Summary
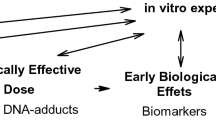
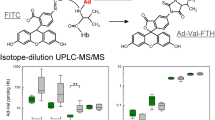
Analysis of hemoglobin adducts in blood samples is suitable for the biological monitoring of genotoxic chemicals. The method is specific because the compound to which the individual was exposed is identified. The sensitivity of the method depends on the analytical procedure applied, but is hardly limiting since large amounts of the protein can be obtained. The method provides not only information about the internal exposure to the environmental chemical, but also about the individual's capacity to generate ultimate genotoxic metabolites from it. Since macromolecular damage in blood cells is correlated to that in potential target tissues, this information is relevant to risk assessment, insofar as macromolecular damage produced by a specific chemical can be correlated with the development of tumors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Albrecht W, Neumann H-G (1985a) Biomonitoring of N-substituted aryl compounds. Binding of aniline and nitrobenzene to rat hemoglobin. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 109:A12
Albrecht W, Neumann H-G (1985b) Biomonitoring of aniline and nitrobenzene. Hemoglobin binding in rats and analysis of adducts. Arch Toxicol 57:1–5
Birner G, Neumann H-G (1987) Biomonitoring of aromatic amines. Binding of substituted anilines to rat hemoglobin. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol [Suppl] 335:73
Bolt HM, Neumann H-G, Lewalter J (1985) Zur Problematik von BAT-Werten für aromatische Amine. Arbeitsmed Sozialmed Präventivmed 20:197–201
Dölle B, Töpner W, Neumann H-G (1980) Reaction of arylnitroso compounds with mercaptans. Xenobiotica 10:527–536
Ehrenberg L, Hiesche KD, Osterman-Golkar S, Wennberg I (1974) Evaluation of genetic risks of alkylating agents: tissue dose in the mouse from air contaminated with ethylene oxide. Mutat Res 24:83–103
Ehrenberg L, Moustacchi E, Osterman-Golkar S (1983) Dosimetry of genotoxic agents and dose-response relationships of their effects. Mutat Res 123:121–182
Eyer P (1979) Reactions of nitrosobenzene with reduced glutathione. Chem Biol Interact 24:227–239
Eyer P (1983) The red cell as a sensitive target for activated toxic arylamines. Arch Toxicol [Suppl] 6:3–12
Eyer P (1985) Reactions of nitrosoarenes with sulphydryl groups: reaction mechanism and biological significance. In: Gorrod JW, Damani LA (eds) Biological oxidation of nitrogen in organic molecules. Ellis Horwood, Ltd, Chichester, and VCH Verlagsgesellschaft, Weinheim, pp 386–399
Green LC, Skipper PL, Turesky RJ, Bryant MS, Tannenbaum SR (1984) In vivo dosimetry of 4-aminobiphenyl in rats via a cysteine adduct in hemoglobin. Cancer Res 44:4254–4259
Groth U, Neumann H-G (1971) The relevance of chemicobiological interactions for the toxic and carcinogenic effects of aromatic amines. V. The pharmacokinetics of related aromatic amines in blood. Chem Biol Interact 4:409–419
Henschler D (ed) (1986) Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft: maximum concentrations at the workplace and biological tolerance values for working materials 1986. VCH Verlagsgesellschaft mbH, Weinheim
Kennelly JC, Beland FA, Kadlubar FF, Martin CN (1984) Binding of N-acetylbenzidine and N,N′-diacetylbenzidine to hepatic DNA of rat and hamster in vivo and in vitro. Carcinogenesis 5:407–412
Kiese M (1974) Methemoglobinemia: a comprehensive treatise. CRC Press, Cleveland, OH
Lewalter J, Korallus U (1985) Blood protein conjugates and acetylation of aromatic amines. New findings on biological monitoring. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 56:179–196
Lotlikar PD, Miller EC, Miller JA, Margreth A (1965) The enzymatic reduction of the N-hydroxy derivatives of 2-acetylaminofluorene and related carcinogens by tissue preparations. Cancer Res 25:1743–1752
Lutz WK (1979) In vivo covalent binding of organic chemicals to DNA as a quantitative indicator in the process of chemical carcinogenesis. Mutat Res 65:289–356
Miller EC, Miller JA (1969) The metabolic activation of carcinogenic aromatic amines and amides. Progr Exp Tumor Res 11:273–301
Murthy MSS, Calleman CJ, Osterman-Golkar S, Segerback D, Svensson K (1984) Relationships between ethylation of hemoglobin, ethylation of DNA and administered amount of ethyl methanesulfonate in the mouse. Mutat Res 127:18
Neumann H-G (1980) Dose response relationship in the primary lesion of strong electrophilic carcinogens. Arch Toxicol [Suppl] 3:69–77
Neumann H-G (1983) The dose dependence of DNA interactions of aminostilbene derivatives and other chemical carcinogens. In: Hayes AW, Schnell RC, Miya TS (eds) Developments in the science and practice of toxicology. Elsevier Science Publishers BV, Amsterdam, pp 135–144
Neumann H-G (1986) The role of DNA damage in chemical carcinogenesis of aromatic amines. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 112:100–106
Neumann H-G (1987) Concepts for assessing the internal dose of chemicals in vivo. In: Fowler BA (ed) Mechanism of cell injury: implications for human health. John Wiley and Sons, Chichester, New York, Brisbane, Toronto, Singapore, pp 241–254
Neumann H-G, Gaugler BJM, Taupp W (1978) The metabolic activation of trans-4-dimethylaminostilbene after oral administration of doses ranging from 0.025 to 250 μmol/kg. Proc First Int Congr on Toxicology. Plaa GL Duncan WAM (Eds) Academic Press, New York, London, pp 177–190
Neumann H-G, Metzler M, Töpner W (1977) Metabolic activation of diethylstilbestrol and aminostilbene derivatives. Arch Toxicol 39:21–30
Osterman-Golkar S, Farmer PB, Segerbäck D, Bailey E, Calleman CJ, Svensson K, Ehrenberg L (1983) Dosimetry of ethylene oxide in the rat by quantitation of alkylated histidine in hemoglobin. Teratogen Carcinog Mutagen 3:395–405
Pereira MA, Chang LW (1981) Binding of chemical carcinogens and mutagens to rat hemoglobin. Chem Biol Interact 33:301–305
Pereira MA, Lin L-HC, Chang LW (1981) Dose-dependency of 2-acetylaminofluorene binding to liver DNA and hemoglobin in mice and rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 60:472–478
Rjosk HK, Neumann H-G (1971) Zur Bedeutung chemischbiologischer Wechselwirkungen für die toxische und krebserzeugende Wirkung aromatischer Amine. II. Verteilung der Radioaktivität nach Applikation des Tritium-markierten Carcinogens trans-4-Dimethylaminostilben und der beiden unwirksamen Vergleichssubstanzen cis-4-Dimethylaminostilben und 4-Dimethylaminobibenzyl in der Ratte. Z Krebsforsch 75:209–220
Segerbäck D, Calleman CJ, Ehrenberg L, Löfroth G, Osterman-Golkar S (1978) Evaluation of genetic risk of alkylating agents IV. quantitative determination of alkylated amino acids in hemoglobin as a measure of the dose after treatment of mice with methyl methanesulfonate. Mutat Res 49:71–82
Wieland E, Neumann H-G (1978) Methemoglobin formation and binding to blood constituents as indicators for the formation, availability and reactivity of activated metabolites derived from trans-4-aminostilbene and related aromatic amines. Arch Toxicol 40:17–35
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neumann, HG. Biomonitoring of aromatic amines and alkylating agents by measuring hemoglobin adducts. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 60, 151–155 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378690
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00378690