M. Distribution and coexistence of peptides in nerve fibers of the external muscle of the human gastrointestinal tract.Gastroenterology 1988;95: 32–41.
Wattchow DA, Cass DT, Furness JB, Costa M, O'Brien PE, Little KE, Pitkin J. Abnormalities of peptide-containing nerve fibers in infantile hypertrophic stenosis.Gastroenterology 1987;92: 443–448.
Ferri GL, Adrian TE, Soimero L, Blank M, Cavalli D, Biliotti G, Polak JM, Bloom SR. Intramural distribution of immunoreactive vasoactive intestinal polypeptide (VIP), substance P, somatostatin and mammalian bombesin in the oesophago-gastro-pyloric region of the human gut.Cell Tissue Res 1989;256: 191–197.
Vogalis F, Ward SM, Sanders KM. Correlation between electrical and morphological properties of canine pyloric circular muscle.Am J Physiol 1991;260: G390-G398.
Vogalis F, Sanders KM. Excitatory and inhibitory neural regulation of canine pyloric smooth muscle.Am J Physiol 1990;259: G125-G133.
Coons AH. Fluorescent antibody method. In: Danielli JF, ed.General Cytochemical Methods. New York: Academic Press, 1958: 339–422.
Lidberg P, Edin R, Lundberg JM, Dahlstrom A, Rossel S, Folkers K, Ahlman H. Substance P is involved in the vagal excitatory motor control of the pylorus.Acta Physiol Scand 1982;144: 307–309.
Papasova M. Sphincteric function. In: Schultz SG, Wood JD, Bauner BB, eds.Handbook of Physiology, Section 6, The Gastrointestinal System, Vol. 1, Motility and Circulation, Part 2. Am Physiol Soc 1989; 987–1023.
Reynolds JC, Quyang A, Cohen S. Evidence for an opiate-mediated pyloric sphincter reflex.Am J Physiol 1984;246: G130-G136.
Anuras S, Cooke AR, Christensen J. An inhibitory innervation at the gastroduodenal junction.J Clin Invest 1974;54: 529–535.
Milenov K, Golenhofen K. Differentiated contractile responses of gastric smooth muscle to substance P.Pflüegers Arch 1983;397: 29–34.
Cai W-Q, Gabella G. Structure and innervation of the musculature at the gastroduodenal junction of the guinea-pig.J Anat 1984;139: 93–104.
Ekblad E, Winther C, Ekman R, Håkanson R, Sundler F. Projections of peptide-containing neurons in rat small intestine.Neuroscience 1987;20: 169–188.
Furness JB, Costa M. Studies of neuronal circuitry of the enteric nervous system. In:The Enteric Nervous System. Edinburgh: Churchill Livingstone, 1987: 111–136.
Allescher HD, Daniel EE, Dent J, Fox JET. Inhibitory function of VIP-PHI and galanin in canine pylorus.Am J Physiol 1989;256: G789-G797.
Allescher HD, Kostolanska F, Tougas G, Fox JET, Regoli D, Drapeau G, Daniel EE. The actions of neurokinins and substance P in canine pylorus, antrum and duodenum.Peptides 1989;10: 671–679.
Merlo A, Cohen S. Mechanics and neuropeptide responses of feline pylorus and gastric rousclein vitro.Am J Physiol 1989;256: G862-G867.
Inui T, Chiba T, Okimura Y, Morishita T, Nakamura A, Yamaguchi T, Yamatani T, Kadowaki S, Chihara K, Fujita T. Presence and release of calcitonin gene-related peptide in rat stomach.Life Sci 1989;45: 1199–1206.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Domoto, T., Oki, M., Kotoh, T. et al. Heterogenous distribution of peptide-containing nerve fibres within the circular muscle layer of the human pylorus. Clinical Autonomic Research 2, 403–407 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01831399
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01831399