Summary
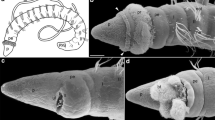
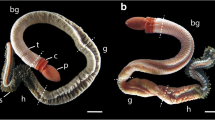
The settlement and metamorphosis of the marine bryozoan Bowerbankia gracilis has been examined by light and electron microscopy. The period of rapid morphogenesis consists of the following sequence of morphogenetic movements: 1) eversion of the internal sac, 2) retraction of the apical disc, 3) coronal involution and exposure of the pallial epithelium, and 4) closure of the internal coronal cavity. The eversion of the internal sac at the onset of metamorphosis coincides with a sudden reversal of the direction of beat of the coronal cilia. The reversed beating of the coronal cilia wafts the adhesive secreted by the internal sac over the metamorphosing larva, forming the pellicle. The internal sac is subsequently internalized and histolyzed with the corona and the other transitory larval tissues, and the extensive pallial epithelium forms the epidermis of the ancestrular body wall (cystid). Type I mesenchyme cells form an incomplete somatic mesothelium beneath the differentiating cystid epidermis, and Type II mesenchyme cells become mobile phagocytes. The main body cavity develops by the histolytic enlargement of the internal cavity formed during coronal involution. The apical disc degenerates and the polypide develops from rudiments in the oral hemisphere of the larva. The distinctive larval morphology and metamorphosis of vesicularioid ctenostomes are compared with other bryozoans, and possible evolutionary trends are considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aiello E (1974) Control of ciliary activity in Metazoa. In: Sleigh MA (ed) Cilia and Flagella. Academic Press, New York pp. 353–376
Atkins D (1955) The ciliary feeding mechanism of the cyphonautes larva (Polyzoa Ectoprocta). J mar biol Ass UK 34:451–466
Atkins D (1960) The ciliary feeding mechanism of the Megathiridae (Brachiopoda) and the growth stages of the lophophore. J mar biol Ass UK 39:459–479
Baba SJ (1974) Developmental changes in the pattern of ciliary response and the swimming behavior in some invertebrate larvae. In: Wu TY-T, Brokaw CJ, Brennan C (eds) Swimming and flying in nature. Vol. 1 Cal Inst Techn pp 317–324
Barrois J (1982) Embryogénie des Bryozoaires. Essai d'une théorie générale du developement basee sur l'étude de la métamorphose. J Anat Physiol (Paris) 18:124–157
Barrois J (1886) Mémoire sur la métamorphose de quelques Bryozoaires. Biblitque Éc ht Étud (Paris) Sect Sci Nat 32(5):1–94; 4 pls
Bogoiavlenskii H (1905) To the knowledge of embryonic development, budding, and regeneration in Zoobotryon pellucidus. Obshchestro liubitele estestvoznania, antropologii i etnografii, Moscow, izviestiia vol 108:1–90; pls I–III (Union List of Serials, vol 4, pp 3131
Braem F (1951) Über Victorella und einige ihrer nächsten Verwandten sowie die Bryozoenfauna des Ryck bei Greifswald. Zoologica (Stuttgart) 102:1–59; 12 pls
Brien P (1970) Considérations phylogénétiques à propos des Lophophoriens Acad Roy Sci (Brussels) Classe Sci Bull ser 5, 56:565–579
Browning JL, Nelson DL (1976) Biochemical studies of the excitable membrane of Paramecium aurelia. I. 45Ca++ fluxes across resting and excited membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta 448:338–351
Browning JL, Nelson DL, Hansma HG (1976) Ca++ influx across the excitable membrane of behavioral mutants of Paramecium. Nature 259:491–494
Burden-Jones C (1952) Development and biology of the larva of Saccoglossus horsti (Enteropneusta). Phil Trans Soc London B 236:553–590
Calvet L (1900) Contribution à l'histoire naturelle des Bryozoaires Ectoproctes marins. Trav Inst Zool Univ Montpellier (N.S.) 8:1–488
Carter GS (1926) On the nervous control of the velar cilia of the nudibranch veliger. J Exp Biol 4:1–26
Chia FS, Burke RD (1978) Echinoderm metamorphosis: Fate of larval structures. In: Chia FS, Rice ME (eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, New York pp 219–234
Child CM (1933) The swimming plate rows of the ctenophore, Pleurobranchia, as gradients: with comparative data on other forms. J Comp Neurol 57:199–252
Chuang SH (1968) The larvae of a Discinid (Inarticulata, Brachiopoda) Biol Bull 135:263–272
Coonfield BR (1934) Co-ordination and movement of the swimming-plates of Mnemiopsis leidyi Agassiz Biol Bull 66:10–21
Eckert R (1972) Bioelectric control of ciliary activity. Science 176:473–481
Friedrich H (1933) Vergleichende Studien zur Bewegungs- und Nervenphysiologie bei Nemertinen. Zool Jahrb, Abt Allgem Zool Physiol Tiere 52:537–560
Galt CP, Mackie GO (1971) Electrical correlates of ciliary reversal in Oikopleura. J Exp Biol 55:205–212
Hondt JL d' (1973) Étude anatomique, histologique, et cytologique de la larva d'Alcyonidium polyoum (Hassal, 1841), Bryozoaire Cténostome. Arch Zool exp gén 114:537–602
Hondt JL d' (1974) La métamorphose de la larve et la formation du “cystide” chez Alcyonidium polyoum (Hassal, 1841), Bryozoaire Cténostome. Arch Zool exp gén 115:577–605
Hondt JL d' (1975) Étude anatomique et cytologique comparée de quelques larves de Bryozoaires Cténostomes. In: Pouyet S (ed) Bryozoa 1974. Docum Lab Geol Sci Lyon H.S. 3(1). Universite Claude Bernard, Lyon pp 125–134
Hondt JL d' (1976) Evolution des lignées cellulaires larvaires des Bryozoaires Gymnolaemates au cours de la métamorphose et de l'organogenèse ancestrulaire. Bull Soc Zool Fr 101 (Supp 5):41–47
Hondt JL d' (1977a) Structure larvaire et organogenèse post-larvaire chez Flustrellidra hispida (Fabricius, 1780), Bryozoaire Cténostome. Zoomorphology 87:165–189
Hondt JL d' (1977b) Structure larvaire et histogenèse post-larvaire chez Bowerbankia imbricata (Adams, 1798), Bryozoaire Cténostome (Vesicularines). Arch Zool exp gén 118:211–243
Ikeda I (1901) Observations on the development, structure, and metamorphosis of Actinotrocha. J Coll Sci Imp Univ Tokyo 13:508–592
Jebram D (1969) Bryozoen als Holzschädlinge im Brackwasser. Kiel Meeresforsch 25:224–230
Jebram D (1973) Stolonen-Entwicklung und Systematik bei den Bryozoa Ctenostomata. Z Zool Syst Evolutionforsch 11:1–48
Jennings HS (1906) Behavior of lower organisms. Indiana Univ Press, Bloomington, Indiana
Joliet L (1877) Contributions à l'histoire naturelle des bryozoaires des côtes de France. Arch Zool exp gén 6:193–304
Kinosita H (1952) Response of a single cilium. I. Stimulating effect of isotonic KCl solution on a large abfrontal cilium of Mytilus. Annot Zool Japon 25:8–14
Kinosita H, Murakami A (1967) Control of ciliary motion. Physiol Rev 47:53–82
Kleinenberg N (1886) Die Entstehung des Annelids aus der Larve von Lopadorhynchus. Zeitschr wiss Zool 44:1–227
Knight-Jones EW (1952) On the nervous system of Saccoglossus cambrensis (Enteropneusta). Phil Trans Roy Soc London B 236:315–354
Kupelweiser H (1905) Untersuchungen über den feineren Bau und die Metamorphose des Cyphonautes. Zoologica (Stuttgart) 47:1–50
Loeb MJ, Walker G (1977) Origin, composition, and function of secretions from pyriform organs and internal sacs of four settling Cheilo-ctenostome bryozoan larvae. Mar Biol 42:37–46
Machemer H (1978) Motor activity and bioelectric control of cilia. Fortschr Zool 24:195–210
Mackie GO, Spencer AN, Strathmann R (1969) Electrical activity associated with ciliary reversal in an echinoderm larva. Nature, London 223:1384–1385
Mackie GO, Paul DH, Singla CM, Sleigh MA, Williams DE (1974) Branchial innervation and ciliary control in the ascidian Corella. Proc Roy Soc London B 187:1–35
Mackie GO, Singla CL, Thiriot-Quievreux C (1976) Nervous control of ciliary activity in Gastropod larvae. Biol Bull 151:182–199
Mawatari S, Mawatari SF (1975) Development and metamorphosis of the cyphonautes of Membranipora serrilamella Osburn. In: Pouyet S (ed) Bryozoan 1974. Docum Lab Geol Sci Lyon H.S. 3(1). Universite Claude Bernard, Lyon pp 13–18
Naitoh Y (1966) Reversal response elicited in nonbeating cilia of Paramecium by membrane depolarization. Science 154:660–662
Naitoh Y (1968) Ionic control of the reversal response of cilia in Paramecium caudatum. A calcium hypothesis. J Gen Physiol 51:85–103
Naitoh Y, Kaneko H (1972) Reactivated triton-extracted models of Paramecium. Modification of ciliary movement by calcium ions. Science 176:523–524
Naitoh Y, Eckert R (1974) The control of ciliary activity in Protozoa. In: Sleigh MA (ed) Cilia and Flagella. Academic Press, New York pp 305–352
Nelson DL, Kung C (1978) Behavior of Paramecium: Chemical, physiological, and genetic studies. In: Hazelbauer GL (ed) Taxis and behavior. Elementary Sensory Systems in Biology; Receptors and Recognition Series B 5:75–100
Nielsen C (1981) On morphology and reproduction of ‘Hippodiplosia’ insculpta and Fenestrulina malusii (Bryozoa, Cheilostomata). Ophelia 20:91–125
Nott JA (1973) Settlement of the larvae of Spirorbis spirorbis L. J mar biol Ass UK 53:437–453
Ostrooumoff MA (1885) Note sur la métamorphose de Cyphonautes. Zool Anz 8:219
Ostroumoff AA (1886) Contribution a l'étude zoologique et morphologique des bryozoaires du Golfe de Sébastopol. Archs Slaves Biol 1:557–569; 2:184–190; 2:329–355; 5 pls
Parker GH (1905) The reversal of ciliary movement in metazoans. Amer J Physiol 13:1–16
Parker GH, Marks AP (1928) Ciliary reversal in the sea anemone Metridium. J Exp Zool 52:1–6
Prouho H (1890) Recherches sur la larve de Flustrella hispida: Structure et métamorphose. Arch Zool exp gén 2 ser, 8:409–459
Prouho H (1892) Contribution a l'histoire des bryozoaires. Arch Zool exp gén 2 ser, 10:557–656
Reed CG (1978) Larval morphology and settlement of the bryozoan, Bowerbankia gracilis (Vesicularioidea, Ctenostomata): Structure and eversion of the internal sac. In: Chia FS, Rice ME (eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, New York pp 41–48
Reed CG (1980) The reproductive biology, larval morphology and metamorphosis of the marine bryozoan, Bowerbankia gracilis (Vesicularioidea, Ctenostomata). Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Washington, Seattle, Washington 291 pp
Reed CG (1981) The role of ciliary reversal in the settlement of the marine bryozoan, Bugula neritina. J Cell Biol 91:45a
Reed CG, Cloney RA (1980) The role of ciliary motility in the metamorphosis of a bryozoan. Amer Zool 20:953
Reed CG, Cloney RA (1982) The larval morphology of the marine bryozoan, Bowerbankia gracilis (Ctenostomata: Vesicularioidea). Zoomorphology 100:23–54
Reed CG, Woollacott RM (1982) Mechanisms of rapid morphogenetic movements in the metamorphosis of the bryozoan Bugula neritina (Cheilostomata: Cellularioidea). I. Attachment to the substratum. J Morph 172:335–348
Reisinger E (1924) Bei Gattung Rhynchoscolex. Z. Morphol Ökol Tiere 1:1–37
Rice ME (1973) Morphology, behavior, and histogenesis of the pelagosphera larva of Phascolosoma agassizii (Sipuncula). Smithsonian Cont Zool No. 132:1–51
Ryland JS (1974) Behavior, settlement, and metamorphosis of bryozoan larvae: A review. Thalassia Jugoslavica 10:239–262
Ryland JS (1976) Physiology and ecology of marine bryozoans. Adv mar biol 14:285–443
Sterrer W (1972) Systematics and Evolution within the Gnathostomulida. Syst Zool 21:151–173
Sterrer W, Reiger RM (1974) Retronectidae — a new cosmopolitan marine family of Catenulida (Turbellaria). In: Riser NW, Morse MP (eds) Biology of Turbellaria, McGraw-Hill, pp 63–92
Strathmann RR (1971) The feeding behavior of planktotrophic echinoderm larvae: mechanisms, regulation, and rates of suspension feeding. J exp mar Biol Ecol 6:109–160
Strathmann RR (1973) Function of lateral cilia in suspension feeding of lophophorates (Brachiopoda, Phoronida, Ectoprocta). Mar Biol 23:129–136
Strathmann RR (1975) Larval feeding in echinoderms. Amer Zool 15:717–730
Strathmann RR, Bonar D (1976) Ciliary feeding of tornaria larvae of Ptychodera flava (Hemichordata: Enteropneusta). Mar Biol 34:317–324
Strathmann RR, Jahn TL, Fonseca JRC (1972) Suspension feeding by marine invertebrate larvae: clearance of particles by ciliated bands of a rotifer, pluteus, and trochophore. Biol Bull 142:505–519
Tamm S (1980) Cilia and ctenophores. Oceanus 23:50–59
Tamm SL, Tamm S (1981) Ciliary reversal without rotation of axonemal structures in ctenophore comb plates. J Cell Biol 89:495–509
Twitty VC (1928) Experimental studies on the ciliary action of amphibian embryos. J Exp Zool 50:319–334
Vigelius WJ (1886) Zur Ontogenie der marinen Bryozoen. Mitt Zool Stn Neapel 6:499–541
Waller TR (1981) Functional morphology and development of veliger larvae of the european oyster, Ostrea edulis Linné. Smithsonian Cont Zool No. 328:1–70
Winston JE (1977) Distribution and ecology of estuarine ectoprocts: A critical review. Ches Sci 18:34–57
Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (1971) Attachment and metamorphosis of the Cheiloctenostome bryozoan, Bugula neritina (Linné). J Morph 134:351–382
Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (1978) Metamorphosis of cellularioid bryozoans. In: Chia FS, Rice ME (eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae. Elsevier/North-Holland Biomedical Press, New York pp 49–63
Yatsu N (1902) On the development of Lingula anatina. J Coll Sci Imp Univ Tokyo 17:1–112
Zimmer RL (1964) Reproductive biology and development of Phoronida. Ph.D. dissertation, Department of Zoology, University of Washington, Seattle Washington 416 pp
Zimmer RL (1973) Morphological and developmental affinities of the lophophorates. In: Larwood GP (ed) Living and fossil bryozoa. Proc Int Bryozool Assoc; Academic Press, New York pp 593–599
Zimmer RL, Woollacott RL (1977a) Structure and classification of gymnolaemate larvae. In: Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (eds) Biology of Bryozoans. Academic Press, New York pp 57–89
Zimmer RL, Woollacott RM (1977b) Metamorphosis, ancestrulae, and coloniality in bryozoan life cycles. In: Woollacott RM, Zimmer RL (eds) Biology of Bryozoans. Academic Press, New York pp 91–142
Zirpolo G (1933) Zoobothryon verticillatum (Delle Chiaje). Mem Accad Nuovi Lincei (2) 17:109–442
Zschiesche A (1909) Untersuchungen über die Metamorphose von Alcyonidium mytili. Zool Jahrb, Abt Anat Ontog Tiere 28:1–72
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reed, C.G., Cloney, R.A. The settlement and metamorphosis of the marine bryozoan Bowerbankia gracilis (Ctenostomata: Vesicularioidea). Zoomorphology 101, 103–132 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312018
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00312018