Summary
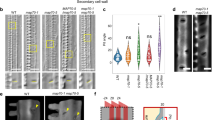
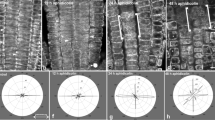
The outer tangential wall (OTW) of epidermal cells of azuki bean epicotyls has a crossed polylamellate structure, in which lamellae of longitudinal cellulose microfibrils alternate with lamellae of transverse cellulose microfibrils. This implies that the cyclic reorientation of cortical microtubules (MTs) from longitudinal to transverse and from transverse to longitudinal occurs on the OTW. Treatment with a solution that contained no auxin caused the accumulation of cells with longitudinal MTs, suggesting that auxin is required for the reorientation of MTs from longitudinal to transverse during the reorientation cycle. Treatment with 6-dimethylaminopurine (DMAP), an inhibitor of protein kinases that promoted the reorientation of MTs from transverse to longitudinal, resulted in the accumulation of cells with longitudinal MTs. Subsequent treatment with auxin caused a marked increase in the percentage of cells with transverse MTs and then a decrease in the percentage, indicating that the reorientation of MTs from longitudinal to transverse and then from transverse to longitudinal occurred during treatment with auxin. The percentage of cells with transverse MTs decreased more slowly in segments that had been pretreated with gibberellin A3 (GA) than in segments that had been pretreated without GA, suggesting that GA, in cooperation with auxin, caused the suppression of the reorientation of MTs from transverse to longitudinal.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BL:
-
brassinolide
- BSA:
-
bovine serum albumin
- GA:
-
gibberellin A3
- DMAP:
-
6-dimethylaminopurine
- DMSO:
-
dimethylsulfoxide
- FITC:
-
fluorescein isothiocyanate
- IAA:
-
indoleacetic acid
- MT:
-
microtubule
- OTW:
-
outer tangential wall
- PBS:
-
phosphate-buffered saline
References
Akashi T, Shibaoka H (1987) Effects of gibberellin on the arrangement and the cold stability of cortical microtubules in epidermal cells of pea internodes. Plant Cell Physiol 28: 339–348
Bergfeld R, Speth V, Schopfer P (1988) Reorientation of microfibrils and microtubules at the outer epidermal wall of maize coleoptiles during auxin-mediated growth. Bot Acta 101: 57–67
Chafe SC, Wardrop AB (1972) Fine structural observation on the epidermis. I. The epidermal cell wall. Planta 107: 269–278
Ishida K, Katsumi M (1992) Effects of gibberellin and abscisic acid on the cortical microtubule orientation in hypocotyl cells of light-grown cucumber seedlings. Int J Plant Sci 153: 155–163
Iwata K, Hogetsu T (1989) The effects of light irradiation on the orientation of microtubules in seedlings ofAvena sativa L. andPisum sativum L. Plant Cell Physiol 30: 1011–1016
Kaneta T, Kakimoto T, Shibaoka H (1993) Actinomycin D inhibits the GA3-induced elongation of azuki bean epicotyls and the reorientation of cortical microtubules. Plant Cell Physiol 34: 1125–1132
Mayumi K, Shibaoka H (1995) A possible double role for brassinolide in the reorientation of cortical microtubules in the epidermal cells of azuki bean epicotyls. Plant Cell Physiol 36: 173–181
Mita T, Katsumi M (1986) Gibberellin control of microtubule arrangement in the mesocotyl epidermal cells of the d5 mutant ofZea mays L. Plant Cell Physiol 27: 651–659
—, Shibaoka H (1984) Gibberellin stabilizes microtubules in onion leaf sheath cells. Protoplasma 119: 100–109
Mizuno K (1994) Inhibition of gibberellin-induced elongation, reorientation of cortical microtubules and change of isoform of tubulin in epicotyl segments of azuki bean by protein kinase inhibitors. Plant Cell Physiol 35: 1149–1157
Nakamura Y, Shibaoka H (1980) Increase in the gibberellin response by low temperature pretreatment of azuki bean epicotyls. Bot Mag Tokyo 93: 77–87
Nick P, Bergfeld R, Schäfer E, Schöpfer P (1990) Unilateral reorientation of microtubules at the outer epidermal wall during photoand gravitropic curvature of maize coleoptiles and sunflower hypocotyls. Planta 181: 162–168
Sakiyama M, Shibaoka H (1990) Effects of abscisic acid on the orientation and cold stability of cortical microtubules in epicotyl cells of the dwarf pea. Protoplasma 157: 165–171
Sakoda M, Hasegawa K, Ishizuka K (1992) Mode of action of natural growth inhibitors in radish hypocotyl elongation — influence of raphanusanin on auxin-mediated microtubule orientation. Physiol Plant 84: 509–513
Sauter M, Seagull RW, Kende H (1993) Internodal elongation and orientation of cellulose microfibrils and microtubules in deepwater rice. Planta 190: 354–362
Shibaoka H (1991) Microtubules and the regulation of cell morphogenesis by plant hormones. In: Lloyd CW (ed) The cytoskeletal basis of plant growth and form. Academic Press, London, pp 159–168
— (1993) Regulation by gibberellins of the orientation of cortical microtubules in plant cells. Aust J Plant Physiol 20: 461–470
— (1994) Plant hormone-induced changes in the orientation of cortical microtubules: alterations in the cross-linking between microtubules and the plasma membrane. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 45: 527–544
Takeda K, Shibaoka H (1978) The fine structure of the epidermal cell wall in azuki bean epicotyl. Bot Mag Tokyo 91: 235–245
— — (1981) Effects of gibberellin and colchicine on microfibril arrangement in epidermal cell walls ofVigna angularis Ohwi et Ohashi epicotyls. Planta 151: 393–398
Yuan M, Warn RM, Shaw PJ, Lloyd CW (1995) Dynamic microtubules under the radial and outer tangential walls of microinjected pea epidermal cells observed by computer reconstruction. Plant J 7: 17–23
Zandomeni K, Schopfer P (1993) Reorientation of microtubules at the outer epidermal wall of maize coleoptiles by phytochrome, blue-light photoreceptor, and auxin. Protoplasma 173: 103–112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Eldon H. Newcomb in recognition of his contributions to cell biology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mayumi, K., Shibaoka, H. The cyclic reorientation of cortical microtubules on walls with a crossed polylamellate structure: effects of plant hormones and an inhibitor of protein kinases on the progression of the cycle. Protoplasma 195, 112–122 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279190
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01279190