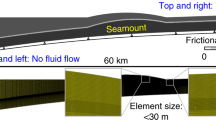
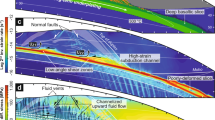
Abstract
Many geological and geophysical investigations, particularly the Deep Sea Drilling Project, have shown that convergent plate margins are highly diverse features. For example, at some sites of subduction, such as the Lesser Antilles, the bedded sediment atop the incoming oceanic plate is extensively offscraped, whereas at others, such as Mariana, not only is the incoming sediment completely subducted beneath crystalline rock but portions of the overriding plate are undergoing subduction erosion. Earthquakes indicate wide variations in stress distribution within and between sites of plate convergence. Many ancient accretionary complexes include tracts of intensely-deformed subduction melange that contain blocks of mafic greenstones. Some contain bodies of thoroughly recrystallized blueschist that were uplifted from depths of 20 to 30 km. A comprehensive model for convergent plate margins must explain these and numerous other observations. Although the still widely cited imbricatethrust model for prism accretion qualitatively explains some observations at subduction zones, it does not account for many others, such as deep sediment subduction and subduction erosion.
The subduction-channel model postulates essentially the same basic mechanics for all convergent plate margins that have attained a quasi-steady state (typically reached after about 20 Ma of subduction at speeds of 10 to 20 km Ma−1). It assumes that the subducting sediment deforms approximately as a viscous material once it is dragged into a relatively thin shear zone, or subduction channel, between the downgoing plate and the overriding one. It predicts the overall movement patterns of the sediment deforming within the channel and near its inlet, accounts for most of the observed features at convergent plate margins, and quantifies the processes of sediment subduction, offscraping, and underplating, and the formation of subduction melange. The predicted variations in tectonic behavior depend upon such site-specific variables as the speed of subduction, the supply of sediment, the geometry of the descending plate, and the topography and structure of the overriding block.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aalto, K. R. (1982),The Franciscan Complex of Northernmost California: Sedimentation and Tectonics, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 419–432.
Allegre, C. J., Hamelin, B., andDupre, B. (1984),Statistical Analysis of Isotopic Ratios in MORB: The Mantle Blob Cluster Model and the Convective Regime of the Mantle, Earth and Planetary Science Letters71, 71–84.
Aoki, Y., Tamano, T., andKato, S. (1983),Detailed Structure of the Nankai Trough from Migrated Seismic Section, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir34, 309–324.
Arculus, R. J. andPowell, R. (1986),Source Component Mixing in the Regions of Arc Magma Generation, Journal of Geophysical Research91, 5913–5926.
Armstrong, R. L. (1971),Isotopic and Chemical Constraints on Models of Magma Genesis in Volcanic Arcs, Earth and Planetary Science Letters12, 137–142.
Armstrong, R. L. (1981),Radiogenic Isotopes: The Case for Crustal Recycling on a Near-Steady-State No-Continental-Growth Earth, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of LondonA 301, 443–472.
Aubouin, J., Bourgois, J., andAzema, J. (1984),A New Type of Active Margin: The Convergent-Extensional Margin, as Exemplified by the Middle America Trench off Guatemala, Earth and Planetary Science Letters67, 211–218.
Bachman, S. B. (1978),A Cretaceous and Early Tertiary Subduction Complex, Mendocino Coast, Northern California, InMesozoic Palegeography of the Western United States (eds. Howell, D. G., and McDougall, K. A.) (Pacific Coast Paleogeography Symposium2) pp. 419–430.
Bachman, S. B. (1982),The Coastal Belt of the Franciscan: Youngest Phase of Northern California Subduction, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 401–418.
Barreiro, B. (1983),Lead Isotopic Compositions of South Sandwich Island Volcanic Rocks and Their Bearing on Magmagenesis in Intra-Oceanic Island Arcs, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta47, 817–822.
Beck, R. M. andLehner, P. (1974),Oceans, New Frontier in Exploration, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin58, 376–395.
Becker, D. G. andCloos, M. (1985),Melange Diapirs into the Cambria Slab: A Franciscan Trench Slope Basin near Cambria, California, Journal of Geology93, 101–110.
Biju-Duval, B., Le Quellec, P., Mascle, A., Renard, V., andVallery, P. (1982),Multibeam Bathymetric Survey and High Resolution Seismic Investigations on the Barbados Ridge Complex (Eastern Caribbean): A Key to the Knowledge and Interpretation of an Accretionary Wedge, Tectonophysics86, 275–304.
Bird, P. (1978),Stress and Temperature in Subduction Shear Zones: Tonga and Mariana, Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society55, 411–434.
Bloomer, S. H. (1983),Distribution and Origin of Igneous Rocks from the Landward Slopes of the Mariana Trench: Implications for Its Structure and Evolution, Journal of Geophysical Research88, 7411–7428.
Boggs, S. (1984),Quaternary Sedimentation in the Japan Arc-Trench System, Geological Society of America Bulletin95, 669–685.
Brace, W. F. (1980),Permeability of Crystalline and Argillaceous Rocks, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science and Geomechanics Abstracts17, 241–251.
Brace, W. F. (1984),Permeability of Crystalline Rocks: New In-Situ Measurements, Journal of Geophysical Research89, 4327–4330.
Brandon, M. T. (1986),Comment and Reply on “Comments on the Growth of Accretionary Wedges,” Geology14, 184–186.
Breen, N. A., Silver, E. A., andHussong, D. M. (1986),Structural Styles of an Accretionary Wedge South of the Island of Sumba, Indonesia, Revealed by SeaMARC II Side Scan Sonar, Geological Society of America Bulletin97, 1250–1261.
Brown, L., Klein, J., Middleton, R., Sacks, I. S., andTera, F. (1982),10 Be in Island-Arc Volcanoes and Implications for Subduction, Nature229, 718–720.
Bryant, W. R., Hottman, W., andTrabant, P. (1975),Permeability of Unconsolidated and Consolidated Marine Sediments, Gulf of Mexico, Marine Geotechnology1, 1–14.
Byrne, T. (1982),Structural Evolution of Coherent Terranes in the Ghost Rocks Formation, Kodiak Island, Alaska, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 229–242.
Byrne, T. (1984),Early Deformation in Melange Terranes of the Ghost Rocks Formation, Kodiak Islands, Alaska, Geological Society of America Special Paper198, 21–52.
Cande, S. C. andLeslie, R. B. (1986),Late Cenozoic Tectonics of the Southern Chile Trench, Journal of Geophysical Research91, 471–496.
Carlson, W. D. andRosenfeld, J. L. (1981).Optical Determination of Topotactic Aragonite-Calcite Growth Kinetics: Metamorphic Implications, Journal of Geology89, 615–638.
Carson, B. (1977),Tectonically Induced Deformation of Deep-Sea Sediments off Washington and Northern Oregon: Mechanical Consolidation, Marine Geology24, 289–307.
Carson, B. andBerglund, P. L. (1986),Sediment Deformation and Dewatering under Horizontal Compression: Experimental Results, Geological Society of America Memoir166, 135–150.
Carson, B., von Huene, R., andArthur, M. (1982),Small-Scale Deformation Structures and Physical Properties Related to Convergence in Japan Trench Slope Sediments, Tectonics1, 277–302.
Carson, B., Yuan, J., Myers, P. B., andBarnard, W. D. (1974),Initial Deep-Sea Sediment Deformation at the Base of the Washington Continental Slope: A Response to Subduction, Geology2, 561–564.
Chapple, W. M. (1978),Mechanics of Thin-Skinned Fold-and-Thrust Belts, Geological Society of America Bulletin89, 1189–1198.
Chase, R. L. andBunce, E. T. (1969),Underthrusting of the Eastern Margin of the Antilles by the Floor of the Western North Atlantic Ocean and the Origin of the Barbados Ridge, Journal of Geophysical Research74, 1413–1420.
Chen, A. T., Frohlich, C., andLathan, G. V. (1982),Seismicity of the Forearc Marginal Wedge (Accretionary Prism), Journal of Geophysical Research87, 3679–3690.
Chopin, C. (1984),Coesite and Pure Pyrope in High Grade Blueschists of the Western Alps: A First Record and Some Consequences, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology86, 107–118.
Church, S. E. (1973),Limits of Sediment Involvement in the Genesis of Orogenic Volcanic Rocks, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology39, 17–32.
Cloos, M. (1982),Flow Melanges: Numerical Modeling and Geologic Constraints on Their Origin in the Franciscan Subduction Complex, Geological Society of America Bulletin93, 330–345.
Cloos, M. (1984),Flow Melanges and the Structural Evolution of Accretionary Wedges, Geological Society of America Special Paper198, 71–80.
Cloos, M. (1985),Thermal Evolution of Convergent Plate Margins: Thermal Modeling and Reevaluation of Isotopic Ar Ages for Blueschists in the Franciscan Complex of California, Tectonics4, 421–433.
Cloos, M. (1986),Blueschists in the Franciscan Complex of California: Petrotectonic Constraints on Uplift Mechanisms, Geological Society of America Memoir164, 77–93.
Cloos, M. andShreve, R. L. (1988),Subduction-Channel Model of Prism Accretion, Melange Formation, Sediment Subduction, and Subduction Erosion at Convergent Plate Margins: 2. Implications and Discussion, Pure and Applied Geophysics128, 314, 501–545.
Clowes, R. M., Brandon, M. T., Green, A. G., Yorath, C. J., Sutherland-Brown, A., Kanasewich, E. R., andSpencer, C. (1987),Lithoprobe—Southern Vancouver Island: Cenozoic Subduction Complex Imaged by Deep Seismic Reflections, Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences24, 31–51.
Coats, R. R. (1962),Magma Type and Crustal Structure in the Aleutian Arc, American Geophysical Union Monograph6, 92–109.
Cohen, R. S. andO'nions, R. K. (1982),Identification of Recycled Continental Material in the Mantle from Sr, Nd, and Pb Isotope Investigations, Earth and Planetary Science Letters61, 73–84.
Coleman, R. G. (1980),Tectonic Inclusions in Serpentinites, Société de Physique et d'Histoire Naturelle de Genève, Archives des Sciences33, 89–102.
Connelly, W. (1978),Uyak Complex, Kodiak Islands, Alaska: A Cretaceous Subduction Complex, Geological Society of America Bulletin89, 755–769.
Couch, R., Whitsett, R., Huehn, B., andBriceno-Guarupe, L. (1981),Structures of the Continental Margin of Peru and Chile, Geological Society of America Memoir154, 569–586.
Coulbourn, W. T. (1981),Tectonics of the Nazca Plate and the Continental Margin of Western South America, 18° S to 23° S, Geological Society of America Memoir154, 587–618.
Coulbourn, W. T. andMoberly, R. (1977),Structural Evolution of Forearc Basins off Southern Peru and Northern Chile, Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences14, 102–116.
Cowan, D. S. (1982),Origin of “Vein Sturcture” in Slope Sediments on the Inner Slope of the Middle America Trench off Guatemala, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project67, 645–650.
Cowan, D. S. (1985),Structural Styles in Mesozoic and Cenozoic Melanges in the Western Cordillera of North America, Geological Society of America Bulletin96, 451–462.
Cowan, D. S. andSilling, R. M. (1978),A Dynamic Scaled Model of Trenches and Its Implications for the Tectonic Evolution of Subduction Complexes, Journal of Geophysical Research83, 5389–5396.
Dahlen, F., Suppe, J., andDavis, D. (1984),Mechanics of Fold-and-Thrust Belts and Accretionary Wedges: Cohesive Coulomb Theory, Journal of Geophysical Research89, 10,125–10,133.
Davidson, J. P. (1986),Isotopic and Trace Element Constraints on the Petrogenesis of Subduction-Related Lavas from Martinique, Lesser Antilles, Journal of Geophysical Research91, 5943–5962.
Davidson, J. P. (1987),Crustal Contamination Versus Subduction Zone Enrichment: Examples from the Lesser Antilles and Implications for Mantle Source Compositions of Island Arc Volcanic Rocks, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta51, 2185–2198.
Davies, T. A. andGorsline, D. S. (1976),Oceanic Sediments and Sedimentary Processes, Chemical Oceanography5, 1–80.
Davis, D., Suppe, J., andDahlen, F. A. (1983),Mechanics of Fold-and-Thrust Belts and Accretionary Wedges, Journal of Geophysical Research88, 1153–1172.
Davis, D. M. andvon Huene, R. (1987),Inferences on Sediment Strength and Fault Friction from Structures at the Aleutian Trench, Geology15, 517–522.
Dewey, J. F. andBird, J. M. (1970),Mountain Belts and the New Global Tectonics, Journal of Geophysical Research75, 2625–2647.
Dickinson, W. R. (1973),Widths of Modern Arc-Trench Gaps Proportional to Past Duration of Igneous Activity in Associated Magmatic Arcs, Journal of Geophysical Research,78, 3395–3417.
Dickinson, W. R. andSeely, D. R. (1979),Structure and Stratigraphy of Forearc Regions, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin62, 2–31.
Dickinson, W. R. andSnyder, W. S. (1979),Geometry of Subducted Slabs Related to San Andreas Transform, Journal of Geology87, 609–627.
Draper, G. (1986),Blueschists and Associated Rocks in Eastern Jamaica and Their Significance for Cretaceous Plate-Margin Development in the Northern Caribbean, Geological Society of America Bulletin97, 48–60.
Draper, G. andBone, R. (1980),Denudation Rates, Thermal, Evolution, and Preservation of Blueschist Terrains, Journal of Geology89, 601–613.
Elliot, D. (1976),The Motion of Thrust Sheets, Journal of Geophysical Research81, 949–963.
Emerman, S. H. andTurcotte, D. L. (1983),A Fluid Model for the Shape of Accretionary Wedges, Earth and Planetary Science Letters63, 379–384.
England, P. C. andHolland, T. J. B. (1979),Archimedes and the Tauren Eclogites: The Role of Buoyancy in the Preservation of Exotic Eclogite Blocks, Earth and Planetary Science Letters44, 287–294.
England, P. C. andThompson, A. B. (1984),Pressure-Temperature-Time Paths of Regional Metamorphism I. Heat Transfer during the Evolution of Regions of Thickened Continental Crust, Journal of Petrology25, 894–928.
Ernst, W. G. (1970),Tectonic Contact between the Franciscan Melange and Great Valley Sequence, Crustal Expression of a Late Mesozoic Benioff Zone, Journal of Geophysical Research75, 886–902.
Ernst, W. G. (1971),Do Mineral Parageneses Reflect Unusually High Pressure Conditions of Franciscan Metamorphism?, American Journal of Science271, 879–914.
Ernst, W. G. (1975),Systematics of Large-Scale Tectonics and Age Progressions in Alpine and Circum-Pacific Blueschist Belts, Tectonophysics26, 229–246.
Evans, B. andBrown, E. H. (eds.) (1986),Blueschists and Related Rocks, Geological Society of America Memoir164, 423.
Farhoudi, G. andKarig, D. E. (1977),Makran of Iran and Pakistan as an Active Arc System, Geology5, 664–668.
Fisher, D. andByrne, T. (1987),Structural Evolution of Underthrusted Sediments, Kodiak Islands, Alaska, Tectonics6, 775–793.
Frohlich, C., Billington, S., Engdahl, E. R., andMalahoff, A. (1982),Detection and Location of Earthquakes in the Central Aleutian Subduction Zone Using Island and Ocean Bottom Seismograph Stations, Journal of Geophysical Research87, 6853–6864.
Fryer, P., Ambos, E. L., andHussong, D. M. (1985),Origin and Emplacement of Mariana Forearc Seamounts, Geology13, 774–777.
Griffin, J. J., Windom, H., andGoldberg, E. D. (1968),The Distribution of Clay Minearals in the World Ocean, Deep-Sea Research15, 433–459.
Grow, J. A. (1973),Crustal and Upper Mantle Structure of the Central Aleutian Arc, Geological Society of America Bulletin84, 2169–2192.
Gilluly, J. (1969),Oceanic Sediment Volumes and Continental Drift, Science166, 992–993.
Gilluly, J., Reed, J. C., andCady, W. M. (1970),Sedimentary Volumes and Their Significance, Geological Society of America Bulletin81, 353–376.
Habermann, R. E., McCann, W. R., andPerin, B. (1986),Spatial Seismicity Variations Along Convergent Plate Boundaries, Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society85, 43–68.
Hamilton, W. (1979),Tectonics of the Indonesian Region, U. S. Geological Survey Professional Paper1079, 345.
Helwig, J. andEmmet, P. (1981),Structure of the Early Tertiary Orca Group in Prince William Sound and Some Implications for the Plate Tectonic History of Southern Alaska, Journal of the Alaska Geological Survey1, 12–35.
Herron, E. M., Bruhn, R., Winslow, M., andChuaqui, L. (1977),Post Miocene Tectonics of the Margin of Southern Chile, American Geophysical Union Maurice Ewing Series1, 273–284.
Hibbard, J., andKarig, D. E. (1987),Sheath-Like Folds and Progressive Fold Deformation in Tertiary Sedimentary Rocks of the Shimanto Accretionary Complex, Japan, Journal of Structural Geology9, 845–857.
Hilde, T. W. C. (1983),Sediment Subduction Versus Accretion around the Pacific, Tectonophysics99, 381–397.
Hill, M., Morris, J. andWhelan, J. (1981),Hybrid Granodiorites Intruding the Accretionary Prism, Kodiak, Shumagin, and Sanak Islands, Southwest Alaska, Journal of Geophysical Research86, 10,591–10,606.
Hole, M. J., Saunders, A. D., Marriner, G. F., andTarney, J. (1984),Subduction of Pelagic Sediments: Implications for the Origin of Ce-Anomalous Basalts from the Mariana Islands, Journal of the Geological Society of London141, 453–472.
Honda, S. andUyeda, S. (1983),Thermal Process in Subduction Zone—A Review and Preliminary Approach on the Origin of Arc Volcanism, InArc Volcanism: Physics and Tectonics (eds. Shimozuru, D., and Yokoyama, I.) (Terra Scientific Publishing Company (TERRAPUB), Tokyo, 1983) pp. 117–140.
Hsui, A. T., Marsh, B. D., andToksöz, M. N. (1983),On Melting of the Subducted Oceanic Crust: Effects of Subduction Induced Mantle Flow, Tectonophysics99, 207–220.
Hsui, A. T. andToksöz, M. N. (1979),The Evolution of Thermal Structures beneath a Subduction Zone, Tectonophysics60, 43–60.
Hussong, D. M. andWipperman, L. K. (1981),Vertical Movement and Tectonic Erosion of the Continental Wall of the Peru-Chile Trench near 11°30′ S Latitude, Geological Society of America Memoir154, 509–524.
Hussong, D. M. andUyeda, S. (1982),Tectonic Processes and the History of the Mariana Arc: A Synthesis of the Results of Deep Sea Drilling Project Leg 60, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project60, 909–929.
Isacks, B. andBarazangi, M. (1977),Geometry of Benioff Zones: Lateral Segmentation and Downards Bending of the Subducted Lithosphere, American Geophysical Union Maurice Ewing Series1, 99–114.
Isacks, B., Oliver, J. andSykes, L. R. (1968),Seismology and the New Global Tectonics, Journal of Geophysical Research73, 5855–5899.
Iverson, R. M. (1985),A Constitutive Equation of Mass-Movement Behavior, Journal of Geology93, 143–160.
Jarrard, R. D. (1986),Relations among Subduction Parameters, Reviews of Geophysics24, 217–284.
Jones, G. M., Hilde, T. W. C., Sharman, G. F., andAgnew, D. C. (1978),Fault Patterns in Outer Trench Walls and Their Tectonic Significance, Journal of the Physics of the Earth26, 85–101.
Karig, D. E. (1974a),Evolution of Arc Systems in the Western Pacific, Annual Reviews of Earth and Planetary Sciences21, 51–75.
Karig, D. E. (1974b),Tectonic Erosion at Trenches, Earth and Planetary Science Letters21 209–212.
Karig, D. E. (1977),Growth Patterns on the Upper Trench Slope, American Geophysical Union Maurice Ewing Series1, 175–186.
Karig, D. E. (1983),Deformation in the Forearc: Implications for Mountain Belts InMountain Building Processes (ed. Hsu, K. J.) (Academic Press, London, 1983) pp. 59–72.
Karig, D. E. (1986),Physical Properties and Mechanical State of Accreted Sediments in the Nankai Trough, Southwest Japan Arc, Geological Society of America Memoir166, 117–133.
Karig, D. E. andKagami, H. (1983),Varied Responses to Subduction in Nankai Trough and Japan Trench Forearcs, Nature304, 148–151.
Karig, D. E. andKay, R. W. (1981),Fate of Sediments on the Descending Plate at Convergent Margins, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A301, 233–251.
Karig, D. E. andSharman, G. F. (1975),Subduction and Accretion in Trenches, Geological Society of America Bulletin86, 377–389.
Karig, D. E., Caldwell, J. G., andParmentier, E. M. (1976),Effects of Accretion on the Geometry of the Descending Lithosphere, Journal of Geophysical Research81, 6281–6291.
Karig, D. E., Cardwell, R. K., Moore, G. F., andMoore, D. G. (1978),Late Cenozoic Subduction and Continental Truncation along the Northern Middle America Trench, Geological Society of America Bulletin89, 265–276.
Karig, D. E., Moore, G. F., Curray, J. R., andLawrence, M. B. (1980),Morphology and Shallow Structure of the Lower Trench Slope off Nias Island, Sunda Arc, American Geophysical Union Monograph23, 179–208.
Katz, R. (1971),Continental Margin in Chile—Is the Tectonic Style Compressional or Extensional?, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin55, 1753–1758.
Kay, R. W. (1980),Volcanic Arc Magmas: Implications of a Melting-Mixing Model for Element Recycling in the Crust-Upper Mantle, Journal of Geology88, 497–522.
Kehle, R. O. (1970),Analysis of Gravity Sliding and Orogenic Translation, Geological Society of America Bulletin81, 1641–1664.
Krantz, R. L. andBlacic, J. D. (1984),Permeability Changes during Time-Dependent Deformation of Silicate Rock, Geophysical Research Letters11, 975–978.
Kulm, L. D. andFowler, G. A.,Oregon Continental Margin Structure and Stratigraphy: A Test of the Imbricate-Thrust Model, InGeology of the Continental Margins (eds. Burk, C. A., and Drake, C. L.) (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1974) pp. 261–283.
Kulm, L. D., Prince, R. A., French, W., Johnson, S. andMasias, A. (1981),Crustal Structure and Tectonics of the Central Peru Continental Margin and Trench, Geological Society of America Memoir154, 445–468.
Kulm, L. D., Scheidegger, K. F., Prince, R. A., Dymond, J., Moore, T. C., andHussong, D. M. (1973),Theoleiitic Basalt Ridge in the Peru Trench, Geology1, 11–14.
Larue, D. K. andHuddleston, P. J. (1987),Foliated Breccias in the Active Portuguese Bend Landslide Complex, California: Bearing on Melange Genesis, Journal of Geology95, 407–422.
Lash, G. G. (1985),Recognition of Trench Fill in Orogenic Flysch Sequences, Geology13, 867–870.
Lay, T., Kanamori, H. andRuff, L. (1982),The Asperity Model and the Nature of Large Subduction Zone Earthquakes, Earthquake Prediction Research1, 3–71.
Leeman, W. P. (1983),The Influence of Crustal Structure on Compositions of Subduction-Related Magmas, Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research18, 561–588.
Leggett, J. K. (1985),Deep-Sea Pelagic Sediments and Palaeo-Oceanography: A Review of Recent Progress, Geological Society of London Special Publication18, 95–121.
Leggett, J., Aoki, Y., andToba, T. (1985),Transition from Frontal Accretion to Underplating in a Part of the Nankai Trough Accretionary Complex off Shikoku (SW Japan) and Extensional Features of the Lower Slope, Marine and Petroleum Geology2, 131–141.
Lonsdale, P. (1978),Ecuadorian Subduction System, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin62, 2454–2477.
Lonsdale, P. (1981),Drifts and Ponds of Reworked Pelagic Sediment in Part of the Southwest Pacific, Marine Geology43, 153–193.
Ludwig, W. H., Ewing, J. I., Ewing, M., Murauchi, S., Den, N., Asano, S., Hotta, H., Hayakawa, M., Asanuma, T., Ichikawa, K., andNoguchi, I. (1966),Sediments and Structure of the Japan Trench, Journal of Geophysical Research71, 2121–2137.
Lundberg, N. (1983),Development of Forearcs of Intraoceanic Subduction Zones, Tectonics2, 51–61.
Lundberg, N., andMoore, J. C. (1981),Structural Features of the Middle America Trench Slope off Southern Mexico, Deep Sea Drilling Project Leg 66, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project66, 793–814.
Lundberg, N. andMoore, J. C. (1986),Macroscopic Structural Features in Deep Sea Drilling Project Cores from Forearc Regions, Geological Society of America Memoir166, 13–44.
Mackenzie, J. S., Needham, D. T., andAgar, S. M. (1987),Progressive Deformation in an Accretionary Complex: An Example from the Shimanto Belt of Eastern Kyushu, Southwest Japan, Geology15, 353–356.
Marshak, R. S. andKarig, D. E. (1977),Triple Junctions as a Cause for Anomalously Near-Trench Igneous Activity between the Trench and Volcanic Arc, Geology5, 233–236.
Maxwell, J. C. (1974),Anatomy of an Orogen, Geological Society of America Bulletin85, 1195–1204.
Matsuzawa, A., Tamano, T., Aoki, Y., andIkawa, T. (1980),Structure of the Japan Trench Subduction Zone, from Multi-Channel Seismic-Reflection Records, Marine Geology35, 171–182.
McCarthy, J. andScholl D. W. (1985),Mechanisms of Subduction Accretion along the Central Aleutian Trench, Geological Society of America Bulletin96, 691–701.
McKenzie, D. P. (1969),Speculations on the Consequences and Causes of Plate Motions, Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society18, 1–32.
McLintock, F. A. andWalsh, J. B. (1962),Friction of Griffith Cracks in Rocks under Pressure. InProceedings of the Fourth U.S. National Congress of Applied Mechanics, 2 (ed. Rosenberg, R. M.) (American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York, 1962) pp. 1015–1021.
McMillen, K. J. andBachman, S. B. (1982),Bathymetric and Tectonic Evolution of the Southern Mexico Active Margin, Deep Sea Drilling Project Leg 66, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project66, 815–822.
Minster, J. B. andJordan, T. H. (1978),Present Day Plate Motions, Journal of Geophysical Research83, 5331–5354.
Moberly, R., Shepherd, G. L., andCoulbourn, W. T. (1982),Forearc and Other Basins, Continental Margin of Northern and Southern Peru and Adjacent Ecuador and Chile, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 171–190.
Moore, G. F. andKarig, D. E. (1976),Development of Sedimentary Basins on the Lower Trench Slope, Geology4, 693–697.
Moore, G. F. andKarig, D. E. (1980),Structural Geology of Nias Island, Indonesia: Implications of Subduction Zone Tectonics, American Journal of Science280, 193–223.
Moore, G. F. andCurray, J. R. (1980),Structure of the Sunda Trench Lower Slope off Sumatra from Multichannel Seismic Reflection Data, Marine Geophysical Researches4, 319–340.
Moore, G. F., Billman, H. G., Henhanussa, P. E., andKarig, D. E. (1980),Sedimentology and Paleobathymetry of Neogene Trench Slope Deposits, Nias Island, Indonesia, Journal of Geology88, 161–180.
Moore, J. C. (1975),Selective Subduction, Geology3, 530–532.
Moore, J. C. andAllwardt, A. (1980),Progressive Deformation of a Tertiary Trench Slope, Kodiak Islands, Alaska, Journal of Geophysical Research85, 4741–4756.
Moore, J. C., Biju-Duval, B., Bergen, J. A., Blackinton, G., Claypool, G. E., Cowan, D. S., Duennebier, F., Guerra, R. T., Hemleben, C. H. J., Hussong, D., Marlow, M. S., Natland, J. H., Pudsey, C. J., Renz, G. W., Tardy, M., Willis, M. E., Wilson, D. andWright, A. A. (1982c),Offscraping and Underthrusting of Sediment at the Deformation Front of the Barbados Ridge: Deep Sea Drilling Project Leg 78A, Geological Society of America Bulletin93, 1065–1077.
Moore, J. C. andByrne, T. (1987),Thickening of Fault Zones: A Mechanism of Melange Formation in Accreting Sediments, Geology15, 1040–1043.
Moore, J. C. andGeigle, J. E. (1974),Slaty Cleavage: Incipient Occurrences in the Deep Sea, Science183, 504–508.
Moore, J. C. andKarig, D. E. (1976),Sedimentology, Structural Geology, and Tectonics of the Shikoku Subduction Zone, Geological Society of America Bulletin87, 1259–1268.
Moore, J. C. andLundberg, N. (1986),Tectonic Overview of Deep Sea Drilling Project Transects of Forearcs, Geological Society of America Memoir166, 1–12.
Moore, J. C. andSilver, E. A. (1987),Continental Margin Tectonics: Submarine Accretionary Prism, Reviews of Geophysics25, 1305–1312.
Moore, J. C., Mascle, A., Taylor, E., Andreieff, P., Alvarez, F., Barnes, R., Beck, C., Behrmann, J., Blanc, G., Brown, K., Clark, M., Dolan, J., Fisher, A., Gieskes, J., Hounslow, M., McLellan, P., Moran, K., Ogawa, Y., Sakai, T., Schoonmaker, J., Vrolijk, P., Wilkens, R., andWilliams, C. (1987),Expulsion of Fluids from Depth along a Subduction-Zone Décollement Horizon, Nature326, 785–788.
Moore, J. C., Roeske, S., Lundberg, N., Schoonmaker, J., Cowan, D. S., Gonzales, E., andLucas, S. E. (1986),Scaly Fabrics from Deep Sea Drilling Project Cores from Forearcs, Geological Society of America Memoir166, 55–73.
Moore, J. C., Watkins, J. S., McMillen, K. J., Bachman, S. B., Leggett, J. K., Lundberg, N., Shipley, T. H., Stephan, J., Beghtel, F. W., Butt, A., Didyk, B. M., Nitsuma, N., Shephard, L. E., andStradner, H. (1982b),Facies Belts of the Middle America Trench and Forearc Region, Southern Mexico: Results from Leg 66, DSDP, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 77–94.
Moore, J. C., Watkins, J. S., Shipley, T. H., McMillen, K. J., Bachman, S. B., andLundberg, N. (1982a),Geology and Tectonic Evolution of a Juvenile Accretionary Terrane along a Truncated Convergent Margin: Synthesis of Results from Leg 66 of the Deep Sea Drilling Project, Southern Mexico, Geological Society of America Bulletin93, 847–861.
Morrow, C. A., Shi, L. Q., andByerlee, J. D. (1984),Permeability of Fault Gouge under Confining Pressure and Shear Stress, Journal of Geophysical Research89, 3193–3200.
Mottl, M. J. (1983),Metabasalts, Axial Hot Springs, and the Structure of Hydrothermal Systems at Mid-Ocean Ridges, Geological Society of America Bulletin94, 161–180.
Mrozowski, C. L. andHayes, D. E. (1980),A Seismic Reflection Study of Faulting in the Mariana Forearc, American Geophysical Union Monograph23, 223–234
Mrozowski, C. L., Hayes, D. E., andTaylor, B. (1982),Multichannel Seismic Reflection Surveys Leg 60 Sites, Deep Sea Drilling Project, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project60, 57–69.
Myers, J. D., Frost, C. D., andAngevine, C. L. (1986),A Test of Quartz Eclogite Source for Parental Aleutian Magmas: A Mass Balance Approach, Journal of Geology94, 811–828.
Nasu, N., von Huene, R., Ishiwada, Y., Langseth, M., Burns, T., andHonza, E. (1980),Interpretation of Multichannel Seismic Reflection Data, Legs 56 and 57, Japan Trench Transect, Deep Sea Drilling Project, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project57, 489–503.
Nilsen, T. H. andZuffa, G. G. (1982),The Chugach Terrane, a Cretaceous Trench-Fill Deposit, Southern Alaska, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 213–228.
O'nions, R. K. (1987),Relationships between Chemical and Convective Layering in the Earth, Journal of the Geological Society of London144, 259–274.
Oxburgh, E. R. andTurcotte, D. L. (1974),Thermal Gradients and Regional Metamorphism in Overthrust Terrains with Special Reference to the Eastern Alps, Schweizerische Mineralogische und Petrographische Mitteilungen54, 641–662.
Page, B. M. (1970),Sur-Nacimiento Fault Zone of California—Continental Margin Tectonics, Geological Society of America Bulletin81, 667–689.
Patchett, P. J., White, W. M., Feldmann, H., Kielinczuk, S., andHofmann, A. W. (1984),Hafnium/Rare Earth Element Fractionation in the Sedimentary System and Crustal Recycling into the Earth's Mantle, Earth and Planetary Science Letters69, 365–378.
Peacock, S. M. (1987),Thermal Effects of Metamorphic Fluids in Subduction Zones, Geology15, 1057–1060.
Piper, D. J. W., von Huene, R., andDuncan, J. R. (1973),Late Quaternary Sedimentation in the Active Eastern Aleutian Trench, Geology1, 19–22.
Plafker, G. (1965),Tectonic Deformation Associated with the 1964 Alaska Earthquake, Science148, 1675–1687.
Platt, J. P. (1986),Dynamics of Orogenic Wedges and the Uplift of High-Pressure Metamorphic Rocks, Geological Society of America Bulletin,97, 1037–1053.
Platt, J. P., Leggett, J. K., Young, J., Raza, H., andAlam, S. (1985),Large-Scale Sediment Underplating in the Makran Accretionary Prism, Southwest Pakistan, Geology13, 507–511.
Prince, R. A. andKulm, L. D. (1975),Crustal Rupture and Initiation of Imbricate Thrusting in the Peru-Chile Trench, Geological Society of America Bulletin86, 1639–1653.
Raymond, L. A. andTerranova, T. (1984),The Melange Problem—A Review, Geological Society of America Special Paper198, 1–5.
Reck, B. H. (1987),Implications of Measured Thermal Gradients for Water Movement through the Northeast Japan Accretionary Prism, Journal of Geophysical Research92, 3683–3690.
Ritger, S. D. (1985),Origin of Vein Structures in the Slope Deposits of Modern Accretionary Prisms, Geology13, 437–439.
Rundle, J. B., Kanamori, H., andMcNally, K. C. (1984),An Inhomogeneous Fault Model for Gaps, Asperities, Barriers, and Seismicity Migration, Journal of Geophysical Research89, 10,219–10,231.
Rutland, R. W. R. (1971),Andean Orogeny and Ocean Floor Spreading, Nature233, 252–255.
Sample, J. C. andFisher, D. M. (1986),Duplex Accretion and Underplating in an Ancient Accretionary Complex, Kodiak Islands, Alaska, Geology14, 160–163.
Sample, J. C. andMoore, J. C. (1987),Structural Style and Kinematics of an Underplated Slate Belt, Kodiak and Adjacent Islands, Alaska, Geological Society of America Bulletin,99, 7–20.
Schliestedt, M. andMatthews, A. (1987),Transformation of Blueschist to Greenschist Facies Rocks as a Consequence of Fluid Infiltration, Sifnos (Cyclades), Greece, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology97, 237–250.
Scholl, D. W. andMarlow, M. S. (1974),Sedimentary Sequences in Modern Pacific Trenches and the Deformed Circum-Pacific Eugeosyncline, Society of Economic Paleontologists and Mineralogists Special Publication19, 193–211.
Scholl, S. W., Marlow, M. S., andCooper, A. K. (1977),Sediment Subduction and Offscraping at Pacific Margins, American Geophysical Union Maurice Ewing Series1, 199–210.
Scholl, D. W., Vallier, T. L., andStevenson, A. J. (1982),Sedimentation and Deformation in the Amlia Fracture Zone Sector of the Aleutian Trench, Marine Geology,48, 105–134.
Scholl, D. W., Vallier, T. L., andStevenson, A. J. (1983),Arc, Forearc, and Trench Sedimentation and Tectonics: Amlia Corridor of the Aleutian Ridge, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir34, 414–439.
Scholl, D. W., von Huene, R., Vallier, T. L., andHowell, T. G. (1980),Sedimentary Masses and Concepts about Tectonic Processes at Underthrust Ocean Margins, Geology8, 564–568.
Schweller, W. J. andKulm, L. D. (1978a)Extensional Rupture of Oceanic Crust in the Chile Trench, Marine Geology28, 271–291.
Schweller, W. J. andKulm, L. D. (1978b),Depositional Patterns and Channelized Sedimentation in Active Eastern Pacific Trenches, InSedimentation in Submarine Canyons, Fans, and Trenches (eds. Stanley, D. J., and Kelling, G.) (Dowden, Hutchison, and Ross, 1978) pp. 311–329.
Schweller, W. J., Kulm, L. D., andPrince, R. A. (1981),Tectonics, Structure, and Sedimentary Framework of the Peru-Chile Trench, Geological Society of America Memoir154, 323–349.
Seely, D. R. (1977),The Significance of Landward Vergence and Oblique Structural Trends on Trench Inner Slopes, American Geophysical Union Maurice Ewing Series1, 187–198.
Seely, D. R. (1979),The Evolution of Structural Highs Bordering Major Forearc Basins, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir29, 245–260.
Seely, D. R., Vail, P. R., andWalton, G. G.,Trench Slope Model, InGeology of the Continental Margins (eds. Burk, C. A., and Drake, C. L.) (Springer-Verlag, New York, 1974) pp. 249–260.
Shepherd, G. L. andMoberly, R. (1981),Coastal Structure of the Continental Margin, Northwest Peru and Southwest Ecuador, Geological Society of America Memoir154, 351–392.
Shi, Y. andWang, C. Y. (1985),High Pore Pressure Generation in Sediments in Front of the Barbados Ridge Complex, Geophysical Research Letters12, 773–776.
Shipley, T. H. andMoore, G. F. (1986),Sediment Accretion Subduction, and Dewatering at the Base of the Trench Slope off Costa Rica: A Seismic Reflection View of the Décollement, Journal of Geophysical Research91, 2019–2028.
Shipley, T. H., McMillen, K. J., Watkins, J. S., Moore, J. C. Sandoval-Ochoa, J. H., andWorzel, J. L. (1980),Continental Margin and Lower Slope Structures of the Middle America Trench near Acapulco (Mexico) Marine Geology35, 65–82.
Shreve, R. L. andCloos, M. (1986),Dynamics of Sediment Subduction, Melange Formation, and Prism Accretion, Journal of Geophysical Research91, 10,229–10,245.
Sillitoe, R. H. (1972),Relation of Metal Provinces in Western America to Subduction of Oceanic Lithosphere, Geological Society of America Bulletin83, 813–818.
Silver, E. A. (1971),Transitional Tectonics and Late Cenozoic Structure of the Continental Margin off Northernmost California, Geological Society of America Bulletin82, 1–22.
Silver, E. A., Ellis, M. J., Breen, N. A., andShipley, T. H. (1985),Comments on the Growth of Accretionary Wedges, Geology13, 6–9.
Speed, R. C. andLarue, D. K. (1982),Barbados: Architecture and Implications for Accretion, Journal of Geophysical Research87, 3633–3643.
Spence, W. (1987),Slab Pull and the Seismotectonics of Subducting Lithosphere, Reviews of Geophysics25, 55–69.
Spooner, E. T. C. andFyfe, W. S. (1973),Sub-Sea-Floor Metamorphism, Heat and Mass Transfer, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology42, 287–304.
Staudigel, H., Hart, S. R., andRichardson, S. H. (1981),Alteration of Oceanic Crust: Processes and Timing, Earth and Planetary Science Letters52, 311–327.
Stevens, S. H. andMoore, G. F. (1985),Deformational and Sedimentary Processes in Trench Slope Basins of the Western Sunda Arc, Indonesia, Marine Geology69, 93–112.
Stockmal, G. S. (1983),Modeling of Large-Scale Accretionary Wedge Deformation, Journal of Geophysical Research88, 8271–8287.
Stride, A. H., Belderson, R. H., andKenyon, N. H. (1982),Structural Grain, Mud Volcanoes and Other Features on the Barbados Ridge Complex Revealed by GLORIA Long Range Side-Scan Sonar, Marine Geology49, 187–196.
Suppe, J. (1972),Interrelationships of High-Pressure Metamorphism, Deformation and Sedimentation in Franciscan Tectonics, U.S.A., International Geological Congress, 24th Session, Section 3, 552–559.
Suppe, J. (1973),Geology of the Leech Lake—Ball Mountain Region, California, University of California Publications in the Geological Sciences107, 82 p.
Suzuki T. (1986),Melange Problem of Convergent Plate Margins in the Circum-Pacific Regions, Memoirs of the Faculty of Science, Kochi University, Series E, Geology,7, 23–48.
Taira, A., Okada, H., Whitaker, J. H. M., andSmith, A. J. (1982),The Shimanto Belt of Japan: Cretaceous—Lower Miocene Active Margin Sedimentation, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 5–26.
Tajima, F. andKanamori, H. (1985),Aftershock Area Expansion and Mechanical Heterogeneity of Fault Zone within Subduction Zones, Geophysical Research Letters12, 345–348.
Tera, F., Brown, L., Morris, J., Sacks I. S., Klein, J., andMiddleton, R. (1986),Sediment Incorporation in Island-Arc Magmas: Inferences from 10 Be, Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta50, 535–550.
Tharp, T. M. (1985),Numerical Models of Subduction and Forearc Deformation, Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society80, 419–437.
Thornburg, T. M. andKulm, L. D. (1987),Sedimentation in the Chile Trench: Depositional Morphologies, Lithofacies, and Stratigraphy, Geological Society of America Bulletin98, 33–52.
Travis, P. B. (1953),LaBrea-Parinas Oil Field, Northwestern Peru, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Bulletin37, 2093–2118.
Underwood, M. B. (1984),A Sedimentologic Perspective on Stratal Disruption within Sandstone-Rich Melange Terranes, Journal of Geology92, 369–386.
Underwood, M. B. (1986a),Transverse Infilling of Central Aleutian Trench by Unconfined Turbidity Currents, Geo-Marine Letter6, 7–13.
Underwood, M. B. (1986b),Sediment Provenance within Subduction Complexes—An Example from the Aleutian Forearc, Sedimentary Geology51, 57–73.
Underwood, M. B. andBachman, S. B. (1982),Sedimentary Facies Associations within Subduction Complexes, Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 537–550.
Underwood, M. B. andKarig, D. E. (1980),Role of Submarine Canyons in Trench and Trench-Slope Sedimentation, Geology8, 432–436.
Uyeda, S. (1982),Subduction Zones: An Introduction to Comparative Subductology, Tectonophysics,81, 133–159.
Uyeda, S. andKanamori H. (1979),Back-Arc Opening and the Mode of Subduction, Journal of Geophysical Research84, 1049–1061.
van den Beukel, J. andWortel, R. (1986),Thermal Modelling of Arc-Trench Regions, Geologie en Mijnbouw65, 133–143.
von Huene, R. (1981),Review of Early Results from Drilling of the IPOD-1 Active Margin Transects across Japan, Mariana, and Middle America Convergent Margins, Society of Economic Paleontologists Special Publication32, 57–66.
von Huene, R. (1984a),Tectonic Processes along the Front of Modern Convergent Margins—Research of the Past Decade, Annual Reviews of Earth and Planetary Sciences12, 359–381.
von Huene, R. (1984b),Structural Diversity along Modern Convergent Margins and the Role of Overpressured Pore Fluids in Subduction Zones, Bulletin de la Société Géologique de France, Series,7, 26, 207–219.
von Huene, R. (1986a),To Accrete or Not Accrete, That Is the Question, Geologische Rundschau,75, 1–15.
von Huene, R. (1986b),Seismic Images of Modern Convergent Margin Tectonic Structure, American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Studies in Geology,26, 60.
von Huene, R. andKulm, L. D. (1973),Tectonic Summary of Leg 18, Initial Reports of the Deep Sea Drilling Project18, 961–976.
von Huene, R. andLee, H. (1983),The Possible Significance of Pore Fluid Pressure in Subduction Zones, American Association of Petroleum Geologists Memoir34, 781–791.
von Huene, R., Aubouin, J., Azema, J., Blackinton, G., Carter, J. A., Coublourn, W. T., Cowan, D. S., Curiale, J. A., Dengo, C. A., Fass, R. W., Harrison, W., Hesse, R., Hussong, D. M., Ladd, J. W., Muzylov, N., Shiki, T., Thompson, P. R., andWestberg, J. (1980),Leg 67: the Deep Sea Drilling Project Mid-America Trench Transect off Guatemala, Geological Society of America Bulletin91, 421–432.
von Huene, R., Kulm, L. D., andMiller, J. (1985),Structure of the Frontal Part of the Andean Convergent Margin, Journal of Geophysical Research90, 5429–5442.
von Huene, R., Langseth, M., Nasu, N., andOkada, H. (1982),A Summary of Cenozoic Tectonic History along IPOD Japan Trench Transect, Geological Society of America Bulletin93, 829–846.
von Huene, R., Suess, E., andEmeis, K. (1987),Convergent Tectonics and Coastal Upwelling: A History of the Peru Continental Margin, Episodes10, 87–93.
Walsh, J. B. (1981),Effect of Pore Pressure and Confining Pressure on Fracture Permeability, International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Science and Geomechanics Abstracts18, 429–435.
Walsh, J. B. andBrace, W. F. (1984),The effect of Pressure on Porosity and the Transport Properties of Rock, Journal of Geophysical Research89, 9425–9431.
Wang, C. Y. andShi, Y. L. (1984),On the Thermal Structure of Subduction Complexes: A Preliminary Study, Journal of Geophysical Research89, 7709–7718.
Warsi, W. E. K., Hilde, T. W. C., andSearle, R. C. (1983),Convergence Structures of the Peru Trench between 10°S and 14°S, Tectonophysics99, 313–329.
Weaver, B. L., Wood, D. A., Tarney, J. andJoron, J. L. (1986),Role of Subducted Sediment in the Genesis of Ocean-Island Basalts: Geochemical Evidence from South Atlantic Ocean Islands, Geology14, 275–278.
Westbrook, G. K. andSmith, M. J. (1983),Long Décollements and Mud Volcanoes: Evidence from the Barbados Ridge Complex for the Role of High Pore-Fluid Pressure in the Development of an Accretionary Complex, Geology11, 279–283.
Westbrook, G. K., Smith M. J., Peacock, J. H., andPoulter, M. J. (1982),Extensive Underthrusting of Undeformed Sediment beneath the Accretionary Complex of the Lesser Antilles Subduction Zone, Nature300, 625–628.
White, R. S., (1982),Deformation of the Makran Accretionary Sediment Prism in the Gulf of Oman (Northwest Indian Ocean), Geological Society of London Special Publication10, 357–372.
White, R. S. andKlitgord, K. (1976),Sediment Deformation and Plate Tectonics in the Gulf of Oman, Earth and Planetary Science Letters32, 199–209.
White, W. M., andDupre, B. (1986),Sediment Subduction and Magma Genesis in the Lesser Antilles: Isotopic and Trace Element Constraints, Journal of Geophysical Research91, 5927–5941.
Williams, P. R., Pigram, C. J., Dow, D. B., andAmiruddin (1984),Melange Production and the Importance of Shale Diapirism in Accretionary Terrains, Nature309, 145–146.
Yardley, B. W. D. (1982),The Early Metamorphic History of the Haast Schists and Related Rocks of New Zealand, Contributions to Mineralogy and Petrology81, 317–327.
Yeats, R. S. (1968),Southern California Structure, Sea Floor Spreading, and the History of the Pacific Basin, Geological Society of America Bulletin79, 1693–1702.
Ziegler, A. M., Barrett, S. F., andScotese, C. R. (1981),Palaeoclimate, Sedimentation and Continental Accretion, Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of LondonA 301, 253–264.
Zindler, A., Staudigel, H., andBatiza, R. (1984),Isotopic and Trace Element Geochemistry of young Pacific Seamounts: Implications for the Scale of Upper Mantle Heterogeneity, Earth and Planetary Science Letters70, 175–195.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cloos, M., Shreve, R.L. Subduction-channel model of prism accretion, melange formation, sediment subduction, and subduction erosion at convergent plate margins: 1. Background and description. PAGEOPH 128, 455–500 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874548
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00874548