Abstract
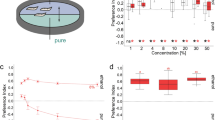
There is a latitudinal cline in attraction to ethanol of newly hatchedD. melanogaster larvae; attraction decreases as one moves from the temperate regions to the Australian tropics. Tropical populations manifest high levels of heterogeneity compared with temperate regions, making tropical populations less dependent on ethanol. Since ethanol is a resource forD. melanogaster, an approach to the genetics of resource utilization in natural populations via behavior genetics of larval ethanol responses is feasible, using isofemale strains as experimental material.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Begg, M., and Hobgen, L. (1946). Chemoreceptivity ofDrosophila melanogaster.Proc. Roy. Soc. Lond. Ser. B133:1–19.
Bock, I. R., and Parsons, P. A. (1977). Species diversities inDrosophila (Diptera): A dependence upon rain forest type of the Queensland (Australian) humid tropics.J. Biogeog. 4:203–213.
David, J., and Bocquet, C. (1975). Similarities and differences in latitudinal adaptation of twoDrosophila sibling species.Nature 257:585–590.
Ehrman, L., and Parsons, P. A. (1976).The Genetics of Behavior, Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, Mass.
Fuyama, Y. (1976). Behavior genetics of olfactory responses inDrosophila. I. Olfactometry and strain differences inDrosophila melanogaster.Behav. Gent. 6:407–420.
Fuyama, Y. (1978). Behavior genetics of olfactory responses inDrosophila. II. An odorantspecific variant in a natural population ofDrosophila melanogaster.Behav. Genet. 8:399–414.
Godoy-Herrera, R. (1977). Inter- and intrapopulational variation in digging inDrosophila melanogaster larvae.Behav. Genet. 7:433–439.
Godoy-Herrera R. (1978). Selection for digging behavior inDrosophila melanogaster larvae.Behav. Genet. 8:475–479.
MacArthur, R. H. (1972).Geographical Ecology, Harper & Row, New York.
McDonald, J. F., and Ayala, F. J. (1978). Gene regulation in adaptive evolution.Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 20:159–175.
McKenzie J. A., and McKechnie, S. W. (1978). Ethanol tolerance and theAdh polymorphism in a natural population ofDrosophila melanogaster.Nature 272:75–76.
McKenzie, J. A., and McKechnie, S. W. (1979). A comparative study of resource utilization in natural populations ofDrosophila melanogaster andD. simulans.Oecologia (Berlin).40:299–309.
McKenzie, J. A., and Parsons, P. A. (1974a). Numerical changes and environmental utilization in natural populations ofDrosophila.Aust. J. Zool. 22:175–187.
McKenzie, J. A., and Parsons, P. A. (1974b). Microdifferentiation in a natural population ofDrosophila melanogaster to alcohol in the environment.Genetics 77:385–394.
Ohnishi, S. (1979). Relationship between larval feeding behavior and viability inDrosophila melanogaster andD. simulans.Behav. Genet. 9:129–134.
Parsons, P. A. (1977). Larval reaction to alchohol as an indicator of resource utilization differences betweenDrosophila melanogaster andD. simulans.Oecologia (Berlin) 30:141–146.
Parsons, P. A. (1978). Habitat selection and evolutionary strategies inDrosophila: An invited address.Behav. Genet. 8:511–526.
Parsons, P. A. (1979a). Larval reactions to possible resources in threeDrosophila species as indicators of ecological divergence.Aust. J. Zool. 27:413–419.
Parsons, P. A. (1979b). Polygenic variation in natural populations ofDrosophila. In Thompson, J. N., Jr., and Thoday, J. M. (eds.),Quantitative Genetic Variation, Academic Press, New York, pp. 61–79.
Parsons, P. A., and Bock, I. R. (1979a). The population biology of AustralianDrosophila.Ann. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 10:229–245.
Parsons, P. A., and Bock, J. R. (1979b). Latitudinal species diversities in Australian endemicDrosophila.Am. Nat. 114:213–220.
Parsons, P. A., and Stanley, S. M. (1980). Special ecological studies—domesticated and widespread species. In Ashburner, M., Carson, H. L., and Thompson, J. N., Jr. (eds.),Genetics and Biology of Drosophila, Vol. 3, Academic Press, New York.
Parson, P. A., Stanley, S. M., and Spence, G. E. (1979). Environmental ethanol at low concentrations: Longevity and development in the sibling speciesDrosophila melanogaster andD. simulans.Aust. J. Zool. 27:747–754.
Pruzan, A., and Bush, G. (1977). Genotypic differences in larval olfactory discrimination in twoDrosophila melanogaster strains.Behav. Genet. 7:457–464.
Sewell, D., Burnet, B., and Connolly, K. (1975). Genetic analysis of larval feeding behaviour inDrosophila melanogaster.Genet. Res. 24:163–173.
Sokal, R. R., and Rohlf, F. J. (1969).Biometry: The Principles and Practice of Statistics in Biological Research, Freeman, San Francisco.
Stalker, H. D. (1976). Chromosome studies in wild populations ofD. melanogaster.Genetics 82:323–347.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by the Australian Research Grants Committee.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Parsons, P.A. Larval responses to environmental ethanol inDrosophila melanogaster: Variation within and among populations. Behav Genet 10, 183–190 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01066268
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01066268