Abstract
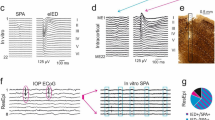
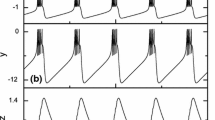
The normal spontaneous bursting behavior of hippocampal pyramidal neurons was investigated. Bursting frequency was found to be membrane potential dependent, the frequency increasing with maintained depolarization and decreasing upon hyperpolarization. Short depolarizing-current pulses would trigger bursts which outlasted the stimulus, and bursting continued when synaptic transmission had been blocked. The spontaneous bursts of these neurons, in contrast to bursts induced by convulsive agents, appear to exhibit the classical behavior of endogenous bursts as observed in invertebrate neurons. The endogenous bursts in hippocampal neurons may result, also, from an interplay of intrinsic membrane currents.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alving, B. O. (1968). Spontaneous activity in isolated somata ofAplysia pacemaker neurons.J. Gen. Physiol. 5129–45.
Andersen, P., Gjerstad, L., Hablitz, J. J., and Langmoen, I. A. (1981). Two types of burst discharges in penicillin treated brain slices. InPhysiology and Pharmacology of Epileptogenic Phenomena (M. Klee, Ed.), Raven Press, New York (in press).
Brown, T. H., Fricke, R. A., and Perkel, D. H. (1981). Passive electrical constants in three classes of hippocampal neurons.J. Neurophysiol. 46812–827.
Carnevale, N. T., and Wachtel, H. (1980). Two reciprocating current components underlying slow oscillations inAplysia bursting neurons.Brain Res. Rev. 245–68.
Carpenter, D. O. (1967). Temperature effects on pacemaker generation, membrane potential, and critical firing threshold inAplysia neurons.J. Gen. Physiol. 501469–1484.
Dichter, M., and Spencer, W. A. (1969). Penicillin-induced interictal discharges from the cat hippocampus. I. Characteristics and topographical features.J. Neurophysiol. 32649–662.
Gainer, H. (1972). Electrophysiological behavior of an endogenously active neurosecretory cell.Brain Res. 38403–418.
Gorman, A. L. F., and Hermann, A. (1979). Internal effects of divalent cations on potassium permeability in molluscan neurones.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 296393–410.
Hagiwara, S. (1975). Ca-dependent action potential. InMembranes—A Series of Advances, Vol. 3, Lipid Bilayers and Biological Membranes: Dynamic Properties (G. Eisenman, Ed.), Dekker, New York, pp. 359–381.
Johnston, D. (1976). Voltage clamp reveals basis for calcium regulation of bursting pacemaker potentials inAplysia neurons.Brain Res. 107418–423.
Johnston, D. (1981). Passive cable properties of hippocampal CA3 pyramidal neurons.Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 141–55.
Johnston, D., and Brown, T. (1981). Giant synaptic potential hypothesis for epileptiform activity.Science 211294–297.
Johnston, D., Hablitz, J. J., and Wilson, W. A. (1980). Voltage clamp discloses slow inward current in hippocampal burst-firing neurones.Nature (Lond.) 286391–393.
Kandal, E. R., and Spencer, W. A. (1961). Electrophysiology of hippocampal neurons. II. After-potentials and repetitive firing.J. Neurophysiol. 24243–259.
McAfee, D. A., and Yarowsky, P. J. (1979). Calcium-dependent potentials in the mammalian sympathetic neurone.J. Physiol. (Lond.) 290507–523.
Puil, E., and Werman, R. (1979). Intracellular cesium blocks K+ conductances in cat motoneurons.Can. Physiol. 10185.
Ranck, J. B., Jr. (1973). Studies on single neurons in dorsal hippocampal formation and septum in unrestrained rats.Exp. Neurol. 41461–555.
Schwindt, P., and Crill, W. (1980). Role of a persistent inward current in motoneuron bursting behavior during spinal seizures.J. Neurophysiol. 431296–1318.
Wong, R. K. S., and Prince, D. A. (1978). Participation of calcium spikes during intrinsic burst firing in hippocampal neurons.Brain Res. 159385–390.
Wong, R. K. S., and Prince, D. A. (1981). Afterpotential generation in hippocampal pyramidal cells.J. Neurophysiol. 4586–97.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hablitz, J.J., Johnston, D. Endogenous nature of spontaneous bursting in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Cell Mol Neurobiol 1, 325–334 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00716267
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00716267