Abstract
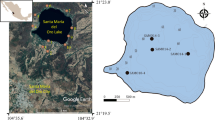
The recent chronology of metal deposition was examined in Lake Pepin, a large natural lake on the Upper Mississippi River about 75 km downstream from the Minneapolis-St. Paul, Minnesota, metropolitan area. The lake, which has a high trapping efficiency for suspended sediments, serves as a sink for metals from industrial and domestic effluents discharged into the river. Sediment cores collected in 1981 from seven locations in the lake were analyzed for Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn, and Al (a reference element). Dating of a core with137Cs indicated that inputs of these metals increased markedly in the late 1950s, peaked in the early 1970s, and decreased in the late 1970s to 1981. Sediment enrichment factors decreased in the order Pb>Cd>Cu⩾Cr>Zn>Ni. The depth of the most highly contaminated strata in the core profiles decreased longitudinally from upstream to downstream—paralleling the upstreamto-downstream decrease in sedimentation rates. Changes in metal inputs to the lake would be most readily detected by analysis of sediments from the uppermost reaches, but the potential for release of sediment-associated metals to the water column is probably greatest in downstream reaches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bailey PA (1983) Distribution and enrichment of trace metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in bottom sediments of Navigation Pools 4 (Lake Pepin), 5, and 9 of the Upper Mississippi River. MS Thesis, Univ Wisconsin-La Crosse, La Crosse, WI
Bailey PA, Rada RG (1984) Distribution and enrichment of trace metals (Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, Zn) in bottom sediments of Navigation Pools 4 (Lake Pepin), 5, and 9 of the Upper Mississippi River. In: Wiener JG, Anderson RV, McConville DR (eds) Contaminants in the Upper Mississippi River. Butterworth Publ. Boston, MA, pp 119–138
Campbel PGC, Lewis AG, Chapman PM, Crowder AA, Fletcher WK, Imber B, Luoma SN, Stokes PM, Winfrey M (1988) Biologically available metals in sediments. Natl Res Counc Can Publ No. 27694, Ottawa, Ontario, Canada
Charles MJ, Hites RA (1987) Sediments as archives of environmental pollution trends. In: Hites RA, Eisenreich SJ (eds) Sources and fates of aquatic pollutants. Am Chem Soc, Washington, DC, pp 365–389
Evans RD, Dillon PJ (1982) Historical changes in anthropogenic lead fallout in southern Ontario, Canada. Hydrobiologia 91:131–137
Förstner U, Wittmann GTW (1981) Metal pollution in the aquatic environment. Springer-Verlag, New York, 486 pp
Fremling CR (1964) Mayfly distribution indicates water quality on the Upper Mississippi River. Science 146:1164–1166
Fremling CR, Claflin TO (1984) Ecological history of the Upper Mississippi River. In: Wiener JG, Anderson RV, McConville DR (eds) Contaminants in the Upper Mississippi River. Butterworth Publ, Boston, MA, pp 5–24
Fremling CR, Johnson DK (in press) Recurrence ofHexagenia mayflies demonstrates improved water quality in Pool 2 and Lake Pepin, Upper Mississippi River. In: Campbell IC (ed) Mayflies and Stoneflies, Life Histories and Biology. Dr W Junk Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands
Fremling CR, Rasmussen JL, Sparks RE, Cobb SP, Bryan CF, Claflin TO (1989) Mississippi River fisheries: a case history. In: Dodge DP (ed) Proc Int Large River Symp, Can Spec Publ Fish Aquat Sci 106. Department of Fisheries and Oceans, Ottawa, Canada, pp 309–351
Great I (Great River Environmental Action Tream) (1980) GREAT I Study of the Upper Mississippi River, Technical Appendixes, Vol 4, Section G: Sediment and erosion, US Government Printing Office, Washington, DC
Jackson GA, Korschgen CE, Thiel PA, Besser JM, Steffeck DW, Bockenhauer MH (1981) Long-term resource monitoring plan for the Upper Mississippi River System. Comprehensive Master Plan for the Management of the Upper Mississippi River System, Tech Rep F, Vol II, Upper Mississippi River Basin Commission, Minneapolis, MN
Kemp ALW, Thomas RL, Dell CI, Jaquet JM (1976) Cultural impact on the geochemistry of sediments in Lake Erie. J Fish Res Board Can 33:440–462
McHenry JR, Ritchie MC, Cooper CM (1980) Rates of recent sedimentation in Lake Pepin. Water Resour Bull 16:1049–1056
MWCC (Metropolitan Waste Control Commission) (1985) Mississippi River assessment in relation to the Metropolitan Waste Water Treatment Plant. Quality Control Department Report, St. Paul, MN
-(1987) 1986 River quality in review. Quality Control Department Report 87-129, St. Paul, MN
Rada RG, Findley JE, Wiener JG (1986) Environmental fate of mercury discharged into the Upper Wisconsin River. Water Air Soil Pollut 29:57–76
Ritchie JC, McHenry JR, Gill AC (1973) Dating recent reservoir sediments. Limnol Oceanogr 18:254–263
Slavin S, Bamett WB, Kahn HL (1972) Determination of atomic absorption detection limits by direct measurement. At Absorp Newsl 11:37–41
Sprafka JM (1981) Evaluation of heavy metal loadings at the Metropolitan Wastewater Treatment Plant. Quality Control Department, Metropolitan Waste Control Commission, St. Paul, MN
Trapp KE (1979) A survey of the benthic macroin vertebrate community of Lake Pepin and a study of the influence of various physical factors on the distribution of selected taxa. MS Thesis, Univ Wisconsin-La Crosse, La Crosse, WI
Trefry JH, Metz S, Trocine RP, Nelson TA (1985) A decline in lead transport by the Mississippi River. Science 230:439–441
USEPA (United States Environmental Protection Agency) (1975) A compendium of lake and reservoir data collected by the National Eutrophication Survey in the northeast and north-central United States. National Eutrophication Survey, Working Paper No. 474, Corvallis, OR
-(1981) Interim methods for the sampling and analysis of priority pollutants in sediments and fish tissue. EPA-600/4-81-055, Washington, DC
-(1983) Methods for chemical analysis of water and wastes. EPA 600/4-79-020 (revised 1983), Washington, DC
Wiener JG, Jackson GA, May TW, Cole BP (1984) Longitudinal distribution of trace elements (As, Cd, Cr, Hg, Pb, and Se) in fishes and sediments in the Upper Mississippi River. In: Wiener JG, Anderson RV, McConville DR (eds) Contaminants in the Upper Mississippi River. Butterworth Publ, Boston, MA, pp 139–170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rada, R.G., Wiener, J.G., Bailey, P.A. et al. Recent influxes of metals into Lake Pepin, a natural lake on the Upper Mississippi River. Arch. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 19, 712–716 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183989
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01183989